Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
هارموني: مزج إنشاء الصوت والفيديو من خلال التآزر بين المهام المختلفة
هارموني: مزج إنشاء الصوت والفيديو من خلال التآزر بين المهام المختلفة
Teng Hu Zhentao Yu Guozhen Zhang Zihan Su Zhengguang Zhou Youliang Zhang Yuan Zhou Qinglin Lu Ran Yi
الملخص
يُعدّ إنشاء محتوى صوتي بصري متماسكًا تحديًا رئيسيًا في الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي، حيث تواجه النماذج المفتوحة المصدر صعوبات في تحقيق محاذاة صوتية-بصرية قوية. تُظهر تحليلاتنا أن هذه المشكلة تنبع من ثلاث تحديات جوهرية في عملية التشتت المشتركة: (1) انحراف التوافق، حيث تعيق التمثيلات الضوضائية التي تتطور بالتوازي التعلم المستقر للمحاذاة؛ (2) آليات الانتباه العالمي غير الفعّالة التي تفشل في التقاط الإشارات الزمنية الدقيقة؛ و(3) التحيّز الداخلي للنمط التقليدي للإرشاد الحر من الفئة (CFG)، الذي يعزز الشروط لكنه لا يعزز التزامن بين الوسائط المختلفة. لتجاوز هذه التحديات، نقدّم "هارموني" (Harmony)، إطارًا جديدًا يفرض التزامن الصوتي-البصري بشكل آلي. نقترح أولًا نموذج تدريب متعدد المهام (Cross-Task Synergy) لتقليل الانحراف من خلال الاستفادة من إشارات إشرافية قوية من مهام إنشاء فيديو مدفوع بالصوت وإنشاء صوت مدفوع بالفيديو. ثم نصمم وحدة تفاعل منفصلة بين العالمي والمحلي (Global-Local Decoupled Interaction Module) لضمان محاذاة زمنية-نمطية فعّالة ودقيقة. وأخيرًا، نقدّم إرشادًا جديدًا يعزز التزامن (SyncCFG) يُعزل ويُضخم إشارة المحاذاة بشكل صريح أثناء عملية الاستدلال. تُظهر التجارب الواسعة أن "هارموني" تُحدث حالة جديدة من الذروة في الأداء، وتتفوّق بشكل ملحوظ على الطرق الحالية من حيث دقة الإنشاء، وبشكل حاسم، في تحقيق التزامن الصوتي-البصري الدقيق.
Summarization
Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Tencent Hunyuan introduce Harmony, a generative framework for synchronized audio-visual synthesis that overcomes alignment drift and attention inefficiencies by employing a Cross-Task Synergy training paradigm, a Global-Local Decoupled Interaction Module, and a Synchronization-Enhanced CFG to achieve state-of-the-art fidelity and temporal precision.
Introduction
The unified synthesis of audio and video is a critical frontier in generative AI, essential for creating immersive digital avatars and virtual worlds. While proprietary models like Sora 2 deliver high-fidelity results, the open-source community faces significant hurdles in achieving precise audio-visual alignment. Existing methods often struggle to synchronize human speech with ambient sounds effectively, largely due to "Correspondence Drift," a phenomenon where the model fails to align two concurrently evolving, noisy modalities during the early diffusion stages. Furthermore, standard architectures frequently conflate global stylistic consistency with frame-level timing, resulting in poor lip-sync and disjointed audio-visual experiences.
To address these gaps, the authors introduce Harmony, a joint audio-video generation framework designed to produce highly synchronized content ranging from ambient noises to human speech.
The authors leverage three core innovations to achieve this stability:
- Cross-Task Synergy: A training paradigm that co-trains joint generation alongside auxiliary audio-driven and video-driven tasks, using strong supervisory signals to prevent correspondence drift and instill robust alignment priors.
- Global-Local Decoupled Interaction: A module that separates global style attention from localized, frame-wise attention, ensuring the model captures both holistic emotional tone and precise temporal synchronization without trading one for the other.
- Synchronization-Enhanced CFG (SyncCFG): A novel inference technique that redefines negative conditioning—using mute audio or static video—to explicitly amplify the guidance vectors responsible for audio-visual alignment.
Dataset
Training Data Composition and Processing
- Source Material: The authors compiled a diverse corpus of over 4 million audio-visual clips, encompassing both human speech and environmental sounds.
- Data Origins: The dataset aggregates public sources, including OpenHumanVid, AudioCaps, and WavCaps, and is supplemented by curated high-quality internal collections.
- Annotation: To ensure consistency across these varied sources, all data was uniformly annotated using Gemini.
Training Strategy
- Curriculum Learning: The model is trained using a three-stage curriculum:
- Foundational audio pre-training utilizing the entire audio dataset.
- Timbre disentanglement finetuning focused specifically on multi-utterance speech data.
- Final cross-task joint audio-visual training, with the video branch initialized from Wan2.2.
- Hyperparameters: The final joint stage is trained for 10,000 iterations using a batch size of 128 and a learning rate of 1e-5.
Harmony-Bench Evaluation Dataset To rigorously assess the model, the authors introduced Harmony-Bench, a benchmark comprising 150 test cases organized into three distinct subsets of 50 items each:
- Ambient Sound-Video: This subset evaluates non-speech acoustic events using synthetically constructed scenarios. It conditions the model on detailed audio and video captions to test temporal alignment and semantic consistency.
- Speech-Video: Designed to assess lip-sync and speech fidelity, this subset includes a balanced mix of 25 real-world and 25 AI-synthesized samples. It utilizes English and Chinese transcripts with minimal video captions, compelling the model to derive visual dynamics directly from the text.
- Complex Scene (Ambient + Speech): This subset represents the most challenging scenarios with co-occurring audio-visual events. It requires the model to process transcripts, ambient sound descriptions, and visual scene descriptions simultaneously to evaluate sound source separation and multi-modal synchronization.
Method
The authors leverage a dual-stream latent diffusion framework for joint audio-video synthesis, where video and audio are encoded into latent representations zv and za respectively. The core of the model, named Harmony, employs a Multi-Modal Diffusion Transformer (MM-DiT) to perform denoising, with the primary task being the joint generation of synchronized audio and video. The model architecture features parallel branches for video and audio generation, with the video branch adapting a pre-trained Wan2.2-5B model. The audio branch is symmetrically designed to synthesize audio conditioned on a speech transcript Ts, a descriptive caption Ta, and a reference audio Ar. These inputs are processed through a multi-encoder setup: an audio VAE encodes the target and reference audio into latents za and zr, while separate text encoders—specifically a speech-encoder for Ts and a T5 encoder for Ta—preserve phonetic precision. During denoising, the reference latent zr is prepended to the noisy target audio latent za,t, forming a composite input za,t′, which, along with the text embeddings, is fed into the MM-DiT to predict the noise.
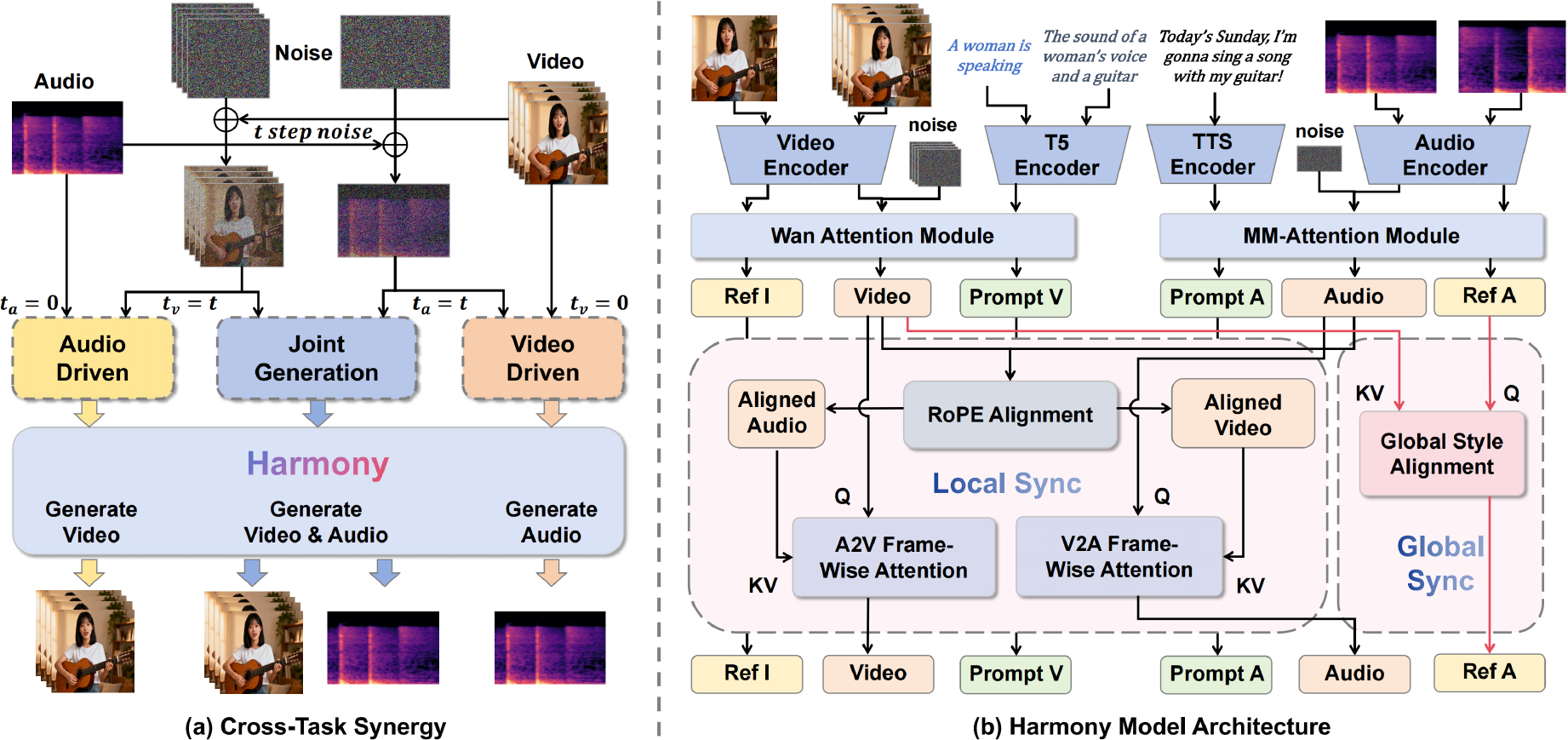
The model's training is governed by a hybrid strategy called Cross-Task Synergy, which combines the standard joint generation task with two auxiliary, deterministic tasks: audio-driven video generation and video-driven audio generation. This approach leverages the strong, uni-directional supervisory signals from the auxiliary tasks to stabilize and accelerate the learning of audio-video alignment. The total training objective is a weighted sum of the three corresponding losses, as defined in the equation below, where the auxiliary tasks are conditioned on the clean, noise-free latent of the driving modality (e.g., ta=0 for audio-driven video generation). This bidirectional synergy enables the model to pre-learn robust alignment knowledge, which then acts as a catalyst for the primary joint generation task.
L=Ljoint+λvLdrivenaudio+λaLdrivenvideoTo ensure effective cross-modal interaction, the authors introduce a Global-Local Decoupled Interaction Module, which resolves the inherent tension between fine-grained temporal alignment and holistic stylistic consistency. This module is composed of two specialized components. The first is a RoPE-Aligned Frame-wise Attention mechanism, which addresses the challenge of mismatched sampling rates between video and audio latents. By dynamically scaling the Rotary Positional Embeddings (RoPE) of the source modality to match the timeline of the target, the module establishes a strong inductive bias for correct temporal correspondence. This is followed by a symmetric, bidirectional cross-attention operation, where each frame attends to a small, relevant temporal window in the other modality, enforcing precise local synchronization.
The second component is the Global Style Alignment module, which is responsible for propagating holistic stylistic attributes such as emotional tone and ambient features. This module operates by modulating the reference audio latent zr with the global context from the entire video latent zv through a residual cross-attention block. The resulting visually-informed reference latent zrupdated is then prepended to the noisy audio latent za,t, allowing the audio generation to condition on a globally consistent style without interfering with the fine-grained temporal alignment process.

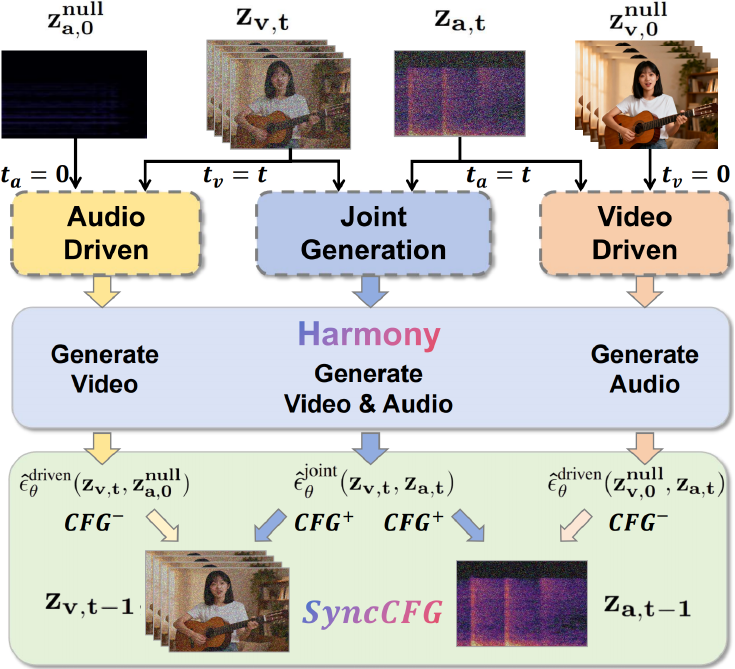
To further enhance synchronization during inference, the authors propose a novel Synchronization-Enhanced CFG (SyncCFG) mechanism. This scheme repurposes the standard Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) to explicitly amplify the audio-video correspondence signal. For video guidance, SyncCFG uses a "silent audio" negative anchor, which is the model's prediction for the video latent conditioned on a muted audio input za,0null. The guided prediction for the video noise is formulated by subtracting this baseline from the joint generation prediction, thereby isolating and amplifying the visual dynamics directly correlated with the audio. A symmetric formulation is applied for audio guidance, using a "static video" negative anchor zv,0null to isolate motion-driven sounds. This targeted approach transforms CFG from a generic conditional amplifier into a mechanism that specifically enforces fine-grained audio-visual correspondence.
Experiment
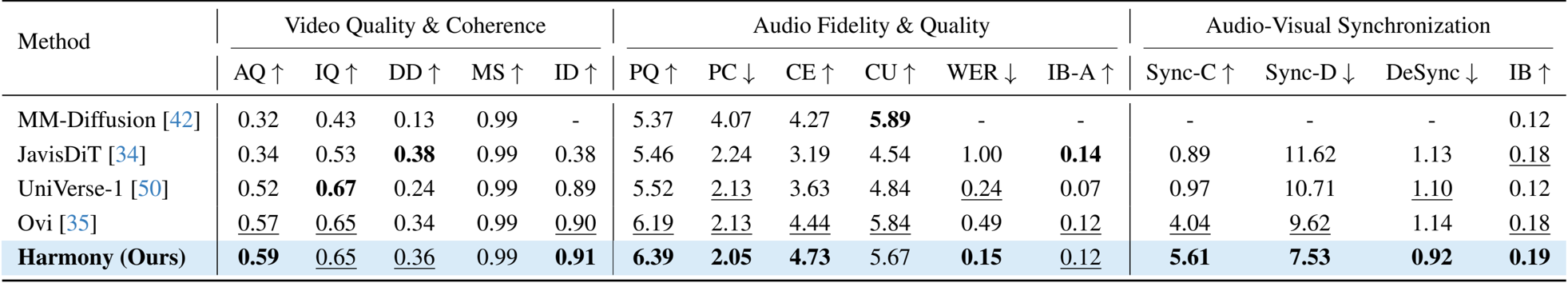
- Quantitative comparisons with state-of-the-art methods: Evaluations against MM-Diffusion, JavisDiT, UniVerse-1, and Ovi across ambient sound, speech, and complex scene datasets validate the model's superior performance in joint audio-video generation.
- Core performance metrics: The proposed Harmony model achieved state-of-the-art results in audio-visual synchronization, attaining a Sync-C score of 5.61 and a Sync-D score of 7.53, significantly outperforming baselines while maintaining competitive video quality and audio fidelity.
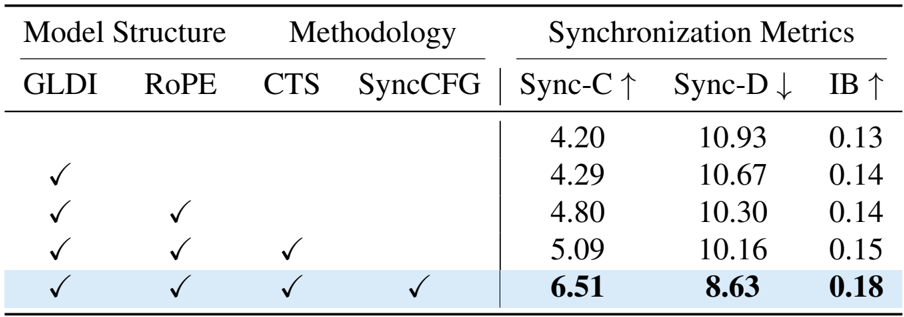
- Ablation studies: Experiments confirm the effectiveness of core components, particularly the Synchronization-Enhanced Classifier-Free Guidance (SyncCFG), which increased the Sync-C score from 5.09 to 6.51 on the human speech dataset.
- Qualitative and visual analysis: Attention map visualizations and qualitative comparisons demonstrate precise spatial-temporal alignment, showing the model effectively localizes sound sources (such as speaker lips or animals) and excels in diverse tasks including cross-lingual generation and artistic style rendering.
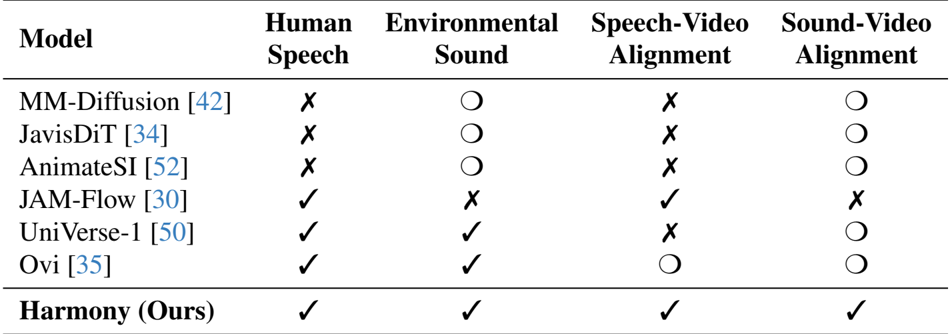
The authors compare their model, Harmony, with several state-of-the-art methods across different audio-video generation tasks. Results show that Harmony achieves the highest performance in both human speech and environmental sound generation, as well as in speech-video and sound-video alignment, outperforming all other models in these categories.
The authors use a comprehensive evaluation framework to compare Harmony with state-of-the-art audio-video generation models across video quality, audio fidelity, and audio-visual synchronization. Results show that Harmony achieves the highest scores in key synchronization metrics, including Sync-C and IB, while also excelling in video quality and audio fidelity, demonstrating its superior cross-modal alignment and overall performance.
The authors use an ablation study to evaluate the impact of their proposed components on audio-visual synchronization. Results show that adding the Global-Local Decoupled Interaction (GLDI) module improves synchronization, and further integrating RoPE Alignment, Cross-Task Synergy (CTS), and Synchronization-Enhanced CFG (SyncCFG) leads to consistent gains. The full model, which includes all components, achieves the highest Sync-C score of 6.51 and the lowest Sync-D score of 8.63, demonstrating the effectiveness of each contribution.