Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Error-Free Linear Attention ist ein kostenloses Mittagessen: Exakte Lösung aus kontinuierlichen Zeitdynamiken
Error-Free Linear Attention ist ein kostenloses Mittagessen: Exakte Lösung aus kontinuierlichen Zeitdynamiken
Jingdi Lei Di Zhang Soujanya Poria
Zusammenfassung
Lineare Zeit-Attention und State-Space-Modelle (SSMs) versprechen, die quadratische Kostenbarriere in Sprachmodellen mit langen Kontexten, die auf Softmax-Attention basieren, zu überwinden. Wir stellen Error-Free Linear Attention (EFLA) vor, eine numerisch stabile, vollständig parallele und verallgemeinerte Formulierung der Delta-Regel. Insbesondere formulieren wir die Online-Lern-Update-Regel als ein kontinuierliches dynamisches System und beweisen, dass ihre exakte Lösung nicht nur erreichbar, sondern auch in linearer Zeit mit vollständiger Parallelisierung berechenbar ist. Durch Ausnutzung der Rang-1-Struktur der Dynamikmatrix leiten wir direkt die exakte geschlossene Lösung ab, die effektiv der unendlich-ten Ordnung eines Runge-Kutta-Verfahrens entspricht. Diese Attention-Mechanismus ist theoretisch frei von Fehlerakkumulation, erfasst die kontinuierlichen Dynamiken perfekt und bewahrt gleichzeitig die Linearzeit-Komplexität. Durch eine umfassende Reihe von Experimenten zeigen wir, dass EFLA eine robuste Leistung in geräuschbehafteten Umgebungen ermöglicht, wobei die Sprachmodellierungs-Perplexität niedriger ist und die Ergebnisse auf nachgeschalteten Benchmarks gegenüber DeltaNet überlegen sind – ohne zusätzliche Parameter einzuführen. Unsere Arbeit legt eine neue theoretische Grundlage für die Entwicklung hochgenauer, skalierbarer Linearzeit-Attention-Modelle dar.
One-sentence Summary
Nanyang Technological University and Fudan University researchers propose Error-Free Linear Attention (EFLA), which eliminates discretization errors in linear attention by deriving the exact closed-form solution of continuous-time dynamics through rank-1 matrix properties, achieving linear-time complexity without error accumulation and demonstrating superior robustness in noisy environments, lower perplexity, and better benchmark performance than DeltaNet without additional parameters.
Key Contributions
- Identifies that existing linear attention methods suffer from numerical instability due to low-order discretization of continuous-time dynamics, causing truncation errors especially in long-context scenarios where Euler-based approximations fail. This explains performance degradation in noisy environments and extended sequences.
- Reformulates linear attention as a continuous-time dynamical system governed by a first-order ordinary differential equation, revealing that standard implementations correspond to suboptimal numerical integration schemes like Euler discretization. This theoretical perspective bridges attention mechanisms with continuous-time system modeling.
- Derives an exact closed-form solution for the rank-1 dynamics matrix that eliminates discretization errors while maintaining linear-time complexity, validated through language modeling perplexity improvements and superior downstream benchmark performance over DeltaNet without additional parameters.
Introduction
Long-context modeling is critical for efficiently processing lengthy sequences in applications like language understanding, where standard attention mechanisms become computationally prohibitive at scale due to quadratic complexity. Prior approaches such as linear attention often face numerical instability from approximate discretization of continuous dynamics, introducing errors that degrade performance. The authors address this by proving that rank-1 linear attention admits an exact, error-free discretization when derived from its continuous-time formulation, providing a rigorous theoretical foundation to enhance the reliability of existing linear attention implementations without proposing new architectural primitives. This insight offers a pathway to more stable long-context models while complementing alternative linear-time frameworks like RetNet or Hyena.

Method
The authors leverage a continuous-time dynamical systems perspective to reformulate linear attention as an exact, error-free solution to a first-order ordinary differential equation (ODE). Rather than relying on low-order numerical approximations such as Euler or Runge-Kutta discretizations, they derive a closed-form analytical solution that captures the continuous evolution of the attention state without truncation error. This solution is made computationally tractable by exploiting the rank-1 structure of the underlying dynamics matrix, enabling linear-time complexity while preserving mathematical fidelity.
The core formulation begins by interpreting the DeltaNet update — which minimizes a reconstruction loss via gradient descent — as a discretization of the continuous-time ODE:
dtdS(t)=−AtS(t)+bt,where At=ktkt⊤ and bt=ktvt⊤. Under the Zero-Order Hold assumption for discrete input sequences, this ODE governs the evolution of the state matrix S(t), which accumulates key-value associations over time. Standard linear attention methods correspond to first-order Euler integration of this system, introducing local truncation errors of O(βt2) and suffering from instability under stiff dynamics.
To eliminate these errors, the authors derive the exact solution to the ODE by taking the infinite-order limit of the Runge-Kutta family. This yields:
St=e−βtAtSt−1+∫0βte−(βt−τ)Atbtdτ.While matrix exponentials typically incur O(d3) cost, the rank-1 property of At allows for a closed-form simplification. Specifically, Atn=λtn−1At for n≥1, where λt=kt⊤kt. This enables the exponential to be collapsed into:
e−βtAt=I−λt1−e−βtλtAt.Similarly, the integral term simplifies due to the identity Atbt=λtbt, yielding:
∫0βte−(βt−τ)Atbtdτ=λt1−e−βtλtbt.Combining these results, the final Error-Free Linear Attention (EFLA) update rule becomes:
St=(I−λt1−e−βtλtktkt⊤)St−1+λt1−e−βtλtktvt⊤.This update retains the same algebraic structure as DeltaNet, enabling seamless adoption of existing hardware-efficient parallelization techniques. The authors further derive a chunkwise parallel formulation by unrolling the recurrence and expressing the state as a product of decay operators and accumulated inputs. This allows for efficient batched computation over sequence chunks, maintaining O(Ld2) complexity while enabling full parallelism.
The spectral properties of At also reveal an implicit gating mechanism: the key norm λt controls the decay rate along the direction of kt. Large λt induces rapid forgetting, while small λt results in near-linear decay, effectively prioritizing retention of historical context. In the limit λt→0, EFLA recovers the delta rule, confirming that prior linear attention methods are first-order approximations valid only under non-stiff dynamics.
By grounding the attention mechanism in continuous-time dynamics and deriving its exact solution, EFLA eliminates the numerical error inherent in discretized approximations, offering a theoretically grounded, scalable, and stable alternative to existing linear attention formulations.
Experiment
- Numerical stability tests on sMNIST: EFLA maintains significantly higher accuracy than DeltaNet under pixel dropout, OOD intensity scaling, and additive Gaussian noise, especially with a learning rate of 3e-3, validating its robustness against error accumulation and state explosion.
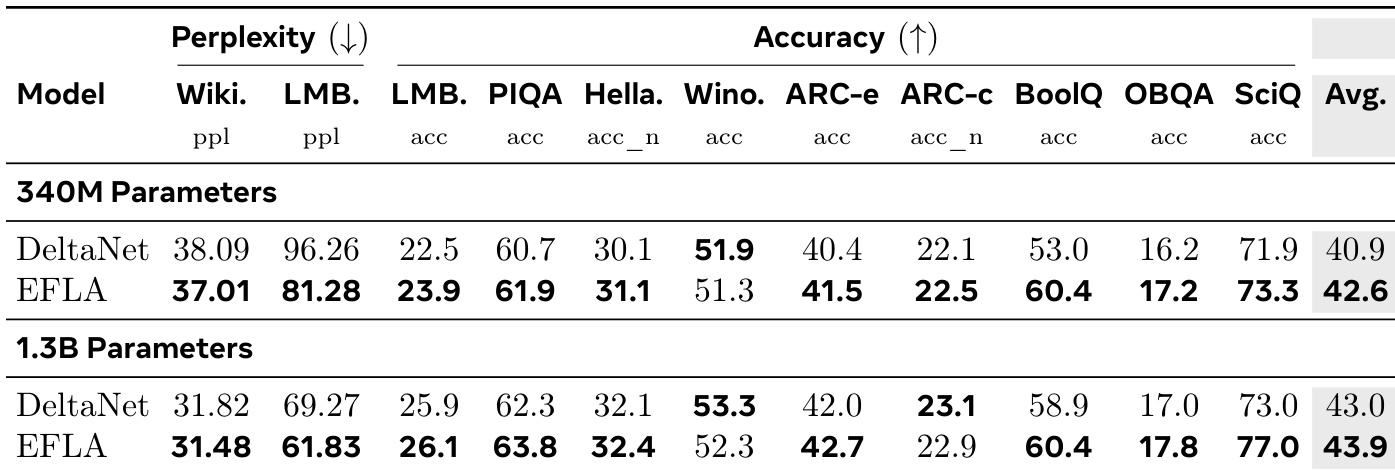
- Language modeling on Wikitext and LAMBADA: EFLA achieves 81.28 perplexity (vs. DeltaNet's 96.26) and 23.9% accuracy on LAMBADA, while surpassing DeltaNet by +7.4% absolute accuracy on BoolQ, confirming superior long-sequence information fidelity.
- Learning rate analysis: EFLA requires a larger learning rate (3e-3) to counteract saturation effects, empirically validated by improved robustness under interference compared to conservative rates (1e-4).
The authors compare EFLA and DeltaNet on language modeling and reasoning tasks using 340M and 1.3B parameter models. Results show EFLA consistently outperforms DeltaNet across most benchmarks, achieving lower perplexity on Wikitext and LAMBADA and higher accuracy on tasks like BoolQ and SciQ, with the performance gap widening at larger scale. This improvement is attributed to EFLA’s exact decay mechanism, which preserves long-range context fidelity more effectively than DeltaNet’s Euler-based approximation.