Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Paper2Rebuttal: Ein Multi-Agenten-Framework zur transparenten Unterstützung bei der Autorenantwort
Paper2Rebuttal: Ein Multi-Agenten-Framework zur transparenten Unterstützung bei der Autorenantwort
Qianli Ma Chang Guo Zhiheng Tian Siyu Wang Jipeng Xiao Yuanhao Yue Zhipeng Zhang
Zusammenfassung
Das Verfassen wirksamer Widerspruchstexte ist eine hochriskante Aufgabe, die mehr erfordert als nur sprachliche Geschicklichkeit, da eine präzise Abstimmung zwischen dem Intent des Gutachters und den Details des Manuskripts notwendig ist. Aktuelle Ansätze behandeln diese Aufgabe typischerweise als direktes Textgenerierungsproblem und leiden unter Phänomenen wie Halluzinationen, übersehener Kritikpunkte sowie fehlender überprüfbarer Grundlage. Um diese Einschränkungen zu überwinden, stellen wir RebuttalAgent vor – das erste Multi-Agenten-System, das die Generierung von Widerspruchstexten neu formuliert als evidenzzentrierte Planungsaufgabe. Unser System zerlegt komplexe Rückmeldungen in atomare Anliegen und erstellt dynamisch hybride Kontexte, indem es komprimierte Zusammenfassungen mit hochfidelitätsreichen Texten synthetisiert und dabei einen autonomen und bedarfsorientierten externen Suchmodul integriert, um Anliegen zu klären, die auf zusätzliche Literatur zurückgreifen. Durch die Generierung eines überprüfbarer Antwortplans vor der eigentlichen Texterstellung stellt RebuttalAgent sicher, dass jedes Argument explizit auf interner oder externer Evidenz basiert. Wir validieren unseren Ansatz anhand des vorgeschlagenen RebuttalBench und zeigen, dass unsere Pipeline gegenüber starken Baselines in Bezug auf Abdeckung, Treue zum Original und strategische Kohärenz überlegen ist und somit einen transparenten und kontrollierbaren Assistenten für den Peer-Review-Prozess darstellt. Der Quellcode wird veröffentlicht.
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University propose REBUTTALAGENT, a multi-agent framework that treats rebuttal writing as evidence-based planning, dynamically integrating internal summaries and external searches to ensure grounded, faithful responses, outperforming baselines on REBUTTALBENCH for peer review assistance.
Key Contributions
- REBUTTALAGENT reframes rebuttal generation as an evidence-centric planning task using a multi-agent system that decomposes reviewer feedback into atomic concerns and constructs hybrid contexts from internal manuscript passages and external literature to ensure verifiable grounding.
- The framework introduces a “verify-then-write” workflow with human-in-the-loop checkpoints, enabling strategic planning and global consistency checks before drafting, thereby reducing hallucination and improving faithfulness to the original manuscript.
- Evaluated on the proposed REBUTTALBENCH benchmark, the system outperforms direct-generation and chat-LLM baselines in coverage, traceability, and argumentative coherence, offering a transparent, author-controlled tool for high-stakes peer review.
Introduction
The authors leverage a multi-agent framework to transform rebuttal writing from a free-form text generation task into a structured, evidence-driven planning process. Prior approaches—either fine-tuned LLMs or interactive chat interfaces—struggle with hallucination, lack of traceability, and opaque workflows that obscure critical reasoning steps like concern parsing and evidence retrieval. REBUTTALAGENT addresses this by decomposing reviewer feedback into atomic concerns, dynamically constructing hybrid internal/external evidence contexts, and enforcing a “verify-then-write” pipeline with human-in-the-loop checkpoints. This ensures every response is grounded, consistent, and auditable, significantly improving coverage, faithfulness, and strategic coherence over existing methods.
Dataset
The authors use REBUTTALBENCH, a specialized benchmark derived from real ICLR OpenReview peer-review threads, to evaluate rebuttal generation systems. The dataset is built in two main parts:
-
REBUTTALBENCH-CORPUS (9.3K pairs):
- Source: ICLR 2023 subset of RE² dataset (Zhang et al., 2025).
- Filtering: Retains only threads with explicit reviewer follow-up signals; discards ambiguous cases.
- Structure: Each entry contains an initial reviewer critique, author rebuttal, and reviewer’s follow-up reaction, used to classify samples as “positive” (concerns resolved) or “negative” (concerns unaddressed).
- Use: Serves as the broad evaluation pool for analysis and model tuning.
-
REBUTTALBENCH-CHALLENGE (20 papers):
- Construction: Selects top 20 papers with over 100 reviewers and high diversity of resolved/unresolved concerns.
- Purpose: Forms a compact, challenging benchmark for standardized comparison of rebuttal quality.
Evaluation Framework:
- Scores are weighted combinations of three dimensions: Relevance (R), Argumentation (A), and Communication (C), each split into three components (9 total).
- R1–R3: Coverage, semantic alignment, specificity.
- A1–A3: Logic consistency, evidence support, response engagement.
- C1–C3: Professional tone, clarity, constructiveness.
- Stratification: Data is tiered by reliability:
- Tier 1 (Gold): Objective score changes or explicit revision statements.
- Tier 2 (High Confidence): No score change but high LLM sentiment certainty (≥0.7).
- Tier 3 (Medium Confidence): Moderate certainty (0.4 < conf < 0.7).
- Baseline protocol: Multi-round rebuttal generation with fixed prompts, paper text, and prior-round summaries; outputs capped at <200 words per round.
Processing & Use in Model Training:
- The authors do not train on REBUTTALBENCH itself; it is used exclusively for evaluation.
- Training data (not described here) is separate; REBUTTALBENCH tests how well models generate fact-grounded, strategically nuanced rebuttals aligned with reviewer expectations.
- Metadata includes reviewer follow-up signals, tier labels, and component scores to enable fine-grained analysis beyond fluency.
Method
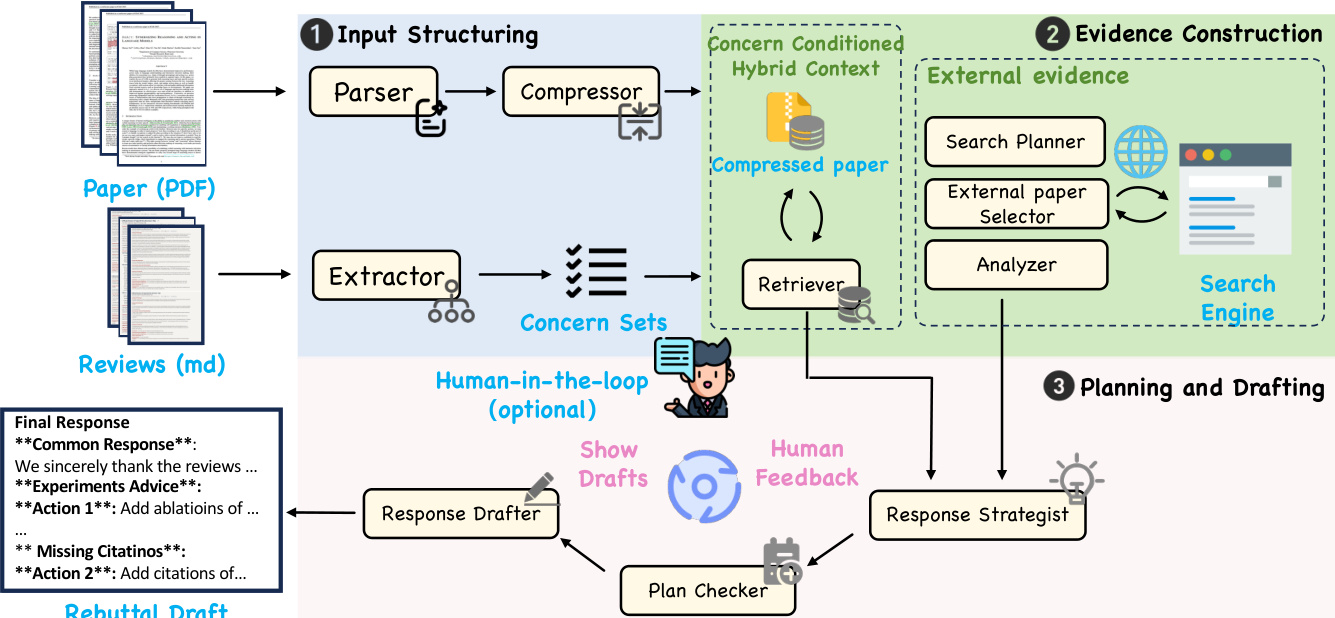
The authors leverage a multi-agent framework, RebuttalAgent, designed to transform the rebuttal process into a structured and inspectable workflow. The system operates through a pipeline that decomposes complex reasoning into specialized agents and lightweight checkers, as illustrated in the framework diagram. This architecture exposes critical decision points and allows authors to retain full responsibility for the strategic stance and final wording of the rebuttal.
The pipeline begins with input structuring, where the raw manuscript and reviews are distilled into condensed representations optimized for downstream reasoning. A parser agent converts the manuscript PDF into a paragraph-indexed format to preserve structural integrity. A compressor agent then distills these paragraphs into a concise representation that retains essential technical statements and experimental results, serving as a navigational anchor for subsequent modules. To ensure fidelity, a consistency checker verifies each condensed unit against its source and triggers reprocessing if it detects missing claims or semantic drift. Concurrently, an extractor agent parses the raw review feedback into discrete and addressable atomic concerns, organizing critiques by grouping related sub-questions and assigning preliminary categories. A coverage checker validates the output for intent preservation and appropriate granularity, ensuring substantive points remain distinct without being over-split or incorrectly merged. The resulting structured list of atomic concerns forms the foundational unit for evidence gathering and response planning.
Following input structuring, the system proceeds to evidence construction. For each atomic concern, the system identifies the most pertinent sections by searching within the compressed manuscript representation. It selectively expands these focal points by retrieving the corresponding raw text to replace the specific condensed units, while retaining the rest of the document in its summarized form. This yields an atomic concern conditioned hybrid context that integrates the efficiency of the compressed view with the precision of the original text, enabling the system to support its reasoning with exact quotations and detailed evidence without overwhelming the context window. When internal data is insufficient, the system augments the evidence bundle with external support. A search planner formulates a targeted search strategy, and a retrieval step gathers candidate papers via scholarly search tools. A screening agent filters these candidates for relevance and utility, and the pipeline concludes by parsing the selected works into a structured evidence brief that highlights key claims and experimental comparisons for citation-ready material.
The final stage involves planning and drafting. The system implements a bifurcated reasoning strategy that strictly distinguishes between interpretative defense and necessary intervention. For concerns resolvable through existing data, the Strategist Agent synthesizes arguments directly from the hybrid context and anchors them in the manuscript text. When the system detects a demand for new experiments or baselines, it explicitly inhibits result generation and instead produces concrete Action Items framed as recommendations. This design prevents the fabrication of outcomes by forcing a structural pause where authors must verify or perform the suggested tasks. The resulting plan serves as an interactive human-in-the-loop checkpoint, allowing authors to actively refine the strategic logic. Only after the author validates these strategic decisions does the Drafter Agent convert the plan into a final response, ensuring that every claim remains grounded in reality. Optionally, the drafter can also produce a submission-style rebuttal draft from the validated plan, rendering any yet-to-be-conducted experiments as explicit placeholders.
Experiment
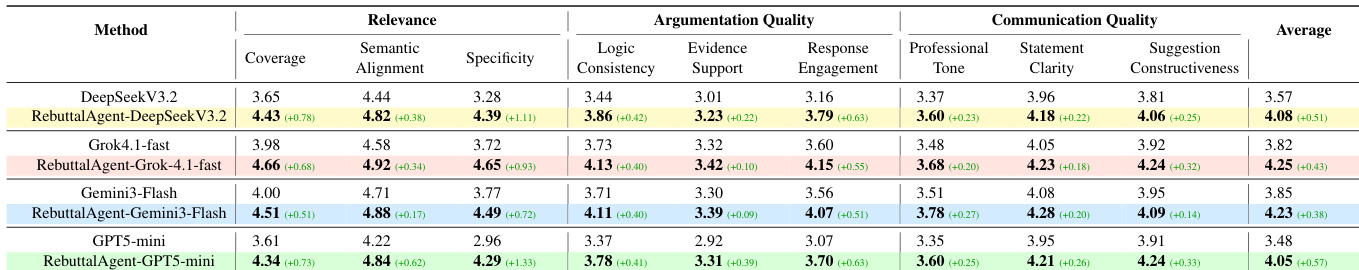
- Evaluated REBUTTALAGENT against SOTA LLMs (GPT-5-mini, Grok-4.1-fast, Gemini-3-Flash, DeepSeekV3.2) on RebuttalBench using a 0–5 LLM-as-judge rubric covering Relevance, Argumentation, and Communication Quality; REBUTTALAGENT consistently outperformed baselines across all dimensions, with largest gains in Relevance (+0.78 for DeepSeekV3.2, +1.33 for GPT5-mini) and Argumentation (+0.63), while Communication gains were smaller but consistent.
- Gains stem from structured pipeline (concern decomposition, evidence synthesis, planning), not model capacity—evidenced by consistent improvements even when using identical base models; weaker base models (e.g., GPT5-mini) saw larger relative gains (+0.55 avg) than stronger ones (Gemini-3-Flash: +0.33), indicating task structuring compensates for limited generation capability.
- Ablation study showed Evidence Construction is most critical—removing it caused largest drops in Relevance and Communication (Coverage: 4.51 → 4.26; Constructiveness: 4.09 → 3.82); Input Structuring and Checkers provided smaller but measurable improvements, confirming complementary module contributions.
- Case studies demonstrated REBUTTALAGENT’s output includes explicit action items, evidence-linked clarifications, and scoped to-do lists, reducing hallucination and over-commitment by surfacing verifiable deliverables before drafting, unlike baseline LLMs that produce ungrounded narratives.
- System validated on real reviewer queries (e.g., theoretical clarity, metric validity), producing structured rebuttal strategies with concrete deliverables (revised propositions, empirical plots, new lemmas) and feasible to-do lists, all without requiring new training or large-scale data collection.
The authors use a structured pipeline to improve rebuttal quality by decomposing the task into concern structuring, evidence construction, and verification. Results show that RebuttalAgent consistently outperforms baseline models across all evaluation dimensions, with the largest gains in Relevance and Argumentation Quality, while Communication Quality improvements are smaller but consistent.
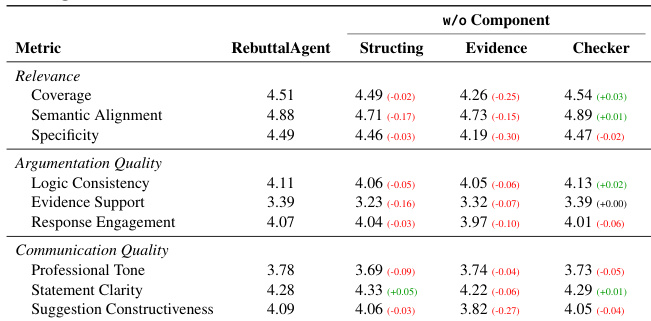
The authors use a structured agent framework, RebuttalAgent, to improve rebuttal responses by decomposing the task into concern structuring, evidence construction, and verification. Results show that RebuttalAgent consistently outperforms strong closed-source LLMs across all evaluation dimensions, with the largest gains in Relevance and Argumentation Quality, indicating that systematic reasoning and evidence organization are more critical than raw model capacity.