Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Flow-GRPO: Training Flow Matching Models via Online RL
Flow-GRPO: Training Flow Matching Models via Online RL
Jie Liu Gongye Liu Jiajun Liang Yangguang Li Jiaheng Liu Xintao Wang Pengfei Wan Di Zhang Wanli Ouyang
Abstract
We propose Flow-GRPO, the first method to integrate online policy gradient reinforcement learning (RL) into flow matching models. Our approach uses two key strategies: (1) an ODE-to-SDE conversion that transforms a deterministic Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) into an equivalent Stochastic Differential Equation (SDE) that matches the original model's marginal distribution at all timesteps, enabling statistical sampling for RL exploration; and (2) a Denoising Reduction strategy that reduces training denoising steps while retaining the original number of inference steps, significantly improving sampling efficiency without sacrificing performance. Empirically, Flow-GRPO is effective across multiple text-to-image tasks. For compositional generation, RL-tuned SD3.5-M generates nearly perfect object counts, spatial relations, and fine-grained attributes, increasing GenEval accuracy from 63% to 95%. In visual text rendering, accuracy improves from 59% to 92%, greatly enhancing text generation. Flow-GRPO also achieves substantial gains in human preference alignment. Notably, very little reward hacking occurred, meaning rewards did not increase at the cost of appreciable image quality or diversity degradation.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from MMLab, CUHK, Kuaishou Technology, and collaborating institutions propose Flow-GRPO, a novel method integrating online policy gradient reinforcement learning into flow matching models via ODE-to-SDE conversion for enhanced exploration and denoising reduction for improved sampling efficiency, achieving state-of-the-art performance in text-to-image generation, compositional accuracy, and human preference alignment with minimal reward hacking.
Key Contributions
-
Flow-GRPO introduces the first integration of online policy gradient reinforcement learning (RL) into flow matching models, addressing the fundamental challenge of their deterministic nature by converting the underlying ODE into an equivalent SDE through an ODE-to-SDE transformation, thereby enabling stochastic sampling essential for RL exploration while preserving the original marginal distributions.
-
The method employs a Denoising Reduction strategy that reduces the number of denoising steps during training—without altering the inference schedule—significantly improving sampling efficiency and reducing data generation costs, while maintaining high-quality outputs and enabling scalable online RL training.
-
Empirically, Flow-GRPO achieves state-of-the-art performance on compositional generation (GenEval accuracy increases from 63% to 95%) and visual text rendering (accuracy from 59% to 92%), while also improving human preference alignment on DrawBench, all with minimal reward hacking and no degradation in image quality or diversity.
Introduction
Flow matching models have emerged as a leading approach in text-to-image generation due to their efficient deterministic sampling and strong image quality, but they struggle with complex compositional tasks and accurate text rendering. Prior alignment methods for generative models have largely relied on offline reinforcement learning or direct fine-tuning, while online reinforcement learning—proven effective in enhancing language model reasoning—remains underexplored for flow-based models. A key challenge lies in the conflict between the deterministic nature of ODE-based flow models and the stochastic sampling required for online RL, compounded by the high computational cost of iterative sampling in large models. To address this, the authors propose Flow-GRPO, which integrates GRPO into flow matching via two core innovations: first, converting the ODE to an SDE to introduce controlled stochasticity without altering marginal distributions; second, applying denoising reduction to cut training sampling steps while preserving full denoising schedules at inference. This enables efficient online RL training with minimal reward hacking. Experiments show Flow-GRPO significantly boosts performance on compositional generation and text rendering—improving GenEval accuracy from 63% to 95% and text rendering from 59% to 92%—surpassing GPT-4o, while maintaining high image quality and generalizing across diverse reward types.
Dataset
- The dataset is composed of image-text pairs sourced from diverse public web crawls, curated for high quality and relevance to multimodal generation tasks.
- Each subset is filtered using a combination of automated quality metrics: aesthetic score (a CLIP-based regressor), DeQA score (a multimodal LLM for low-level artifact detection), ImageReward (a T2I preference model assessing alignment and fidelity), and UnifiedReward (a state-of-the-art unified reward model for human preference prediction).
- The filtering process applies strict thresholds on these metrics to retain only high-quality, visually coherent, and semantically aligned image-text pairs, ensuring robust training signals.
- The final dataset is split into training, validation, and test sets, with the training split used to fine-tune the base model using a mixture of supervised and reinforcement learning objectives.
- Mixture ratios for training are determined based on the relative performance and coverage of each reward model, balancing alignment, quality, and safety.
- Images are cropped to a standardized resolution during preprocessing to ensure consistency, and metadata such as source domain, image dimensions, and quality scores are preserved for downstream analysis and model evaluation.
Method
The authors leverage Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to enhance flow matching models for text-to-image generation, introducing a novel framework that integrates online reinforcement learning into the sampling process. The overall architecture, as illustrated in the figure, consists of three primary components: a stochastic sampling mechanism derived from a deterministic ODE, a denoising reduction strategy for efficient data collection, and a policy optimization loop that updates the model based on group-relative rewards.
The core of the method involves transforming the deterministic Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) used in standard flow matching into an equivalent Stochastic Differential Equation (SDE). This conversion enables the generation of diverse trajectories necessary for effective reinforcement learning. The deterministic ODE, which defines the forward process as dxt=vtdt, is modified to include stochasticity by adding a diffusion term. The resulting reverse-time SDE is formulated as dxt=(vt(xt)−2σt2∇logpt(xt))dt+σtdw, where σt controls the noise level and dw represents Wiener process increments. This SDE ensures that the marginal distribution of the stochastic process matches that of the original deterministic model at all timesteps, preserving the model's generative capabilities while introducing the necessary randomness for exploration.
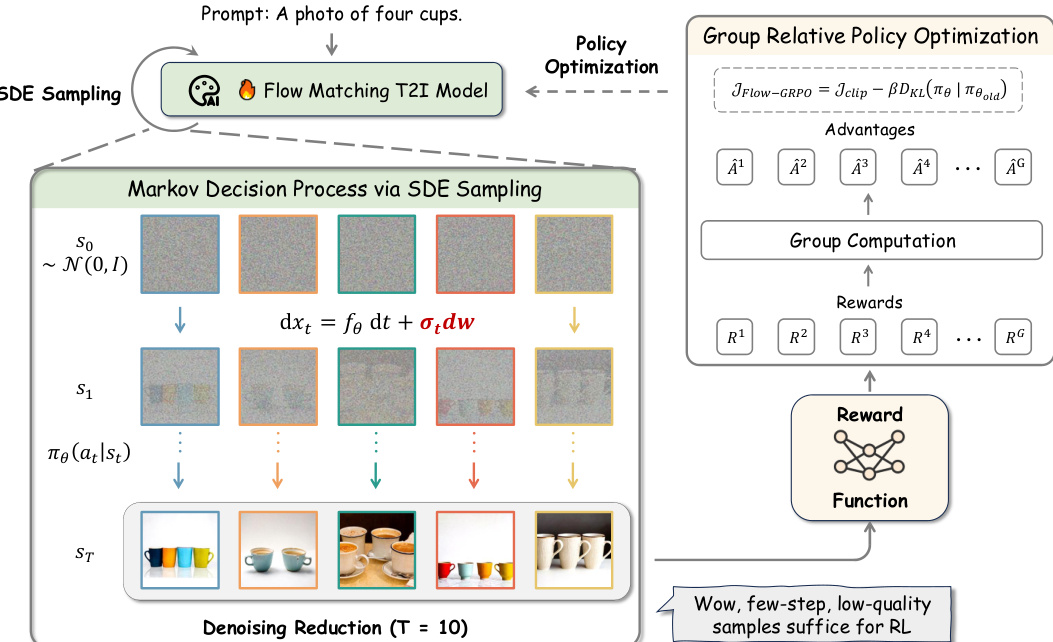
As shown in the figure below, the framework begins with a prompt, such as "A photo of four cups," which is fed into the Flow Matching T2I Model. The model then employs SDE sampling to generate a sequence of images, starting from a noise distribution N(0,I) and iteratively denoising through a Markov decision process. Each step t in this process is defined by a state st, which includes the conditioning text c, the current timestep t, and the noisy image xt. The action at each step is the denoised sample at, predicted by the model's policy πθ(at∣st). The transition between states is deterministic, but the stochasticity introduced by the SDE ensures that the policy can explore different paths, generating diverse trajectories.
To improve training efficiency, the authors implement a Denoising Reduction strategy, which uses a significantly reduced number of denoising steps during the data collection phase for reinforcement learning. In the figure, this is depicted as T=10 steps, which is much fewer than the typical T=40 steps used for high-quality inference. This reduction allows for the rapid generation of low-quality but still informative samples, which are sufficient for the RL process. The rewards for these samples are computed by a reward function, which evaluates the generated images against the prompt. These rewards are then used to compute group-relative advantages, which are fed into the GRPO loss function.
The GRPO loss, as shown in the figure, is defined as JFlow-GRPO=Jclip−βDKL(πθ∣πold). The group relative advantage A^ti for the i-th image in a group of G samples is calculated by normalizing the group-level rewards. The policy is updated by maximizing this objective, which includes a clipping term to stabilize training and a KL divergence penalty to prevent large policy updates. This approach ensures that the model learns to generate images that are not only aligned with the prompt but also maintain high image quality and diversity.
Experiment
- Compositional Image Generation on GenEval: Flow-GRPO achieves superior performance over GPT-4o and all baselines, improving on counting, color, attribute binding, and spatial relations, while maintaining high image quality and diversity on DrawBench.
- Visual Text Rendering: Flow-GRPO significantly enhances text fidelity, achieving high accuracy on OCR tasks without degrading image quality or preference scores on DrawBench.
- Human Preference Alignment: Flow-GRPO outperforms SFT, Flow-DPO, ReFL, and ORW on PickScore, with stable training and no decline in image quality, while preventing diversity collapse through KL regularization.
- Core results: On GenEval, Flow-GRPO surpasses GPT-4o and prior methods; on Visual Text Rendering, it achieves high text fidelity; on Human Preference, it consistently improves PickScore while preserving image quality and diversity across benchmarks.
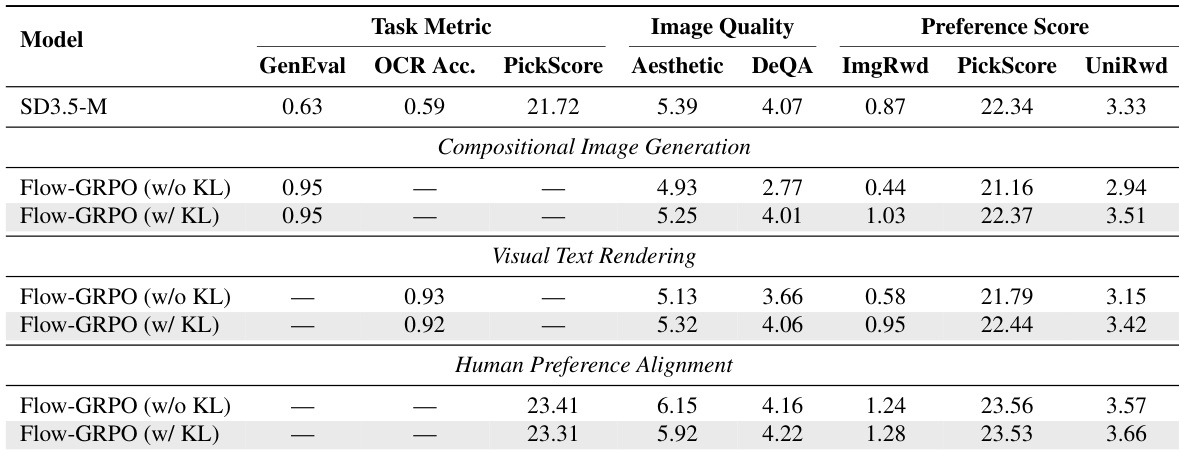
The authors use Flow-GRPO to improve a text-to-image model on compositional image generation, achieving a GenEval score of 0.95, which surpasses GPT-4o's score of 0.84. Results show that Flow-GRPO maintains or improves image quality and preference scores on DrawBench, with no significant degradation in aesthetic, DeQA, or preference metrics.
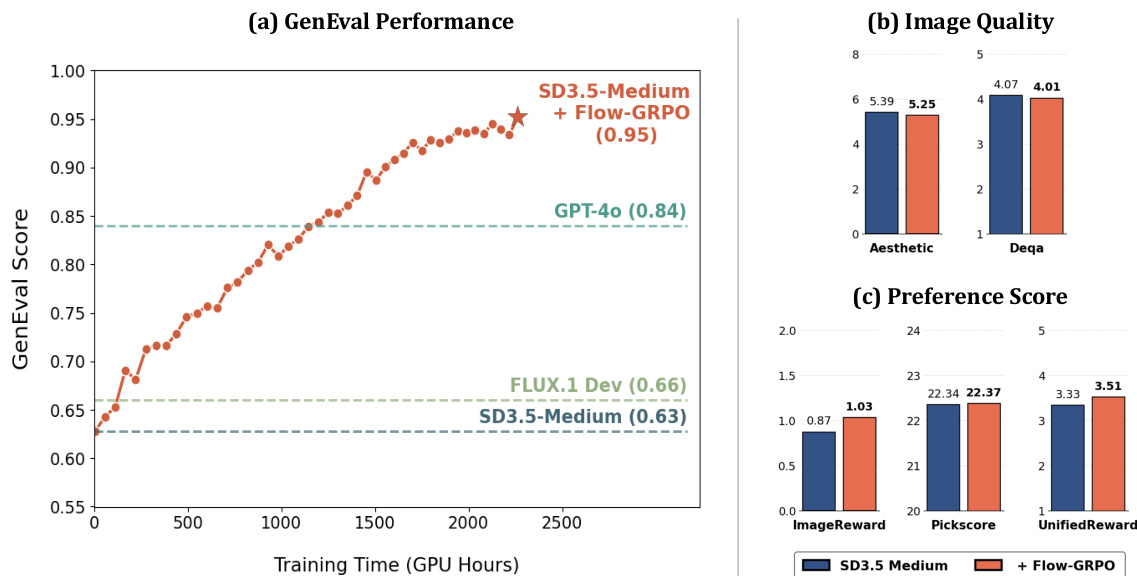
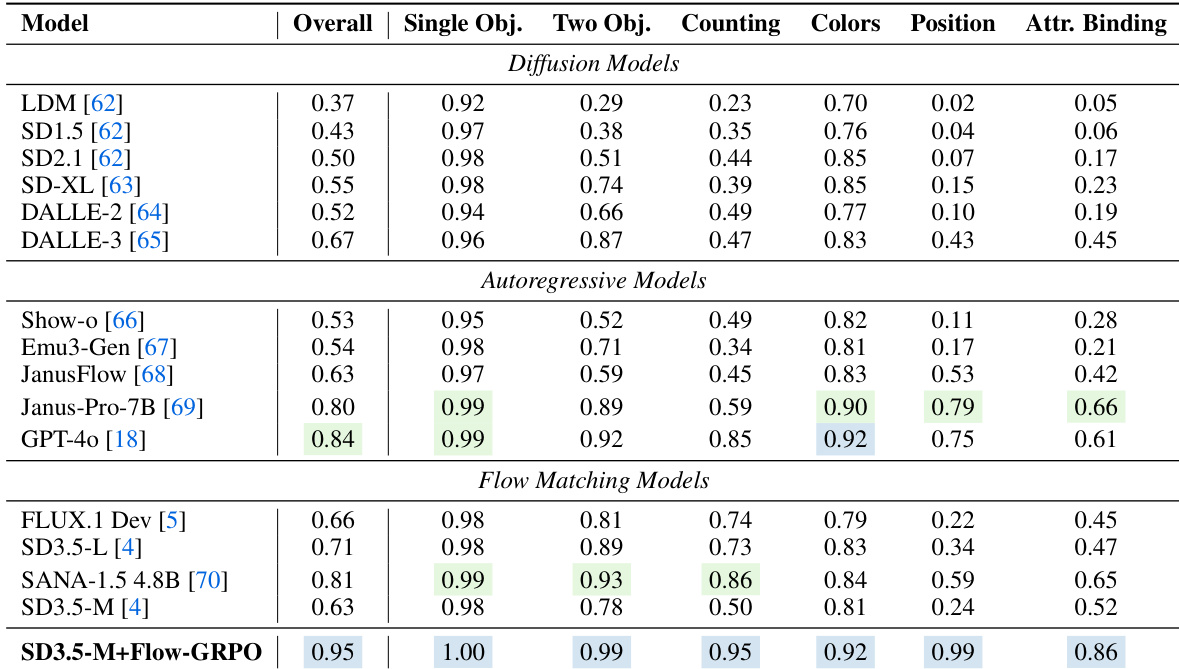
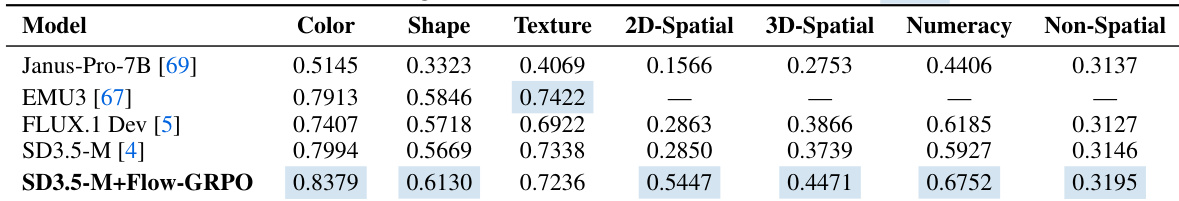
The authors use Flow-GRPO to enhance flow matching models, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the GenEval benchmark across all task categories, including object counting, color recognition, and attribute binding. Results show that SD3.5-M+Flow-GRPO outperforms all baseline models, particularly excelling in single-object and two-object tasks, while maintaining high overall accuracy and surpassing previous diffusion and autoregressive models.
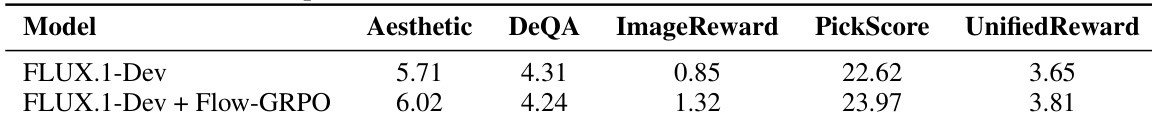
The authors use Flow-GRPO to fine-tune the FLUX.1-Dev model, resulting in improved performance across multiple image quality and preference metrics. Results show that Flow-GRPO enhances the model's aesthetic score, image reward, PickScore, and UnifiedReward while maintaining or slightly improving DeQA, indicating better alignment with human preferences without compromising image quality.
The authors use Flow-GRPO to enhance the SD3.5-M model, achieving significant improvements across multiple GenEval tasks, particularly in color, shape, and spatial reasoning, while maintaining competitive performance on other metrics. Results show that SD3.5-M+Flow-GRPO outperforms baseline models like Janus-Pro-7B and EMU3, with notable gains in color accuracy, shape recognition, and 2D/3D spatial understanding.
The authors use Flow-GRPO to improve text-to-image models on three tasks, showing that adding KL regularization maintains image quality and diversity while achieving higher task-specific performance. Results show that Flow-GRPO with KL regularization outperforms the base model and the version without KL across all tasks, with improvements in GenEval, OCR accuracy, and preference scores, while also preserving or enhancing image quality metrics.