Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Gemma 3 Technischer Bericht
Gemma 3 Technischer Bericht
Zusammenfassung
Wir stellen Gemma 3 vor, eine multimodale Erweiterung der Gemma-Familie leichtgewichtiger, offener Modelle mit Größenordnungen zwischen 1 und 27 Milliarden Parametern. Diese Version verfügt über Fähigkeiten zur visuellen Wahrnehmung, umfasst eine breitere Sprachpalette und verarbeitet längere Kontexte – mindestens 128.000 Tokens. Zudem haben wir die Architektur des Modells angepasst, um den KV-Cache-Speicher zu reduzieren, der bei langen Kontexten tendenziell explodiert. Dies erreichen wir durch eine Erhöhung des Verhältnisses lokaler zu globalen Aufmerksamkeitslayer und durch eine Verkürzung des Bereichs der lokalen Aufmerksamkeit. Die Gemma 3-Modelle werden mittels Distillation trainiert und erreichen sowohl für die vortrainierten als auch für die instruktionsfine-tuneten Versionen eine überlegene Leistung im Vergleich zu Gemma 2. Insbesondere unser neuartiges Post-Training-Rezept verbessert signifikant die Fähigkeiten im Bereich Mathematik, Chat, Anweisungsfolge und Mehrsprachigkeit. Dadurch ist Gemma3-4B-IT wettbewerbsfähig mit Gemma2-27B-IT, während Gemma3-27B-IT benchmarkmäßig mit Gemini-1.5-Pro vergleichbar ist. Alle unsere Modelle stellen wir der Community zur Verfügung.
One-sentence Summary
The authors, from Google DeepMind, introduce Gemma 3—a multimodal, long-context, and multilingual open language model family ranging from 1B to 27B parameters—featuring a novel architecture with a 5:1 interleaved local-to-global attention ratio to reduce KV-cache memory by limiting local attention spans to 1024 tokens, enabling 128K context support; the models leverage a distilled training recipe with a tailored SigLIP vision encoder and Pan & Scan method for flexible image input, achieving performance competitive with larger models like Gemma2-27B-IT and Gemini-1.5-Pro across math, coding, instruction-following, and multilingual tasks, while maintaining efficiency on consumer hardware.
Key Contributions
- Gemma 3 introduces multimodal capabilities by integrating a tailored SigLIP vision encoder to process images, encoding them as a sequence of 256 soft tokens, while maintaining compatibility with standard consumer hardware and enabling flexible image resolutions via a Pan and Scan method.
- The model achieves a 128K token context length through a novel architectural design that interleaves local attention layers (with a 1024-token span) with global layers, significantly reducing KV-cache memory usage during inference without sacrificing performance.
- Through a new post-training recipe involving distillation and targeted fine-tuning, Gemma 3-4B-IT outperforms Gemma 2-27B-IT on math, instruction-following, and multilingual benchmarks, while Gemma 3-27B-IT matches Gemini-1.5-Pro on key evaluation tasks.
Introduction
The authors introduce Gemma 3, an open multimodal language model extending the Gemma family with vision understanding, support for over 100 languages, and a context length of at least 128K tokens—significantly advancing the capabilities of lightweight, accessible models. Prior work in open models faced challenges in scaling multimodal and long-context performance without excessive memory demands, particularly due to the growing size of KV-cache in attention mechanisms. To address this, Gemma 3 adopts a hybrid attention architecture with a higher ratio of local to global attention layers and short local spans, reducing memory overhead while preserving performance. The model achieves state-of-the-art results for its size through a novel post-training recipe that enhances math, instruction-following, chat, and multilingual abilities, with the 4B-IT variant matching Gemma 2’s 27B-IT and the 27B-IT version approaching Gemini-1.5-Pro. The release is accompanied by rigorous safety and governance measures, including pre-training data filtering, alignment with Google’s safety policies, and targeted assurance evaluations, ensuring responsible deployment despite expanded capabilities.

Dataset
- The dataset for pre-training consists of a large-scale mixture of text and image data, with total token budgets of 14T for the 27B model, 12T for the 12B model, 4T for the 4B model, and 2T for the 1B model—slightly higher than Gemma 2 to accommodate the inclusion of multimodal content.
- The data mix includes both monolingual and parallel multilingual text, with language representation balanced using a strategy inspired by Chung et al. (2023) to improve coverage across languages.
- A rigorous filtering pipeline removes sensitive information, personal data, and content that could lead to unsafe or unwanted outputs. Evaluation sets are decontaminated to prevent data leakage, and a quality reweighing step based on Sachdeva et al. (2024) reduces the influence of low-quality data.
- The authors use knowledge distillation during pre-training, sampling 256 logits per token based on teacher model probabilities. The student model learns the teacher’s output distribution over these samples using cross-entropy loss, with non-sampled logits set to zero and the distribution renormalized.
- The tokenizer is a SentencePiece-based model with byte-level encoding, digit splitting, and preserved whitespace—same as Gemini 2.0—resulting in a 262k-token vocabulary that offers better balance for non-English languages.
- For model deployment, quantized versions are produced via Quantization Aware Training (QAT) over 5,000 steps, using the non-quantized checkpoint as a target. The training data is adapted to match pre- and post-training distributions.
- Three quantization formats are supported: per-channel int4, per-block int4, and switched fp8, with memory footprints reported in Table 3 for both raw (bfloat16) and quantized models at a 32,768-token context length, including KV cache overhead.
Method
The authors leverage a decoder-only transformer architecture for the Gemma 3 models, consistent with prior versions, but introduce several key architectural enhancements to support multimodality, long-context processing, and improved efficiency. The model employs Grouped-Query Attention (GQA) with post-norm and pre-norm configurations using RMSNorm, and replaces the soft-capping mechanism from Gemma 2 with QK-norm, inspired by recent advancements in attention normalization. The overall framework maintains structural similarities to earlier Gemma iterations while incorporating novel design choices to scale performance and capabilities.
A central architectural innovation is the integration of long-context support up to 128K tokens, with the 1B model limited to 32K. This is achieved through a hybrid attention mechanism that interleaves local and global layers in a 5:1 ratio, starting with a local layer. The local layers use a sliding window self-attention with a span of 1024 tokens, while the global layers attend to the full context. To extend the positional encoding range for global attention, the RoPE base frequency is increased from 10k to 1M, while local layers retain the 10k frequency. This design reduces memory overhead during inference by limiting long-range attention to only the global layers, mitigating the KV cache explosion typically associated with long sequences.
The models are trained with a shared tokenizer derived from Gemini 2.0, featuring a vocabulary of 256k entries. The pre-training recipe builds upon Gemma 2, with modifications to the data mixture to enhance multilingual and image understanding capabilities. All models are trained using knowledge distillation, where a larger teacher model guides the learning of the target model. This approach enables efficient transfer of knowledge while maintaining performance across diverse tasks.
For multimodal capabilities, the models integrate a vision encoder based on a 400M-parameter variant of SigLIP, a Vision Transformer trained with a CLIP-style loss. The encoder processes square images resized to 896×896 and is finetuned on visual assistant data. To handle non-square and high-resolution images without degradation, the system employs a Pan and Scan (P&S) method during inference. This adaptive windowing algorithm segments the image into non-overlapping crops of equal size, each resized to 896×896, and processes them independently. The method is applied only when necessary and can be disabled for faster inference, ensuring flexibility without compromising quality.
Post-training focuses on enhancing instruction-following, reasoning, mathematics, and chat abilities, while integrating the new long-context and visual input capabilities. The authors employ an improved post-training pipeline that combines knowledge distillation from a large instruction-tuned teacher with a reinforcement learning phase. This RL stage uses multiple reward functions to optimize for helpfulness, code execution accuracy, mathematical reasoning, and multilingual performance, while minimizing harmful outputs. The reward models are trained on human feedback data, and the system incorporates ground-truth rewards for math problems and code execution feedback. Data filtering is applied to remove examples containing personal information, unsafe content, or hallucinatory patterns, while preserving subsets that promote factuality and responsible behavior. The instruction-tuned models are formatted with a [BOS] token at the beginning of text and use <end_of_turn> as the generation end token, differing from the pre-trained models that use . This consistent tokenization scheme ensures compatibility across model types and training phases.
Experiment
- Evaluated Gemma 3 27B IT model on LMSys Chatbot Arena, achieving an Elo score of 1338, placing it among the top 10 models and outperforming larger non-thinking models like DeepSeek-V3 (1318) and LLaMA 3 405B (1257), with a significant improvement over Gemma 2 (1220).
- On standard benchmarks, Gemma 3 IT models show improved performance over Gemma 2 and competitive results with Gemini 1.5, particularly in multilinguality and reasoning, despite the addition of vision capabilities.
- Pre-training ability probing demonstrates that Gemma 3 models outperform Gemma 2 across science, code, factuality, multilinguality, reasoning, and vision tasks, with enhanced multilingual quality.
- Ablation studies show minimal impact on perplexity when increasing the local:global attention ratio to 7:1 or reducing sliding window size, while significantly reducing KV cache memory overhead—down to less than 15% compared to 60% in global-only models.
- Vision encoder evaluations confirm that higher input image resolution improves performance, and Pan & Scan (P&S) significantly boosts results on tasks involving text on images and varying aspect ratios.
- Gemma 3 models exhibit substantially lower memorization rates than prior models, with a 24x higher proportion of approximate memorization, and no detected personal information in memorized outputs, indicating strong privacy safeguards.
- Baseline safety evaluations show a significantly low violation rate across adversarial queries, and CBRN knowledge evaluation reveals limited performance in chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear domains.
- On long-context benchmarks, Gemma 3 models generalize effectively to 128K tokens after RoPE rescaling, though performance degrades with further scaling.
- On multimodal benchmarks, Gemma 3 IT models achieve strong results on vision understanding and video QA tasks, with P&S activation improving performance on complex visual inputs.
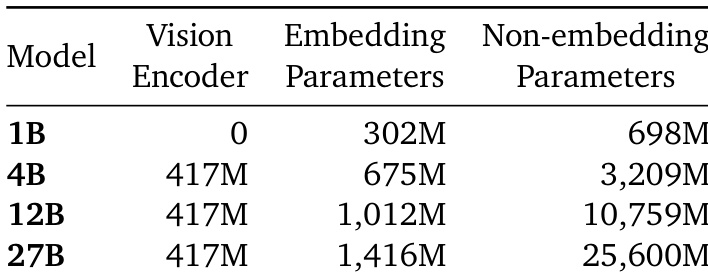
The authors use a vision encoder with 417 million parameters for models larger than 1B, while the 1B model does not use a vision encoder. As model size increases, both embedding and non-embedding parameters grow significantly, with the 27B model having 1.4 billion embedding parameters and 25.6 billion non-embedding parameters.
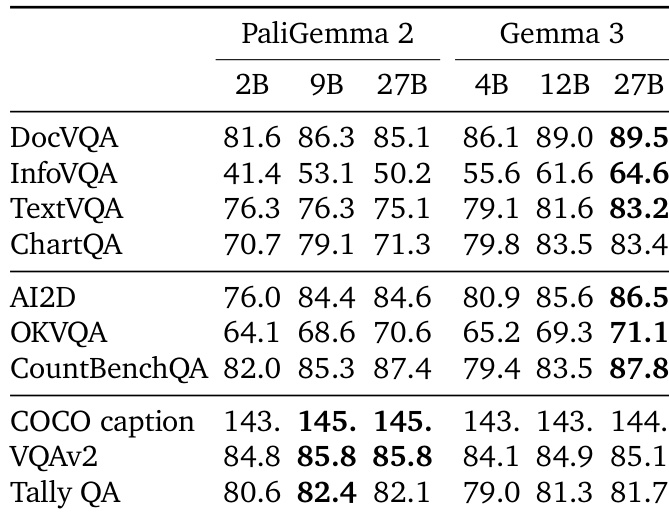
The authors compare the performance of PaliGemma 2 and Gemma 3 models across various vision and language benchmarks, showing that Gemma 3 models consistently outperform PaliGemma 2 across most tasks, with the 27B Gemma 3 model achieving the highest scores in several categories. Results indicate that the improvements in Gemma 3 are particularly notable in vision-language tasks such as DocVQA and TextVQA, where the 27B model achieves a score of 89.5 and 83.2 respectively, surpassing all PaliGemma 2 variants.
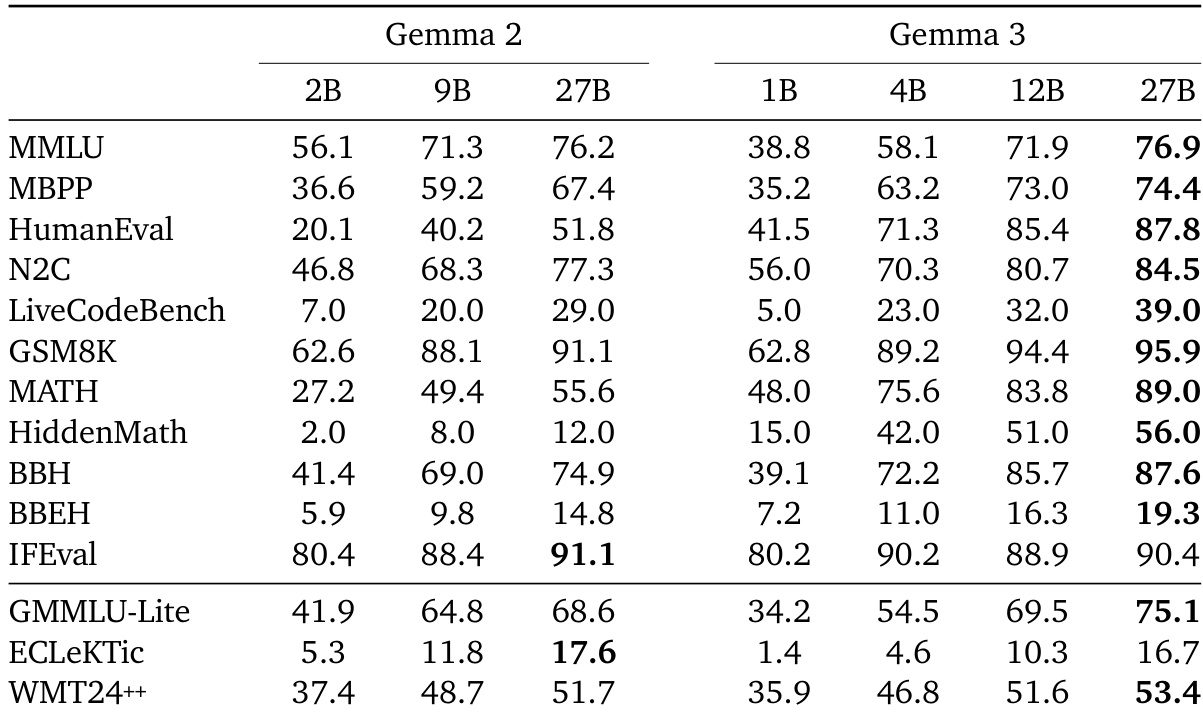
The authors compare the performance of Gemma 2 and Gemma 3 models across various benchmarks, showing that Gemma 3 models generally outperform their Gemma 2 counterparts. For instance, on MMLU, the 27B Gemma 3 model achieves a score of 76.9, surpassing the 76.2 score of the 27B Gemma 2 model, while on HumanEval, the 27B Gemma 3 model scores 87.8 compared to 51.8 for the 27B Gemma 2 model.
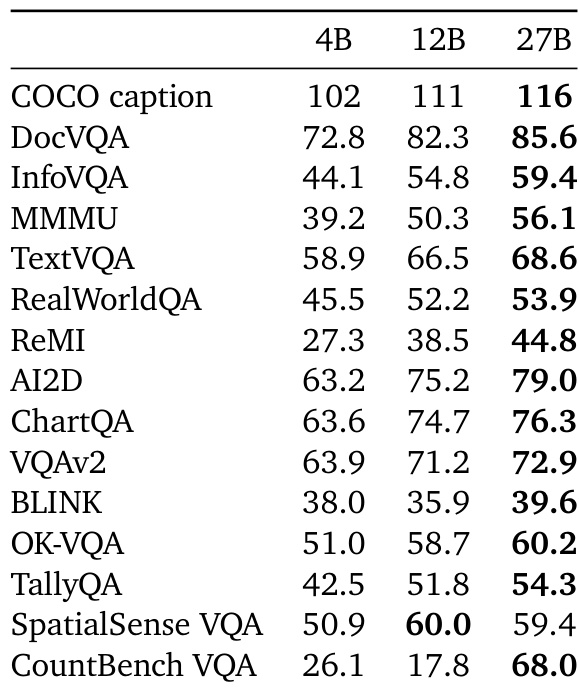
The authors evaluate the performance of their instruction fine-tuned models across various multimodal benchmarks, showing that larger model sizes generally improve results. The 27B model achieves the highest scores on most tasks, with notable improvements in areas like COCO captioning and RealWorldQA, while the 12B model performs best on SpatialSense VQA.
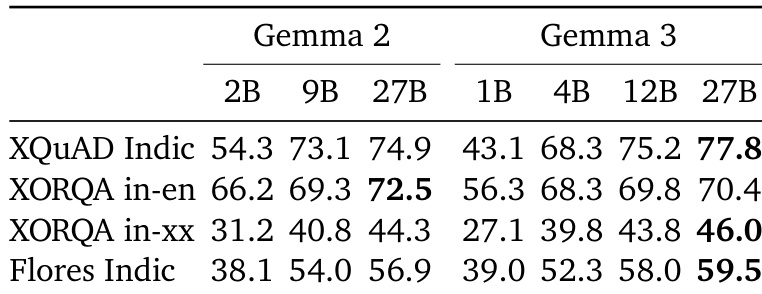
The authors compare the performance of Gemma 2 and Gemma 3 models across several benchmarks, showing that Gemma 3 models generally outperform Gemma 2 models. Specifically, Gemma 3 27B achieves the highest score on XQuAD Indic and XORQA in-xx, while Gemma 3 1B and 4B show improvements over their Gemma 2 counterparts on most tasks.