Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
MMaDA: Multimodal Large Diffusion Language Models
MMaDA: Multimodal Large Diffusion Language Models
Abstract
We introduce MMaDA, a novel class of multimodal diffusion foundation models designed to achieve superior performance across diverse domains such as textual reasoning, multimodal understanding, and text-to-image generation. The approach is distinguished by three key innovations: (i) MMaDA adopts a unified diffusion architecture with a shared probabilistic formulation and a modality-agnostic design, eliminating the need for modality-specific components. This architecture ensures seamless integration and processing across different data types. (ii) We implement a mixed long chain-of-thought (CoT) fine-tuning strategy that curates a unified CoT format across modalities. By aligning reasoning processes between textual and visual domains, this strategy facilitates cold-start training for the final reinforcement learning (RL) stage, thereby enhancing the model's ability to handle complex tasks from the outset. (iii) We propose UniGRPO, a unified policy-gradient-based RL algorithm specifically tailored for diffusion foundation models. Utilizing diversified reward modeling, UniGRPO unifies post-training across both reasoning and generation tasks, ensuring consistent performance improvements. Experimental results demonstrate that MMaDA-8B exhibits strong generalization capabilities as a unified multimodal foundation model. It surpasses powerful models like LLaMA-3-7B and Qwen2-7B in textual reasoning, outperforms Show-o and SEED-X in multimodal understanding, and excels over SDXL and Janus in text-to-image generation. These achievements highlight MMaDA's effectiveness in bridging the gap between pretraining and post-training within unified diffusion architectures, providing a comprehensive framework for future research and development. We open-source our code and trained models at: https://github.com/Gen-Verse/MMaDA
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Princeton University, Peking University, Tsinghua University, and ByteDance Seed propose MMADA, a unified multimodal diffusion foundation model with a modality-agnostic architecture and mixed long chain-of-thought fine-tuning, enabling seamless integration across text, vision, and generation tasks; their novel UniGRPO reinforcement learning algorithm unifies post-training via diversified rewards, significantly improving performance in textual reasoning, multimodal understanding, and text-to-image generation over state-of-the-art models.
Key Contributions
-
MMADA introduces a unified diffusion architecture with a modality-agnostic design and shared probabilistic formulation, enabling seamless integration and processing of diverse modalities—text, images, and beyond—without requiring modality-specific components, thus overcoming limitations of prior multimodal models that rely on separate pipelines for discrete and continuous data.
-
The framework employs a mixed long chain-of-thought (CoT) fine-tuning strategy that standardizes reasoning across modalities, aligning textual and visual reasoning processes to enable effective cold-start training for the subsequent reinforcement learning stage, thereby improving the model’s ability to tackle complex, multi-step tasks from the outset.
-
MMADA incorporates UniGRPO, a unified policy-gradient-based reinforcement learning algorithm with diversified reward modeling, which jointly optimizes reasoning and generation tasks; this leads to state-of-the-art performance across textual reasoning, multimodal understanding, and text-to-image generation, outperforming models like LLaMA-3-7B, Qwen2-7B, Show-o, SEED-X, SDXL, and Janus.
Introduction
The authors leverage multimodal diffusion models to build a unified foundation model capable of handling diverse tasks—textual reasoning, multimodal understanding, and text-to-image generation—within a single architecture. Prior work in multimodal models has largely focused on autoregressive or modality-specific designs, which struggle to balance reasoning and generation, especially in non-autoregressive settings. Existing unified models often lack effective post-training strategies, limiting their adaptability and performance across tasks. To address this, the authors introduce MMADA, a unified diffusion architecture with a modality-agnostic design and shared probabilistic formulation, eliminating the need for modality-specific components. They propose a mixed long chain-of-thought fine-tuning strategy to align reasoning across modalities, enabling effective cold-start training. Additionally, they develop UniGRPO, a unified reinforcement learning algorithm that uses diversified reward modeling to improve both reasoning and generation. These innovations enable MMADA-8B to outperform leading models in all three domains, demonstrating strong generalization and a cohesive framework for future multimodal AI development.
Dataset
- The dataset for MMADA is composed of multiple specialized subsets, each serving a distinct training stage: foundational language and multimodal data, instruction tuning, reasoning, and reinforcement learning.
- Foundational data includes RefinedWeb for text generation and a collection of open-sourced image-text datasets for multimodal understanding and generation.
- Instruction tuning data consists of Alpaca for textual instruction following and LLaVA-1.5 for visual instruction tuning.
- Reasoning data combines textual reasoning datasets (ReasonFlux, LIMO, s1k, OpenThoughts, AceMath-Instruct) with multimodal reasoning instances generated by the LMM-R1 model on GeoQA and CLEVR, retaining only correctly answered examples. Additionally, GPT-4.1 synthesizes factual item-description pairs across science, culture, and landmarks, formatted as CoT-style traces for world knowledge-aware image generation.
- Reinforcement learning data uses the original mathematical and logical datasets from the reasoning stage, specifically from GeoQA and CLEVR.
- The model is trained in three stages: Stage 1 (200K steps) uses foundational data with RefinedWeb and ImageNet-1k, later replacing ImageNet with more diverse image-text pairs; Stage 2 (50K steps) combines instruction tuning and reasoning data; Stage 3 (50K steps) applies UniGRPO with reinforcement learning data.
- Training is conducted on 64 A100 (80GB) GPUs with a global batch size of 1,280, using AdamW optimizer and a cosine learning rate scheduler starting at 5e-5.
- For evaluation, image generation is assessed using 50K test prompts via CLIP Score, ImageReward, GenEval, and WISE, while text generation is evaluated on MMLU and GSM8K.
- The model is initialized with LLaDA-8B-Instruct weights and a pretrained image tokenizer from Show-o.
Method
The authors leverage a unified diffusion architecture to model both textual and visual data under a single probabilistic framework, enabling joint understanding and generation tasks. The overall training pipeline consists of three stages: pretraining, mixed long-CoT finetuning, and UniGRPO reinforcement learning. The core of the model is a discrete diffusion framework that operates on tokenized sequences from both modalities. For text, the LLaDA tokenizer is used, while for images, a pretrained quantizer based on MAGVIT-v2 converts pixel data into a sequence of discrete tokens, with a downsampling factor of 16 resulting in a 32×32 token map for a 512×512 image. This unified tokenization allows the model to treat both modalities as sequences of discrete tokens, which are processed by a shared mask token predictor.
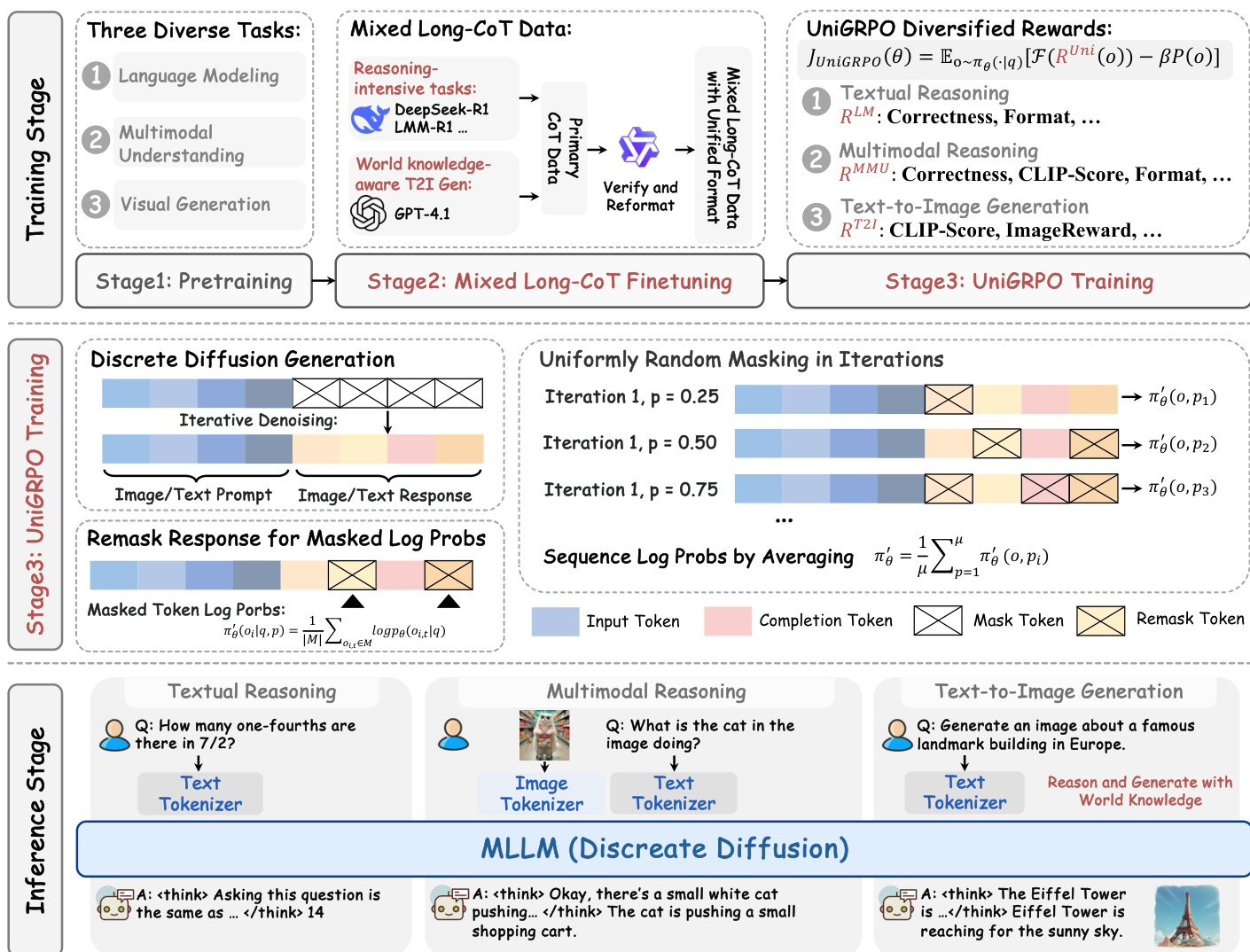
As shown in the figure below, the pretraining stage (Stage 1) employs a unified cross-entropy loss to train the model as a mask token predictor. The model, parameterized as pθ(⋅∣xt), takes a noisy input sequence xt and predicts all masked tokens simultaneously. The forward diffusion process corrupts the ground truth sequence x0 by progressively adding noise, and the model is trained to recover the original tokens. The loss is computed only on the masked tokens, ensuring the model learns to predict the correct tokens given the corrupted context. This unified formulation aligns the noise corruption and semantic recovery processes across modalities, facilitating effective cross-modal interactions.
In the second stage, mixed long-CoT finetuning, the model is further optimized on a curated dataset of long-form reasoning trajectories. The authors introduce a task-agnostic CoT format that structures outputs as <special_token> <reasoning_process> <special_token> <result>, which bridges modality-specific outputs and enables knowledge transfer. The finetuning process involves retaining the original prompt and independently masking tokens in the result, then feeding the concatenated input into the model to compute a loss for reconstructing the masked regions. This joint training approach enhances task-specific capabilities while maintaining alignment with the original prompt.

The third stage, UniGRPO training, introduces a novel policy-gradient-based reinforcement learning algorithm tailored for diffusion models. This approach addresses the challenges of adapting autoregressive GRPO to diffusion architectures, such as local masking dependency and the inability to compute sequence-level log-likelihoods via the chain rule. UniGRPO employs a structured noising strategy where a random mask ratio is sampled for each response, ensuring the model is exposed to various denoising stages. It approximates the expected per-token log-likelihood under the perturbed distribution and computes the sequence-level log-likelihood by averaging over masked tokens. The policy gradient objective integrates clipped surrogate rewards and a KL divergence penalty to stabilize training. This design allows the model to learn from multi-step denoising dynamics, leveraging the full generative power of diffusion models.
Experiment
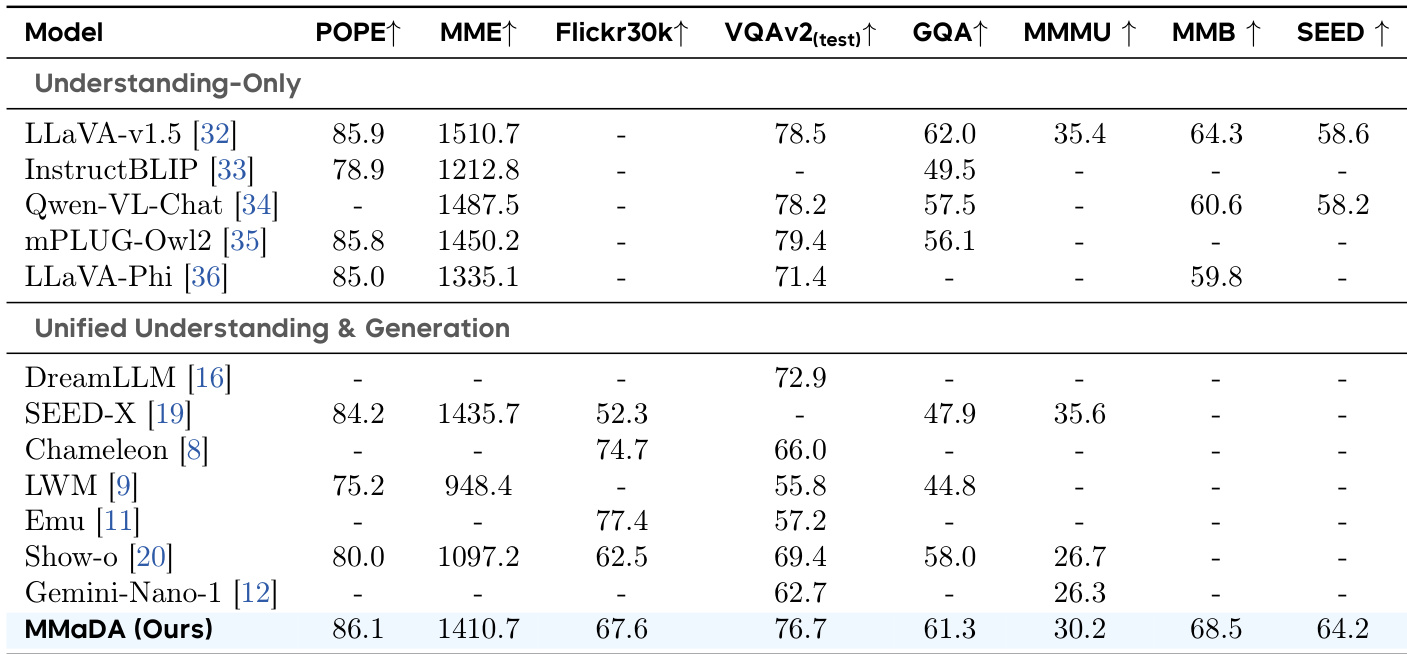
- Multimodal understanding: Achieved state-of-the-art or competitive results on POPE, MME, VQAv2, GQA, and MMMU benchmarks, outperforming dedicated models like LLaVA-v1.5 and unified models such as SEED-X and DreamLLM, validated by Mixed Long-CoT Finetuning and UniGRPO stages.
- Text-to-image generation: Achieved the highest CLIP Score and ImageReward on GenEval and WISE benchmarks, demonstrating superior compositionality, object counting, and world knowledge-aware generation, attributed to UniGRPO training and joint reasoning.
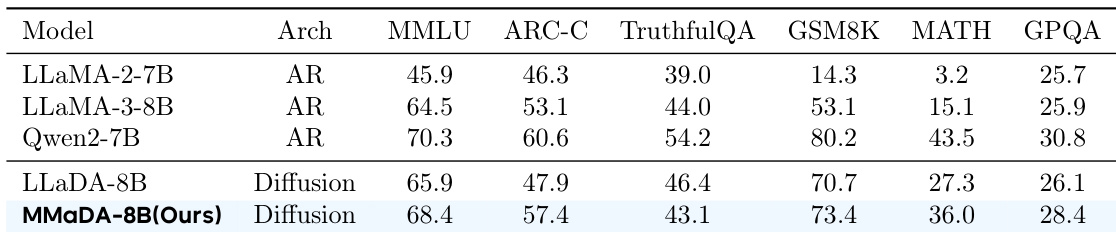
- Textual reasoning: Achieved comparable performance to Qwen2-7B and LLaMA3-8B on MMLU and ARC-C, and outperformed LLaDA-8B on GSM8K, MATH, and GPQA, establishing the viability of a unified diffusion-based model for general language tasks.
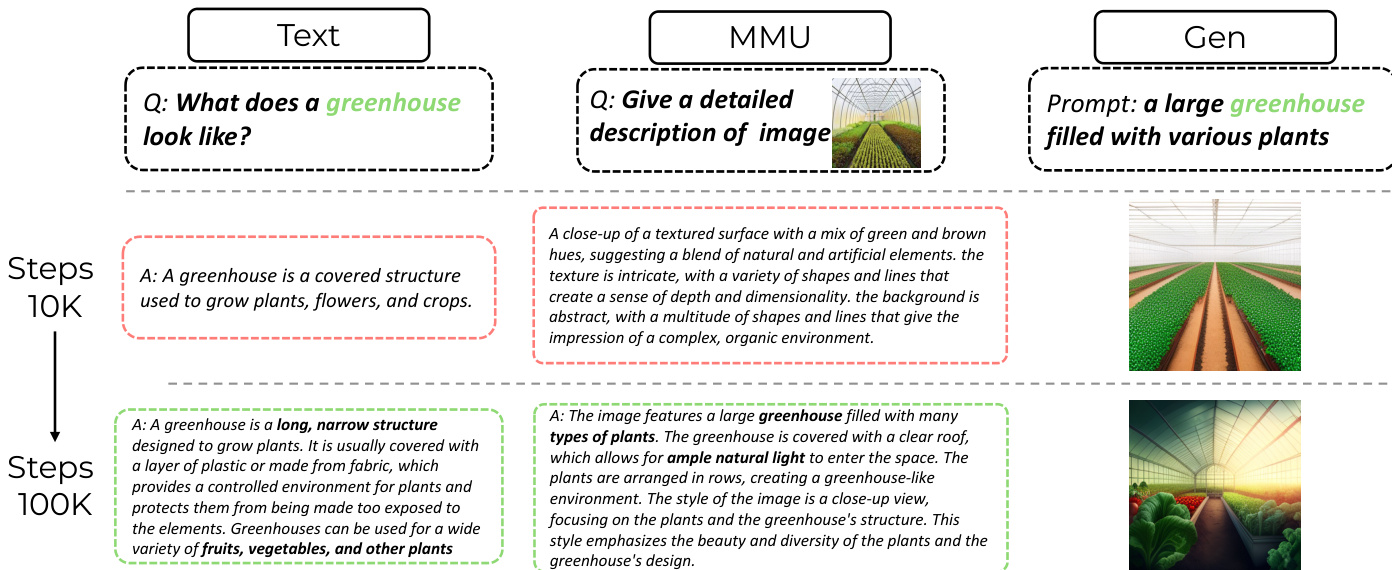
- Ablation studies: Mixed Long-CoT fine-tuning significantly improved reasoning, especially in math and geometry; UniGRPO further enhanced performance across all tasks, confirming its effectiveness in boosting both understanding and generation.
- Design choices in UniGRPO: Uniformly random masking and partial answer masking improved training stability and convergence, while enabling better utilization of diffusion model dynamics.
- Task synergy: Joint training across text generation, multimodal understanding, and image generation led to consistent performance gains and more coherent, accurate cross-modal outputs.
- Sampling efficiency: Diffusion-based generation achieved strong results with as few as 15–50 denoising steps, demonstrating significant efficiency over autoregressive models due to parallel token generation.
The authors use a diffusion-based model, MMaDA-8B, to evaluate its performance on language modeling benchmarks. Results show that MMaDA-8B achieves competitive results across multiple tasks, outperforming strong baselines like LLaMA-8B and Qwen2-7B on several benchmarks, particularly in mathematical reasoning and general language understanding.
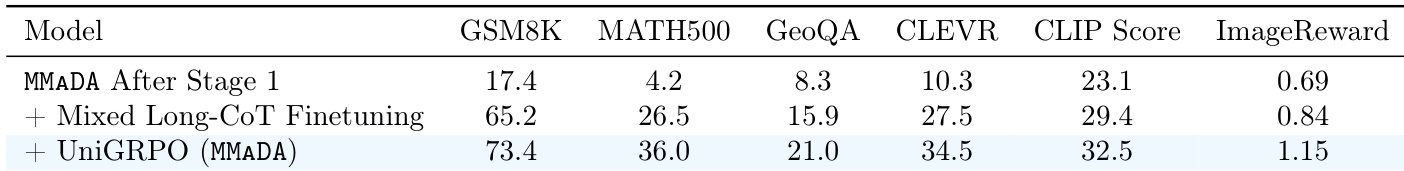
The authors use the table to show the impact of training stages on MMADA's performance across multiple benchmarks. Results show that after Stage 1, the model lags behind baselines, but adding Mixed Long-CoT Finetuning significantly improves performance, especially in reasoning tasks. Further applying UniGRPO leads to substantial gains across all tasks, achieving results comparable to state-of-the-art methods.
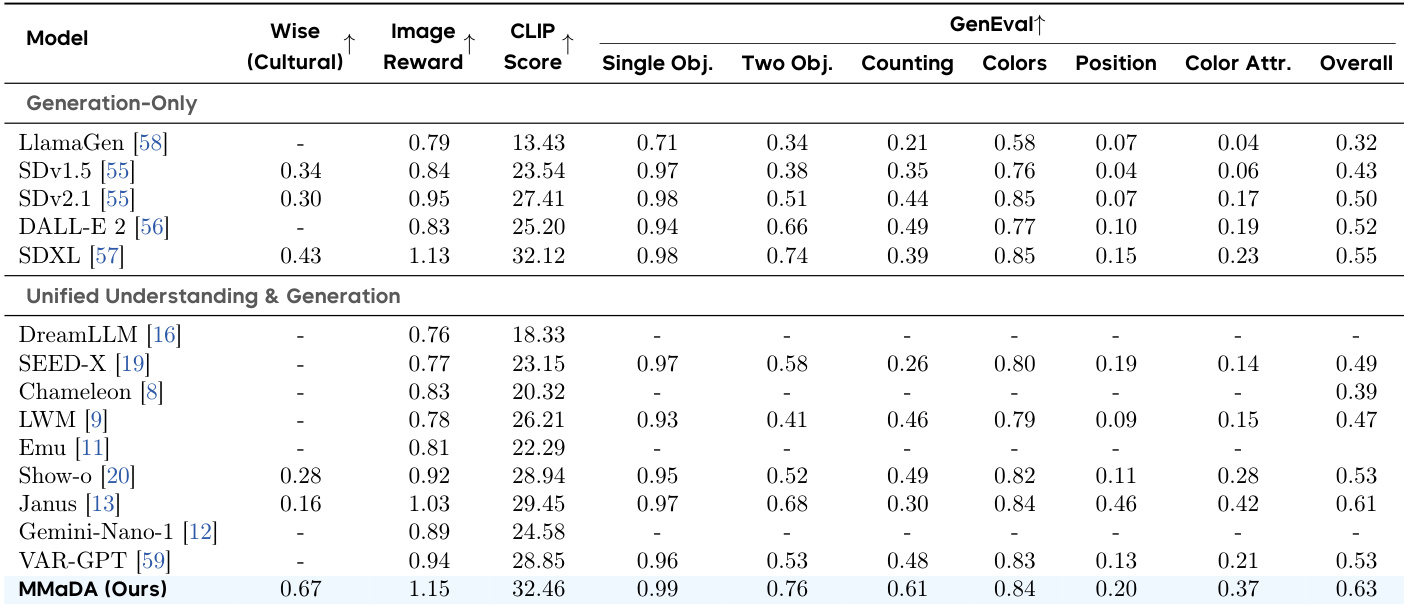
The authors use the table to compare the text-to-image generation performance of their unified model, MMaDA, against generation-only and unified models on benchmarks including CLIP Score, ImageReward, and GenEval. Results show that MMaDA achieves the highest scores in both CLIP Score and ImageReward, outperforming all other models, and demonstrates strong compositional and counting abilities on GenEval, particularly on the WISE cultural benchmark.
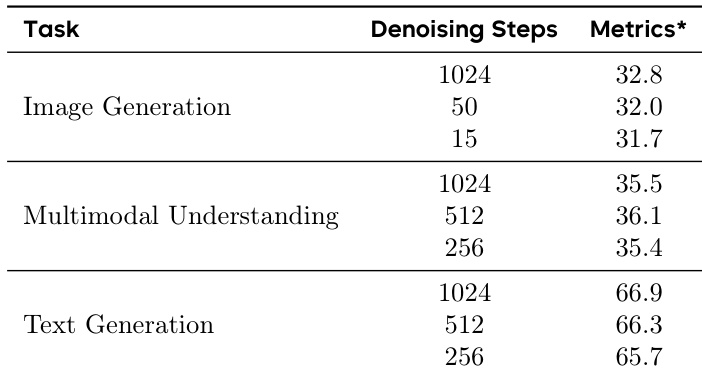
The authors use the table to evaluate the performance of MMaDA under different numbers of denoising steps across image generation, multimodal understanding, and text generation tasks. Results show that the model maintains strong performance in image generation even with as few as 15 denoising steps, while text and multimodal tasks achieve coherent outputs with significantly fewer steps than the full 1024.
The authors use the table to compare the multimodal understanding performance of their model, MMaDA, against various baselines on benchmarks such as POPE, MME, and VQAv2. Results show that MMaDA achieves competitive or superior results across most tasks, particularly outperforming other unified models, which highlights the effectiveness of their proposed training stages.