Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Inferix:世界シミュレーション向け次世代推論エンジンとしてのブロックディフュージョンベースのアーキテクチャ
Inferix:世界シミュレーション向け次世代推論エンジンとしてのブロックディフュージョンベースのアーキテクチャ
概要
世界モデル(World Models)は、エージェント型AIやエンボディドAI、ゲーム開発などの分野における核心的なシミュレータとして機能し、物理的に現実的でインタラクティブな高品質な長時間動画の生成が可能である。さらに、これらのモデルをスケーリングすることで、視覚認識、理解、推論に関する新たな能力が出現し得るため、現在のLLM中心のビジョン基盤モデルにとどまらない、新たなパラダイムの実現が期待される。この進展を可能にする重要な技術的突破は、「準自己回帰型(ブロック・ディフュージョン)デコード」パラダイムである。この手法は、各ブロック内でブロック単位でディフュージョンを適用しながら、前のブロックに条件付けた形で動画トークンを生成することで、ディフュージョン法と自己回帰法の長所を統合している。その結果、より一貫性があり安定した動画シーケンスが得られる。特に重要なのは、従来の動画ディフュージョンモデルの限界を克服し、LLMで用いられるKVキャッシュ管理を再導入することで、効率的かつ可変長で高品質な生成を実現している点である。こうした背景から、Inferixは次世代の推論エンジンとして設計されており、最適化された準自己回帰型デコードプロセスを通じて、没入型の世界生成を実現することを目的としている。この世界シミュレーションに特化した設計は、高並列処理を想定したシステム(例:vLLMやSGLang)や、従来の動画ディフュージョンモデル(例:xDiTs)とは明確に異なる。さらに、Inferixはインタラクティブな動画ストリーミング機能とプロファイリング機能を備えており、リアルタイムでの相互作用と現実的なシミュレーションにより、世界のダイナミクスを正確に再現可能である。また、ミリ秒単位の長時間動画生成を想定した細粒度評価ベンチマーク「LV-Bench」とのシームレスな統合により、効率的なベンチマーク評価も可能となっている。今後、コミュニティが協力してInferixをさらに発展させ、世界モデルの探求を推進することを期待している。
Summarization
The Inferix Team introduces Inferix, a next-generation inference engine for immersive world synthesis that employs optimized semi-autoregressive block-diffusion decoding and LLM-style KV Cache management to enable efficient, interactive, and long-form video generation distinct from standard high-concurrency or classic diffusion systems.
Introduction
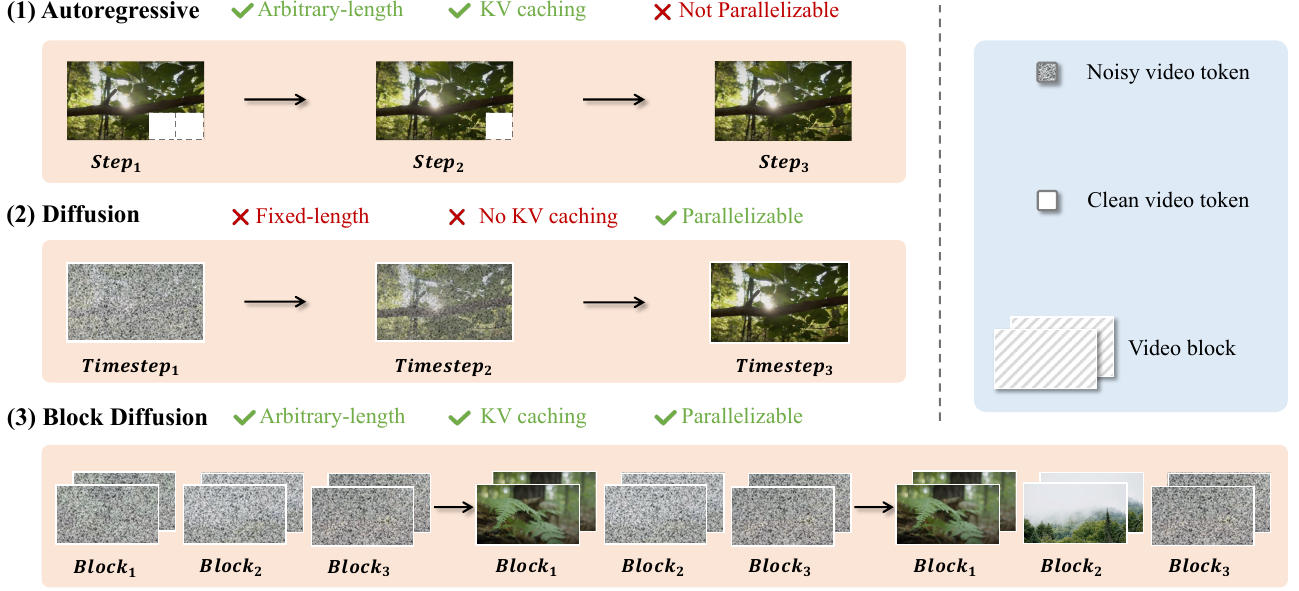
World models are rapidly advancing toward generating long-form, interactive video sequences, creating a critical need for specialized infrastructure capable of handling the immense computational and storage demands of immersive world synthesis. Current approaches face a distinct trade-off: Diffusion Transformers (DiT) offer high-quality, parallelized generation but suffer from inefficient decoding and fixed-length constraints, while Autoregressive (AR) models support variable lengths but often lag in visual quality and lack parallelization capabilities.
To bridge this gap, the authors introduce Inferix, a dedicated inference engine designed to enable efficient, arbitrary-length video generation. By adopting a "block diffusion" framework, the system interpolates between AR and diffusion paradigms, utilizing a semi-autoregressive decoding strategy that reintroduces LLM-style memory management to maintain high generation quality over extended sequences.
Key innovations include:
- Semi-Autoregressive Block Diffusion: The engine employs a generate-and-cache loop where attention mechanisms leverage a global KV cache to maintain context across generated blocks, ensuring long-range coherence without sacrificing diffusion quality.
- Advanced Memory Management: To address the storage bottlenecks of long-context simulation, the system integrates intelligent KV cache optimization techniques similar to PageAttention to minimize GPU memory usage.
- Scalable Production Features: The framework supports distributed synthesis for large-scale environments, continuous prompting for dynamic narrative control, and built-in real-time video streaming protocols.
Dataset
The authors introduce LV-Bench, a benchmark designed to address the challenges of generating minute-long videos. The dataset construction and usage involve the following components:
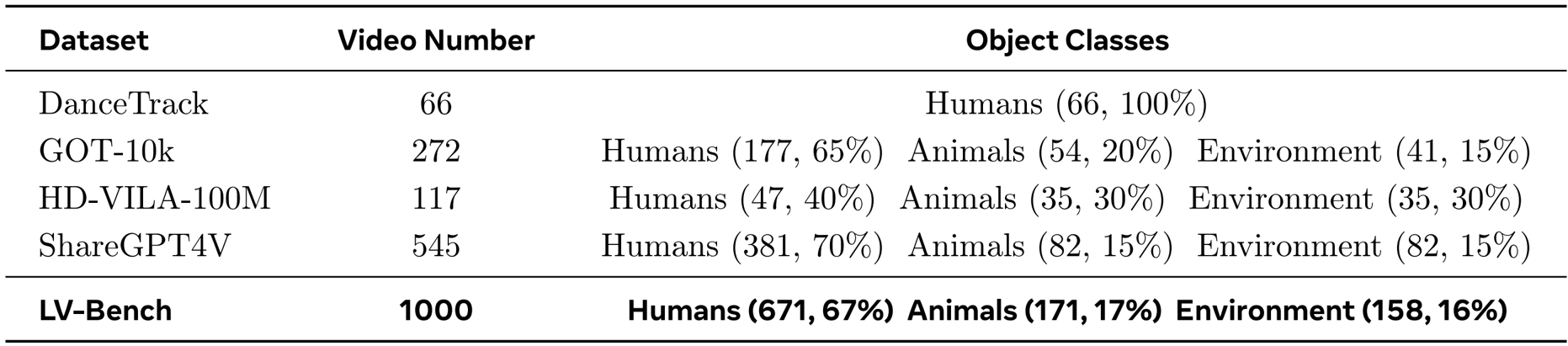
- Composition and Sources: The benchmark comprises 1,000 long-form videos collected from diverse open-source collections, specifically DanceTrack, GOT-10k, HD-VILA-100M, and ShareGPT4V.
- Selection Criteria: The team prioritized high-resolution content, strictly selecting videos that exceed 50 seconds in duration.
- Metadata Construction: To ensure linguistic diversity and temporal detail, the authors utilized GPT-4o as a data engine to generate granular captions every 2 to 3 seconds.
- Quality Assurance: A rigorous human-in-the-loop validation framework was applied across three stages: sourcing (filtering unsuitable clips), chunk segmentation (ensuring coherence and removing artifacts), and caption verification (refining AI-generated text). At least two independent reviewers validated each stage to maintain reliability.
- Model Usage: The final curated dataset is partitioned into an 80/20 split for training and evaluation purposes.
Method
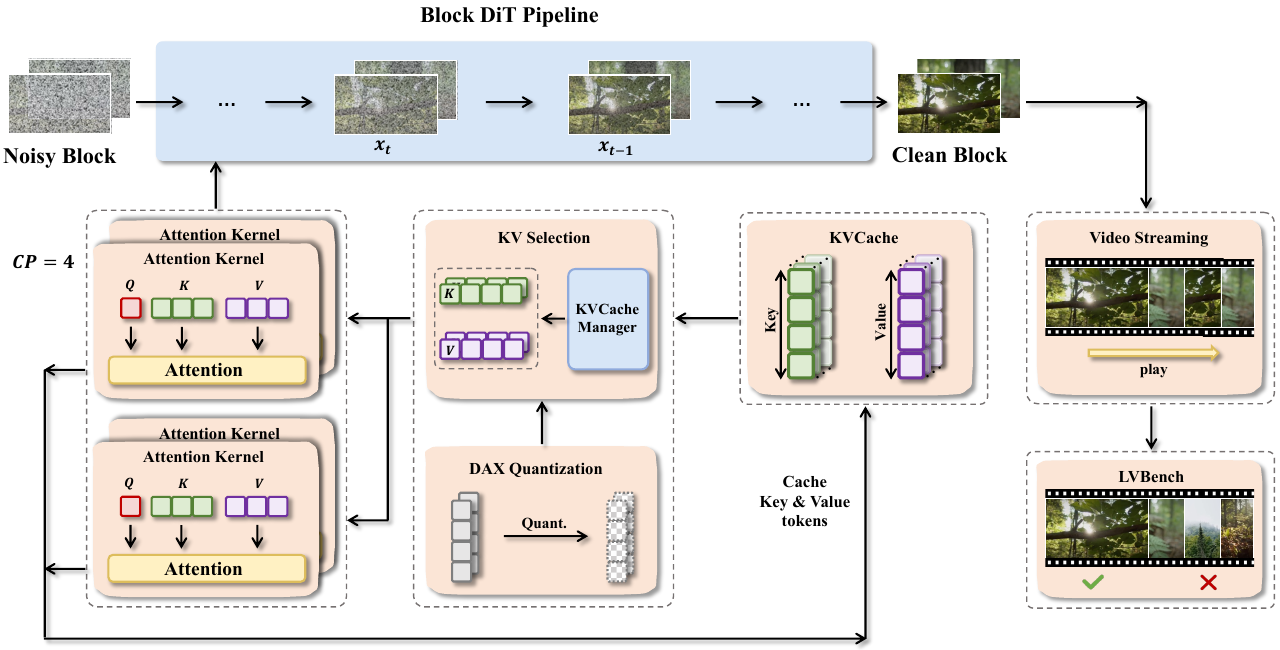
The authors leverage a modular and extensible framework designed to address the unique challenges of block diffusion models for long video generation. The core of the system, as illustrated in the framework diagram, is built around a generalized inference pipeline that abstracts common computational patterns across diverse models such as MAGI-1, CausVid, and Self Forcing. This pipeline orchestrates a sequence of interconnected components to enable efficient and scalable inference.
At the heart of the inference process is the Block DiT Pipeline, which processes video in discrete blocks. Each block undergoes a diffusion-based denoising process, where a noisy block is iteratively refined into a clean block. This process relies on attention mechanisms that require access to key-value (KV) pairs from previous steps. To manage these KV pairs efficiently, the framework employs a block-wise KV memory management system. This system supports flexible access patterns, including range-based chunked access and index-based selective fetch, ensuring scalability and extensibility for future model variants that may require sliding-window or selective global context.
To accelerate computation and reduce memory pressure, the framework integrates a suite of parallelism techniques. Ulysses-style sequence parallelism partitions independent attention heads across multiple GPUs, while Ring Attention distributes attention operations in a ring topology, enabling scalable computation over long sequences. The choice between these strategies is adaptive, based on model architecture and communication overhead, ensuring optimal resource utilization. The framework also incorporates DAX quantization, which reduces the precision of KV cache tokens to minimize memory footprint without significant loss in quality.
The system further supports real-time video streaming, allowing dynamic control over narrative generation through user-provided signals such as prompts or motion inputs. When a new prompt is introduced for a subsequent video chunk, the framework clears the cross-attention cache to prevent interference from prior contexts, ensuring coherent and prompt-aligned generation. This capability is complemented by a built-in performance profiler that provides near-zero-overhead, customizable, and easy-to-use instrumentation for monitoring resource utilization during inference.
Experiment
- Introduces Video Drift Error (VDE), a unified metric inspired by MAPE, designed to quantify relative quality changes and temporal degradation in long-form video generation.
- Establishes five specific VDE variants (Clarity, Motion, Aesthetic, Background, and Subject) to assess drift across different visual and dynamic aspects, where lower scores indicate stronger temporal consistency.
- Integrates these drift metrics with five complementary quality dimensions from VBench (Subject Consistency, Background Consistency, Motion Smoothness, Aesthetic Quality, and Image Quality) to form a comprehensive evaluation protocol.
The authors use the LV-Bench dataset, which contains 1000 videos and is composed of 671 human instances, 171 animal instances, and 158 environment instances, to evaluate long-form video generation. Results show that the dataset spans diverse object classes and video counts, providing a comprehensive benchmark for assessing temporal consistency and visual quality in long-horizon video generation.