Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
KlingAvatar 2.0 Technischer Bericht
KlingAvatar 2.0 Technischer Bericht
Zusammenfassung
Avatar-Videogenerierungsmodelle haben in den letzten Jahren beachtliche Fortschritte erzielt. Dennoch weisen vorangegangene Ansätze begrenzte Effizienz bei der Erzeugung langer, hochauflösender Videos auf und leiden unter zeitlichem Drift, Qualitätsverfall und schwacher Anweisungskonformität, insbesondere bei zunehmender Video-Länge. Um diese Herausforderungen zu bewältigen, stellen wir KlingAvatar 2.0 vor – einen räumlich-zeitlichen Kaskadenframework, der sowohl in räumlicher Auflösung als auch in der zeitlichen Dimension skaliert. Der Framework generiert zunächst niederauflösende Schlüsselbildfolgen, die globale Semantik und Bewegung erfassen, und verfeinert diese anschließend zu hochauflösenden, zeitlich kohärenten Sub-Clips mittels einer First-Last-Frame-Strategie, wobei reibungslose zeitliche Übergänge in langen Videos beibehalten werden. Um die Fusion und Ausrichtung zwischen Modalitäten in erweiterten Videos zu verbessern, führen wir einen Co-Reasoning Director ein, bestehend aus drei modality-spezifischen großen Sprachmodellen (LLM-Experten). Diese Experte analysieren die Modalitätsprioritäten und leiten die zugrundeliegende Benutzerabsicht ab, wodurch Eingaben durch mehrere Dialogrunden in detaillierte Handlungsstränge umgewandelt werden. Ein zusätzlicher Negative Director verfeinert negative Anweisungen, um die Anweisungskonformität weiter zu steigern. Aufbauend auf diesen Komponenten erweitern wir den Framework um die Unterstützung von ID-spezifischer Steuerung mehrerer Charaktere. Umfangreiche Experimente zeigen, dass unser Modell die Herausforderungen der effizienten, multimodalen Ausrichtung bei der Erzeugung langer, hochauflösender Videos erfolgreich bewältigt und dabei verbesserte visuelle Klarheit, realistische Lippen-Zahn-Darstellung mit präziser Lippen-Synchronisation, starke Identitätsbewahrung sowie kohärente multimodale Anweisungsfolge liefert.
One-sentence Summary
Kuaishou Technology's Kling Team proposes KlingAvatar 2.0, a spatio-temporal cascade framework generating long-duration high-resolution avatar videos by refining low-resolution blueprint keyframes via first-last frame conditioning to eliminate temporal drifting. Its Co-Reasoning Director employs multimodal LLM experts for precise cross-modal instruction alignment, enabling identity-preserving multi-character synthesis with accurate lip synchronization for applications in education, entertainment, and personalized services.
Key Contributions
- Current speech-driven avatar generation systems struggle with long-duration high-resolution videos, exhibiting temporal drifting, quality degradation, and weak prompt adherence as video length increases despite advances in general video diffusion models.
- KlingAvatar 2.0 introduces a spatio-temporal cascade framework that first generates low-resolution blueprint keyframes capturing global motion and semantics, then refines them into high-resolution sub-clips using a first-last frame strategy to ensure temporal coherence and detail preservation in extended videos.
- The Co-Reasoning Director employs three modality-specific LLM experts that collaboratively infer user intent through multi-turn dialogue, converting inputs into hierarchical storylines while refining negative prompts to enhance multimodal instruction alignment and long-form video fidelity.
Introduction
Video generation has advanced through diffusion models and DiT architectures using 3D VAEs for spatio-temporal compression, enabling high-fidelity synthesis but remaining limited to text or image prompts without audio conditioning. Prior avatar systems either rely on intermediate motion representations like landmarks or lack long-term coherence and expressive control for speech-driven digital humans. The authors address this gap by introducing KlingAvatar 2.0, which leverages multimodal large language model reasoning for hierarchical storyline planning and a spatio-temporal cascade pipeline to generate coherent, long-form audio-driven avatar videos with fine-grained expression and environmental interaction.
Method
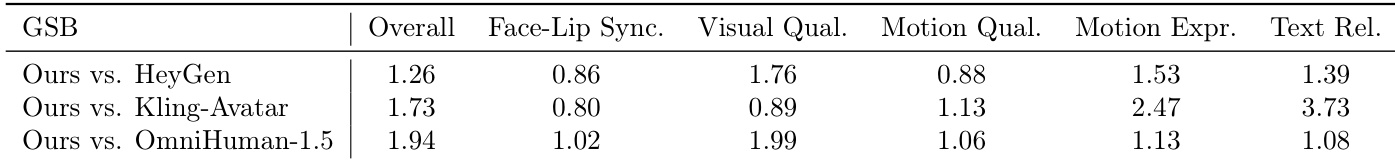
The authors leverage a spatio-temporal cascade framework to generate long-duration, high-resolution avatar videos with precise lip synchronization and multimodal instruction alignment. The pipeline begins with a Co-Reasoning Director that processes input modalities—reference image, audio, and text—through a multi-turn dialogue among three modality-specific LLM experts. These experts jointly infer user intent, resolve semantic conflicts, and output structured global and local storylines, including positive and negative prompts that guide downstream generation. As shown in the framework diagram, the Director’s output feeds into a hierarchical diffusion cascade: first, a low-resolution Video DiT generates blueprint keyframes capturing global motion and layout; these are then upscaled by a high-resolution Video DiT to enrich spatial detail while preserving identity and composition. Subsequently, a low-resolution diffusion model expands the high-resolution keyframes into audio-synchronized sub-clips using a first-last frame conditioning strategy, augmented with blueprint context to refine motion and expression. An audio-aware interpolation module synthesizes intermediate frames to ensure temporal smoothness and lip-audio alignment. Finally, a high-resolution Video DiT performs super-resolution on the sub-clips, yielding temporally coherent, high-fidelity video segments.
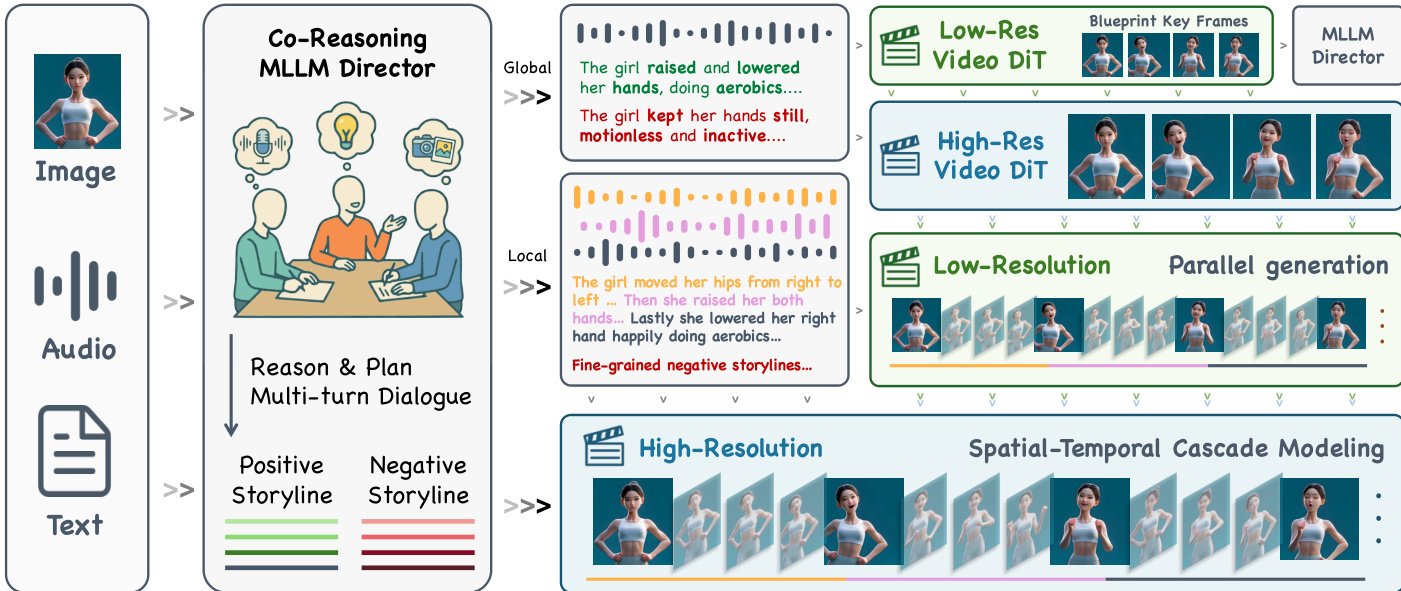
To support multi-character scenes with identity-specific audio control, the authors introduce a mask-prediction head attached to deep layers of the Human Video DiT. These deep features exhibit spatially coherent regions corresponding to individual characters, enabling precise audio injection. During inference, reference identity crops are encoded and cross-attended with video latent tokens to regress per-frame character masks, which gate the injection of character-specific audio streams into corresponding spatial regions. For training, the DiT backbone remains frozen while only the mask-prediction modules are optimized. To scale data curation, an automated annotation pipeline is deployed: YOLO detects characters in the first frame, DWPose estimates keypoints, and SAM2 segments and tracks each person across frames using bounding boxes and keypoints as prompts. The resulting masks are validated against per-frame detection and pose estimates to ensure annotation quality. As shown in the figure, this architecture enables fine-grained control over multiple characters while maintaining spatial and temporal consistency.
Experiment
- Accelerated video generation via trajectory-preserving distillation with custom time schedulers validated improved inference efficiency and generative performance, surpassing distribution matching approaches in stability and flexibility.
- Human preference evaluation on 300 diverse test cases (Chinese/English speech, singing) demonstrated superior (G+S)/(B+S) scores against HeyGen, Kling-Avatar, and OmniHuman-1.5, particularly excelling in motion expressiveness and text relevance.
- Generated videos achieved more natural hair dynamics, precise camera motion alignment (e.g., correctly folding hands per prompt), and emotionally coherent expressions, while per-shot negative prompts enhanced temporal stability versus baselines' generic artifact control.
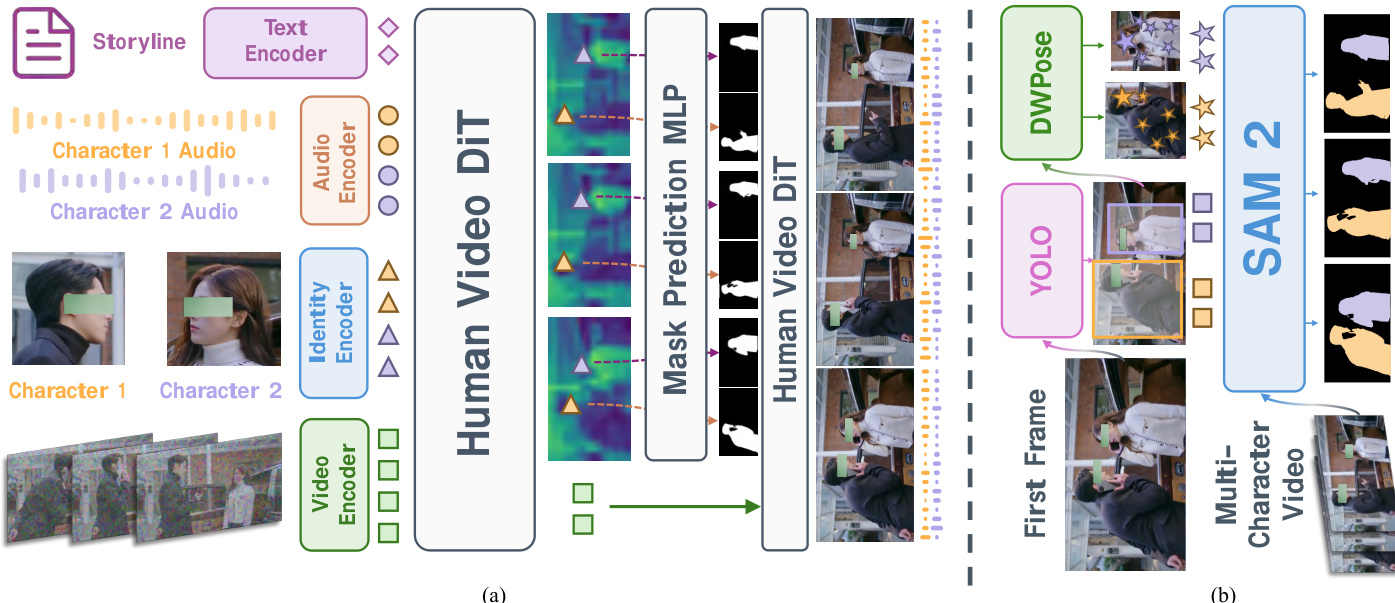
Results show KlingAvatar 2.0 outperforms all three baselines across overall preference and most subcategories, with particularly strong gains in motion expressiveness and text relevance. The model achieves the highest scores against Kling-Avatar in motion expressiveness (2.47) and text relevance (3.73), indicating superior alignment with multimodal instructions and richer dynamic expression. Visual quality and motion quality also consistently favor KlingAvatar 2.0, though face-lip synchronization scores are closer to baselines.
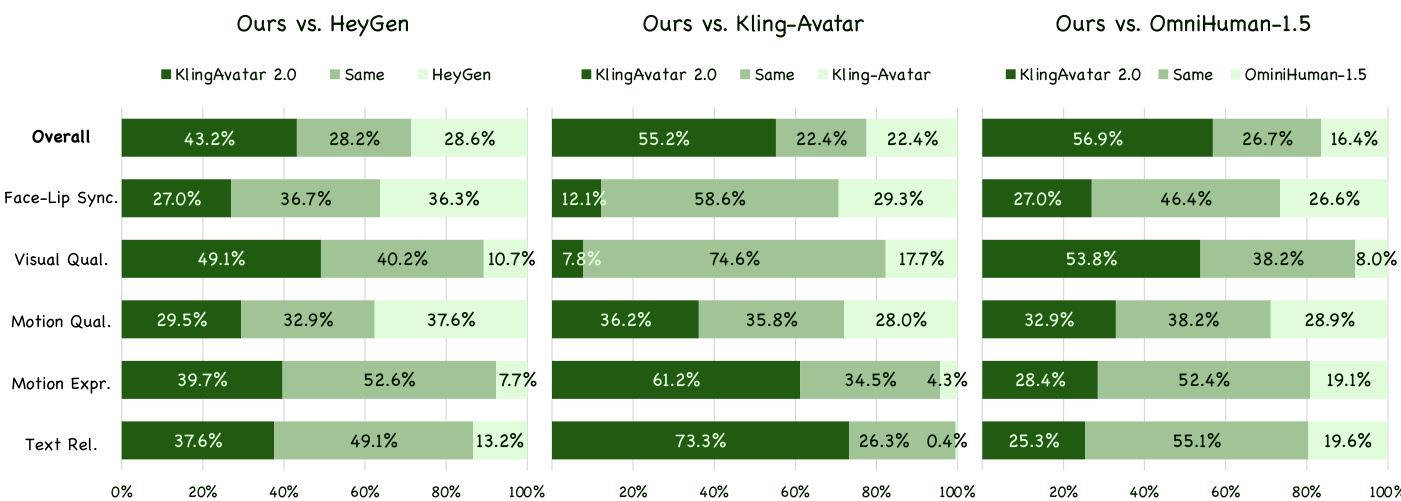
Results show KlingAvatar 2.0 outperforms all three baselines across overall preference and most subcategories, with particularly strong gains in motion expressiveness and text relevance. The model achieves the highest scores against Kling-Avatar in motion expressiveness (2.47) and text relevance (3.73), indicating superior alignment with multimodal instructions and richer dynamic expression. Visual quality and motion quality also consistently favor KlingAvatar 2.0, though face-lip synchronization scores are closer to baselines.