Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
HunyuanOCR Technischer Bericht
HunyuanOCR Technischer Bericht
Zusammenfassung
Diese Arbeit stellt HunyuanOCR vor, ein kommerziell einsetzbares, quelloffenes und leichtgewichtiges (1B Parameter) Vision-Language-Modell (VLM), das speziell für OCR-Aufgaben entwickelt wurde. Die Architektur besteht aus einem Native Vision Transformer (ViT) und einem leichtgewichtigen LLM, die über einen MLP-Adapter verbunden sind. HunyuanOCR zeigt überlegene Leistung und übertrifft kommerzielle APIs, traditionelle Pipelines sowie größere Modelle (z. B. Qwen3-VL-4B). Insbesondere erreicht es Spitzenresultate bei Wahrnehmungsaufgaben (Text Spotting, Parsing) und überzeugt bei semantischen Aufgaben (Information Extraction, Text-Bild-Übersetzung), wobei es den ersten Platz im ICDAR 2025 DIMT Challenge (Small Model Track) belegt. Zudem erzielt es state-of-the-art (SOTA)-Ergebnisse auf OCRBench unter allen VLMs mit weniger als 3B Parametern.HunyuanOCR erzielt bahnbrechende Fortschritte in drei zentralen Aspekten:1) Vereinigung von Vielseitigkeit und Effizienz: Wir implementieren umfassende Unterstützung für zentrale Funktionen wie Text Spotting, Parsing, Information Extraction (IE), VQA und Text-Bild-Übersetzung innerhalb eines leichtgewichtigen Rahmens. Dies behebt die Einschränkungen enger „OCR-Spezialmodelle“ sowie die ineffizienten „Allgemeinen VLMs“.2) Verfeinerte End-to-End-Architektur: Durch die Einführung eines reinen End-to-End-Paradigmas entfallen Abhängigkeiten von Vorverarbeitungsmodulen (z. B. Layout-Analyse). Dies löst grundlegend das Problem der Fehlerpropagation, das in traditionellen Pipelines weit verbreitet ist, und vereinfacht die Systembereitstellung erheblich.3) Datengestützte Ansätze und RL-Strategien: Wir bestätigen die entscheidende Rolle hochwertiger Daten und demonstrieren erstmals in der Industrie, dass Reinforcement Learning (RL) Strategien erhebliche Leistungssteigerungen bei OCR-Aufgaben ermöglichen.HunyuanOCR wurde offiziell auf HuggingFace veröffentlicht. Zusätzlich stellen wir eine hochperformante Bereitstellungslösung basierend auf vLLM bereit, die seine Produktivität in die oberste Liga stellt. Wir hoffen, dass dieses Modell die Forschung an der Spitze voranbringt und eine solide Grundlage für industrielle Anwendungen liefert.
One-sentence Summary
The authors propose HunyuanOCR, a 1B-parameter open-source Vision-Language Model developed by Tencent and collaborators, which unifies end-to-end OCR capabilities—text spotting, parsing, information extraction, and translation—within a lightweight architecture using a ViT-LLM MLP adapter, outperforming larger models and commercial APIs through data-driven training and novel reinforcement learning strategies, enabling high-efficiency deployment for industrial and research applications.
Key Contributions
- HunyuanOCR introduces a lightweight (1B parameter) end-to-end Vision-Language Model that unifies diverse OCR tasks—such as text spotting, document parsing, information extraction, visual question answering, and text image translation—within a single compact framework, overcoming the limitations of both narrow pipeline-based systems and resource-heavy general-purpose VLMs.
- The model leverages a native ViT and lightweight LLM connected via an MLP adapter, trained on 200 million high-quality, application-oriented samples and enhanced with online reinforcement learning (GRPO), achieving state-of-the-art performance on OCRBench and securing first place in the ICDAR 2025 DIMT Challenge (Small Model Track).
- By eliminating the need for pre-processing modules like layout analysis, HunyuanOCR enables streamlined, error-propagation-free inference and offers high deployment efficiency via vLLM, making it suitable for real-world industrial applications with low latency and on-device usability.
Introduction
The authors leverage the growing capabilities of vision-language models (VLMs) to address long-standing limitations in traditional OCR systems, which rely on complex, cascaded pipelines that suffer from error propagation and high maintenance overhead. While recent OCR-specific VLMs have improved performance by integrating layout analysis and recognition, they often still depend on separate layout detection modules, limiting true end-to-end learning and unified multi-task modeling. In response, the authors introduce HunyuanOCR, a compact, open-source multilingual VLM with only 1 billion parameters that adopts a fully end-to-end architecture. This design enables unified, single-pass inference across diverse OCR tasks—including text spotting, document parsing, information extraction, visual question answering, and multilingual translation—without relying on intermediate processing stages. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance on key benchmarks, outperforming both open-source and commercial OCR systems, while maintaining high inference efficiency suitable for on-device deployment. Its success stems from a data-centric training strategy using high-quality, application-aligned data and a targeted reinforcement learning framework that enhances accuracy in complex, knowledge-intensive tasks.
Dataset
- The dataset comprises over 200 million image-text pairs, sourced from a combination of public benchmarks, web-crawled real-world images, and proprietary synthetic data generation tools.
- It covers nine major real-world scenarios: street views, documents, advertisements, handwritten text, screenshots, cards/certificates/invoices, game interfaces, video frames, and artistic typography, with support for more than 130 languages.
- Data curation prioritizes quality, diversity, and difficulty balance: high-quality open-source and synthetic datasets are filtered using LLM-based judgment to ensure image-text alignment and eliminate easily exploitable tasks like multiple-choice questions; samples with low output diversity or zero reward variance are discarded to maintain diversity; and pass-rate filtering based on model performance removes both trivial and unsolvable examples.
- The data is used to train HunyuanOCR across multiple tasks, with training splits designed to reflect real-world usage, and mixture ratios carefully balanced to ensure robustness across different OCR and information extraction (IE) scenarios.
- For information extraction, the dataset includes 30 IE tasks covering over ten card and certificate types (e.g., ID cards, passports, driver’s licenses, business licenses) and over ten receipt types (e.g., shopping receipts, VAT invoices, train tickets, bank slips), with bilingual (Chinese-English) instructions recommended for consistent benchmarking.
- Metadata is constructed to reflect task-specific requirements, and no explicit cropping is mentioned—instead, the pipeline ensures natural scene representation through careful selection and filtering of raw and synthetic inputs.
Method
The authors leverage a collaborative architecture for HunyuanOCR, composed of three core modules: a Native Resolution Visual Encoder, an Adaptive MLP Connector, and a Lightweight Language Model. This framework enables a unified, end-to-end approach to diverse OCR tasks, including text spotting, parsing, information extraction, visual question answering, and text image translation. The architecture is designed to eliminate the error propagation inherent in traditional pipeline-based systems by processing raw images directly and generating structured outputs in a single pass.

The Native Resolution Visual Encoder, based on the SigLIP-v2-400M pre-trained model, employs a hybrid generative-discriminative joint training strategy to enhance visual semantic comprehension. It processes images at their native resolution using an adaptive patching mechanism that preserves the original aspect ratio, thereby avoiding distortion and detail loss. This is particularly beneficial for challenging scenarios involving long-text documents or extreme aspect ratios. The image is divided into patches according to its native proportions, and all patches are processed by a Vision Transformer (ViT) with global attention, ensuring high-fidelity feature extraction.
The Adaptive MLP Connector serves as a bridge between the visual and linguistic domains. It implements a learnable pooling operation that performs spatial-dimension adaptive content compression, reducing the sequence length of tokens from the high-resolution visual feature maps. This process minimizes redundancy while preserving critical semantic information from key areas, such as text-dense regions, enabling an efficient and precise projection of visual features into the input space of the language model.
The Lightweight Language Model, based on the densely architected Hunyuan-0.5B model, incorporates XD-RoPE, which deconstructs the conventional RoPE into four independent subspaces: text, height, width, and time. This design establishes a native alignment mechanism that bridges 1D text sequences, 2D page layouts, and 3D spatiotemporal information, allowing the model to handle complex layout parsing and cross-page document analysis with logical reasoning. The model is trained in a fully end-to-end manner, which eliminates the need for post-processing and associated error accumulation, leading to superior robustness in challenging scenarios such as mixed-layout document understanding.
Experiment
- Evaluated HunyuanOCR on a 900-image in-house benchmark across nine text spotting categories (artistic, document, game, handwritten, advertisement, card/invoice, screen capture, street view, video), achieving state-of-the-art performance as an end-to-end Vision-Language Model, outperforming pipeline-based methods and larger general VLMs with significantly fewer parameters.
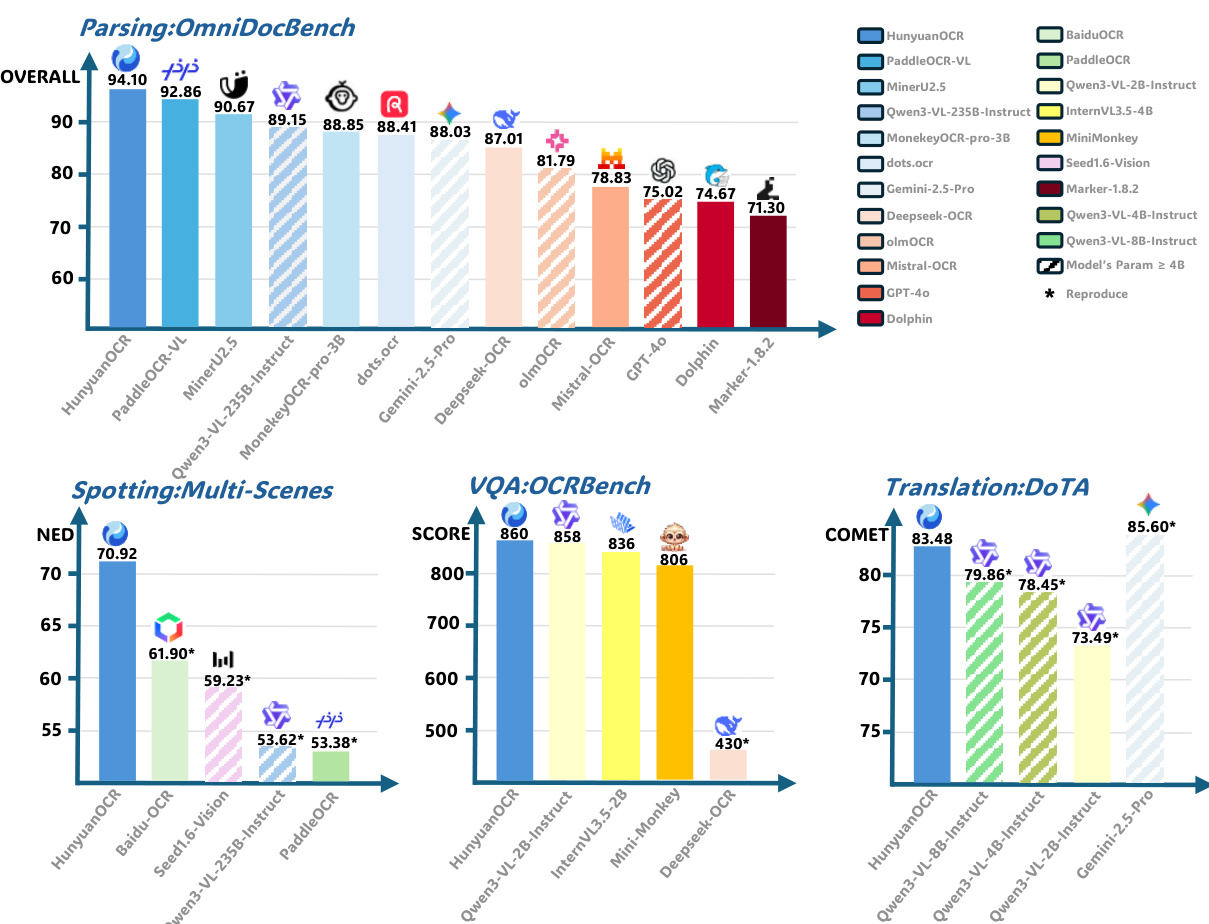
- On OmniDocBench and its Wild variant, HunyuanOCR achieves top results in document parsing across digital, scanned, and real-world captured documents, surpassing larger specialized models despite its 1B parameter size; on DocML, it attains SOTA multilingual parsing performance across 14 non-Chinese/English languages using edit-distance metric.
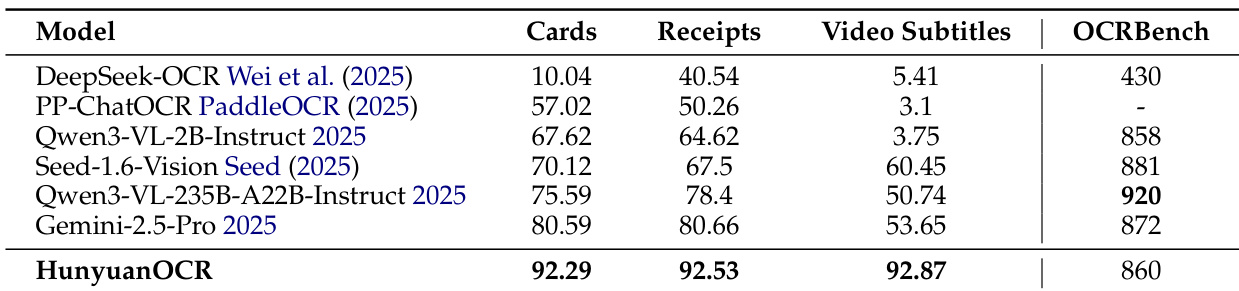
- In information extraction and visual question answering, HunyuanOCR achieves the highest accuracy across 30 document categories and video subtitles, outperforming larger models like Qwen3VL-235B-Instruct and Gemini-2.5-Pro, and matches or exceeds Qwen3VL-2B-Instruct on OCRBench.
- For text image translation, HunyuanOCR surpasses VLMs with over 8B parameters on DoTA and achieves first place in ICDAR 2025 Track 2.2, demonstrating strong multilingual and complex-layout translation capability, outperforming larger models on the in-house DocML benchmark.
- Reinforcement learning significantly improves performance: spotting scores increase by over 2 points on Art and Screen scenarios, parsing score on OmniDocBench rises from 92.5 to 94.1, and IE and VQA tasks improve by ~2 points, with OCRBench average score increasing by 3.3, attributed to fine-grained rule-based and LLM-as-a-judge rewards.
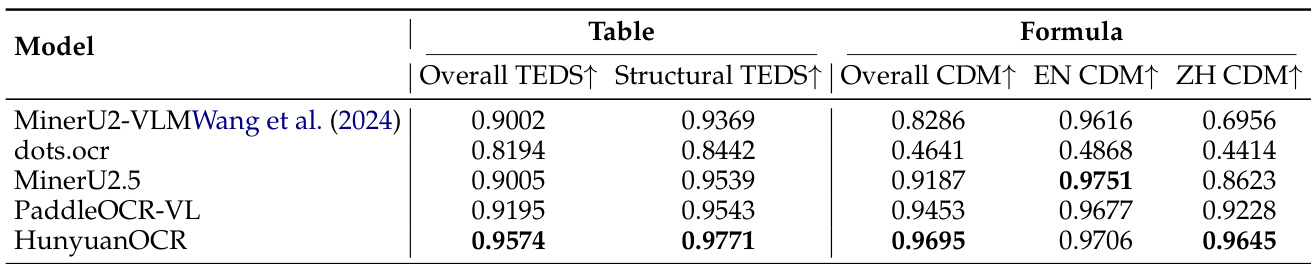
- Element-level evaluation shows strong formula and table recognition on OmniDocBench-Formula-block and OmniDocBench-Table-block, with high precision using targeted prompts for LaTeX and HTML output.
- Qualitative results demonstrate robust text spotting and parsing in dense, complex, and artistic documents, with accurate coordinate output, structured markdown, and correct semantic understanding across diverse real-world scenarios.
The authors use HunyuanOCR to evaluate document parsing performance on OmniDocBench, where it achieves the highest overall score of 94.10, outperforming all other models including larger ones. Results show HunyuanOCR also leads in spotting, visual question answering, and text translation tasks, demonstrating strong performance across diverse scenarios despite its relatively small 1B parameter size.
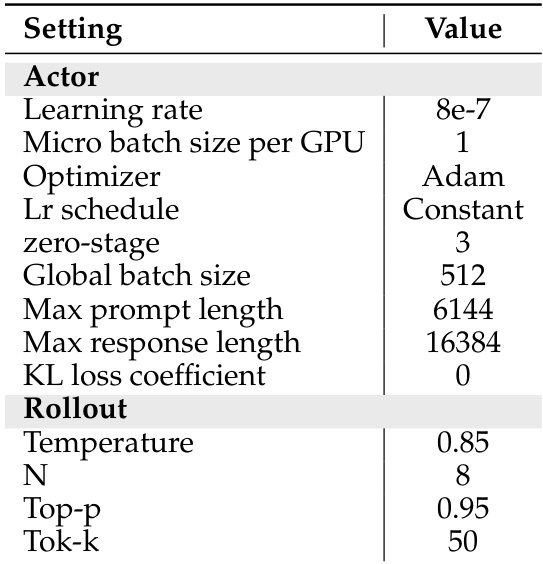
The authors use a reinforcement learning setup with a constant learning rate of 8e-7, Adam optimizer, and a global batch size of 512 to train HunyuanOCR. During rollout generation, they sample 8 responses per prompt with a temperature of 0.85 and a top-p of 0.95 to ensure diverse candidate outputs for reward evaluation.
The authors use HunyuanOCR to evaluate text spotting performance across nine diverse categories, including artistic text, documents, and video frames, on a 900-image benchmark. Results show that HunyuanOCR achieves the best overall performance, significantly outperforming traditional pipeline-based methods and general Vision-Language Models while using substantially fewer parameters.
Results show that HunyuanOCR achieves the highest overall accuracy across all evaluated tasks, outperforming larger models such as Qwen3-VL-235B-Instruct and Gemini-2.5-Pro in card and receipt information extraction, video subtitle extraction, and OCRBench. The model demonstrates strong performance with only around 1B parameters, achieving state-of-the-art results in information extraction and visual question answering despite its compact size.
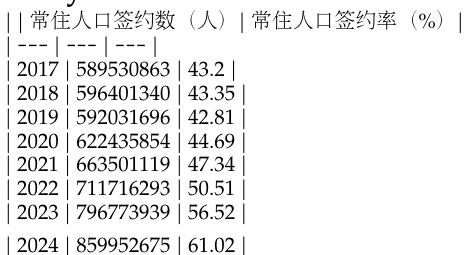
The authors use a table to present annual data on resident population and registration rates from 2017 to 2024, showing a consistent increase in both the number of residents and the registration rate over the years. The data indicates that the resident population grew from 589.5 million in 2017 to 859.9 million in 2024, while the registration rate rose from 43.2% to 61.02% during the same period.