Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
確率的経路積分を用いた忠実度を考慮した推薦説明
確率的経路積分を用いた忠実度を考慮した推薦説明
Oren Barkan Yahlly Schein Yehonatan Elisha Veronika Bogina Mikhail Baklanov Noam Koenigstein
概要
以下は、ご指定の英文の日本語訳です。科技論文や専門誌の標準的なスタイルである「である」調を採用し、専門用語の正確性と文章の流暢さを重視しました。翻訳:推薦システムにおいて、ある説明がモデルの真の推論プロセスをいかに正確に反映しているかを測る「説明の忠実度(Explanation Fidelity)」は、依然として解明が不十分な重要課題です。本稿では、推薦データの持つ疎(スパース)かつ暗黙的な性質に経路積分(Path Integration)の手法を適用させた、モデル非依存型(モデルアグノスティック)のアプローチである「SPINRec(Stochastic Path Integration for Neural Recommender Explanations)」を提案します。既存手法の限界を克服するために、SPINRecは「確率的ベースラインサンプリング(Stochastic Baseline Sampling)」を採用しています。これは、固定されたベースラインや非現実的なベースラインから積分を行うのではなく、経験的なデータ分布から複数の妥当なユーザープロファイルをサンプリングし、最も忠実度の高い寄与経路(Attribution Path)を選択するというものです。この設計により、観測されたインタラクションだけでなく、未観測の要素による影響も捉えることが可能となり、より安定的かつパーソナライズされた説明の生成を実現します。我々は、3つの主要モデル(MF、VAE、NCF)および3つのデータセット(ML1M、Yahoo! Music、Pinterest)を対象に、AUCベースの摂動曲線(Perturbation Curves)や固定長診断(Fixed-length Diagnostics)を含む一連の反事実的(Counterfactual)指標を用いて、現時点で最も包括的な忠実度評価を実施しました。その結果、SPINRecは全てのベースライン手法を一貫して上回り、推薦システムにおける「説明の忠実度」に関する新たなベンチマークを確立しました。なお、本研究のコードおよび評価ツールは、以下のURLにて公開されています:https://github.com/DeltaLabTLV/SPINRec
Summarization
Researchers from The Open University of Israel and Tel Aviv University introduce SPINRec, a model-agnostic framework that enhances explanation fidelity in recommender systems by employing stochastic baseline sampling to integrate attribution paths from plausible user profiles rather than relying on fixed or unrealistic baselines.
Introduction
As recommender systems increasingly shape user decisions in e-commerce and media, the demand for transparency has shifted focus from simple persuasiveness to fidelity, ensuring that explanations accurately reflect the model's actual decision-making process. However, applying established attribution techniques like Path-Integration (PI) to this domain is challenging because recommendation data is inherently sparse and binary. Standard PI methods, which rely on "all-zero" baselines, fail to capture the nuance of user interactions in this setting, often resulting in weak or misleading attribution signals.
To address this gap, the authors introduce SPINRec (Stochastic Path Integration for Neural Recommender Explanations), a novel framework that adapts Path-Integration specifically for neural recommenders. By moving away from static baselines, the authors provide a method that respects the unique data structure of recommendation engines.
Key innovations and advantages include:
- Stochastic Baseline Sampling: Instead of relying on an unrealistic all-zero baseline, the model samples multiple plausible user histories from the empirical data distribution to generate more stable and informative gradient signals.
- Domain-Specific Adaptation: The framework is the first to successfully adapt Path-Integration from computer vision and NLP to recommender systems, specifically addressing the challenges of high-dimensional, sparse, and binary data.
- Superior Fidelity: Extensive evaluations across multiple architectures (including Matrix Factorization and VAEs) and datasets establish SPINRec as the new state-of-the-art benchmark for counterfactual explanation fidelity.
Dataset
The authors conduct experiments using three distinct datasets: ML1M (MovieLens), Yahoo! Music, and Pinterest. The data preparation and evaluation strategy involve the following steps:
- Data Processing: All datasets are binarized to convert interactions into implicit feedback.
- Splitting Strategy: The researchers apply an 80/20 user-based split to divide the data into training and testing sets.
- Validation: An additional 10% of users are withheld from the training data to serve as a validation set for hyperparameter tuning.
- Evaluation Scope: Results are reported on the test set, with explanations specifically targeting the top recommendation for each user.
Method
The authors leverage path-integration methods to develop SPINRec, a framework for generating explanations in recommender systems. The core approach computes feature attributions by integrating gradients along a path from a baseline user representation to the actual user data. Given a user's binary feature vector x and a target item y, the predicted affinity fθy(x) is decomposed into contributions from individual features using a straight-line path r(t)=t⋅x+(1−t)⋅z, where z is a baseline vector and t∈[0,1]. The attribution for each feature is derived from the integral of the gradient of the model's output with respect to the interpolated input, weighted by the path's derivative. This results in an explanation map m, which quantifies the relevance of each feature to the recommendation, as defined in Equation \ref{eq:expl_map}.
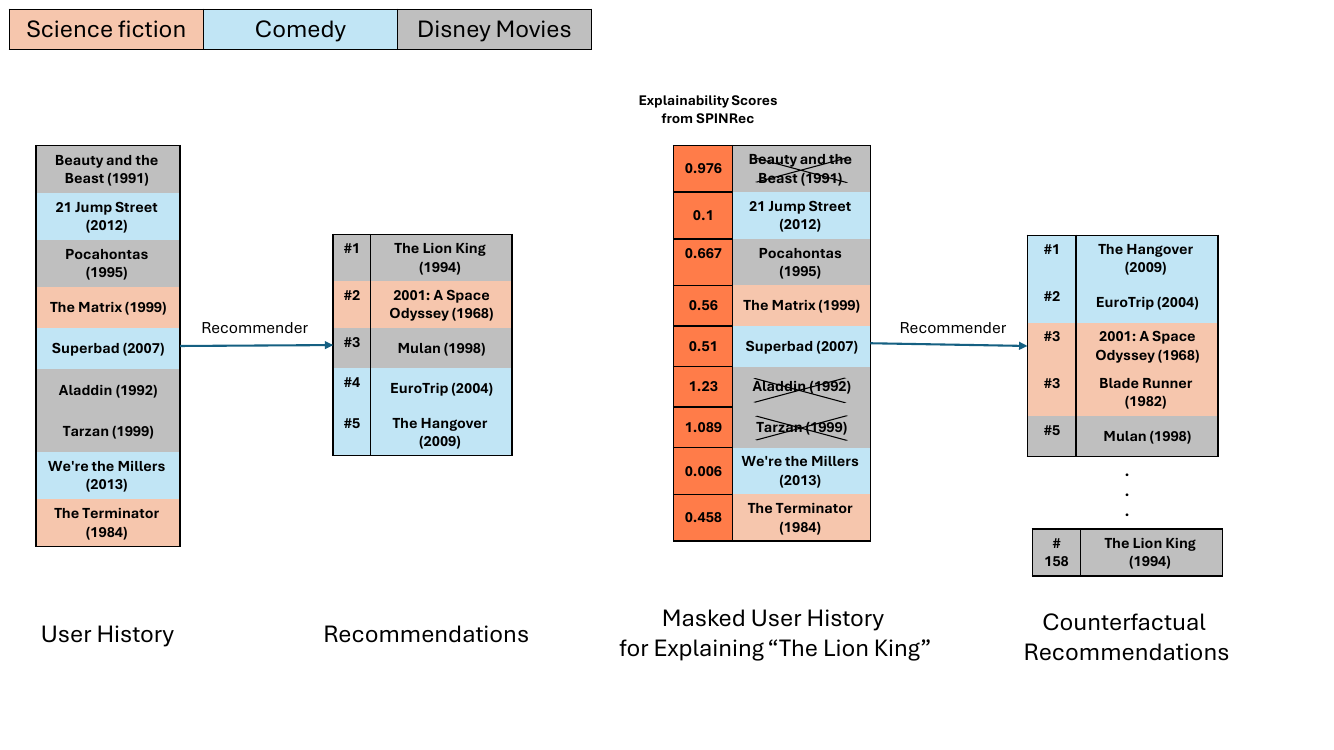
Experiment
- The study evaluates the counterfactual fidelity of SPINRec across three datasets (ML1M, Yahoo! Music, Pinterest) and three recommender architectures (Matrix Factorization, VAE, NCF), comparing it against state-of-the-art baselines including LXR, FIA, and SHAP.
- On AUC-based fidelity metrics, SPINRec achieved the best results across all models and datasets, statistically surpassing strong baselines like LXR and FIA (p≤0.01).
- In fixed-length metric evaluations (POS, DEL, INS, CDCG), the method consistently outperformed all baselines across varying explanation lengths (Ke) and ranking cutoffs (Kr), demonstrating robustness in identifying high-impact features.
- Ablation studies validated the contribution of stochastic baseline sampling, showing that SPINRec significantly outperforms plain path integration (PI) by leveraging unobserved interactions, with performance gains most pronounced in complex models like VAE and NCF.
The authors use counterfactual fidelity metrics to evaluate explanation methods across multiple recommendation models and datasets, with results showing that SPINRec consistently outperforms all baselines in both AUC-based and fixed-length metrics. Across all configurations, SPINRec achieves the best performance, particularly in metrics like POS@K and CDCG, demonstrating superior fidelity in explaining recommendation outcomes.
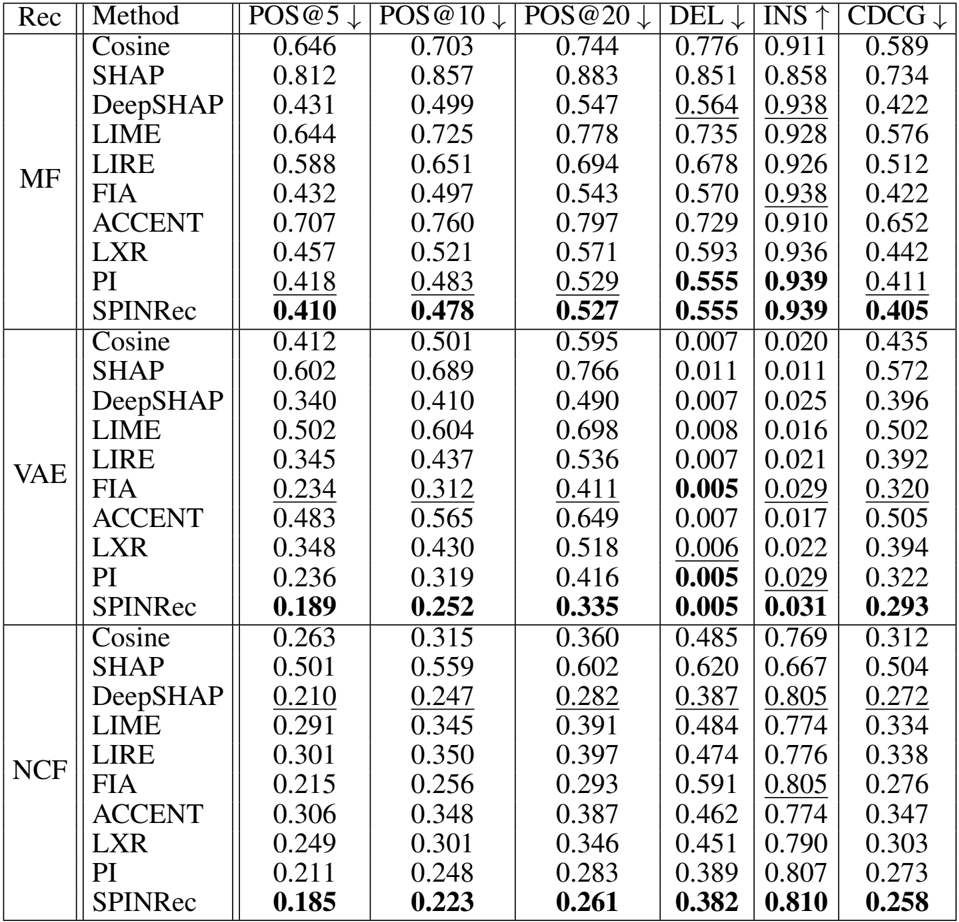
The authors use counterfactual fidelity metrics to evaluate explanation methods across multiple recommendation models and datasets, with results showing that SPINRec consistently outperforms all baselines in both AUC-based and fixed-length metrics. Across all configurations, SPINRec achieves the best performance, particularly excelling in metrics like POS@K and CDCG, while also demonstrating robustness across different recommendation architectures and datasets.