Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Code2World : un modèle de monde GUI basé sur la génération de code rendu
Code2World : un modèle de monde GUI basé sur la génération de code rendu
Yuhao Zheng Li'an Zhong Yi Wang Rui Dai Kaikui Liu Xiangxiang Chu Linyuan Lv Philip Torr Kevin Qinghong Lin
Résumé
Les agents GUI autonomes interagissent avec les environnements en perçant les interfaces et en exécutant des actions. En tant que sandbox virtuel, le modèle GUI World permet aux agents de développer une anticipation humaine grâce à une prédiction conditionnée aux actions. Toutefois, les approches existantes basées sur le texte ou les pixels peinent à atteindre simultanément une fidélité visuelle élevée et une maîtrise fine de la structure. À cet effet, nous proposons Code2World, un modèle vision-langage spécialisé dans la génération de code exécutable pour simuler l’état visuel suivant. Plus précisément, afin de surmonter le problème de la rareté des données, nous avons construit AndroidCode en traduisant des trajectoires GUI en HTML de haute fidélité, puis en affinant le code synthétisé grâce à un mécanisme de révision basé sur un retour visuel, aboutissant à un corpus de plus de 80 000 paires écran-action de haute qualité. Pour adapter les modèles VLM existants à la prédiction de code, nous appliquons d’abord une formation par surapprentissage (SFT) en tant que démarrage à froid pour suivre la mise en page du format, puis nous introduisons une apprentissage par renforcement conscient du rendu (Render-Aware Reinforcement Learning), qui utilise le résultat rendu comme signal de récompense en imposant une fidélité sémantique visuelle et une cohérence d’action. Des expériences étendues démontrent que Code2World-8B atteint les performances les plus élevées en prédiction de l’interface utilisateur suivante, rivalisant avec les modèles de pointe GPT-5 et Gemini-3-Pro-Image. Notamment, Code2World améliore de manière flexible les taux de réussite des tâches de navigation en aval, augmentant le taux de succès de Gemini-2.5-Flash de +9,5 % sur la navigation dans AndroidWorld. Le code source est disponible à l’adresse suivante : https://github.com/AMAP-ML/Code2World.
One-sentence Summary
Yuhao Zheng, Lian Zhong, and colleagues from institutions including Tsinghua and Oxford propose Code2World, a vision-language coder generating renderable UI code for next-state prediction, overcoming fidelity-control tradeoffs via AndroidCode dataset and render-aware RL, boosting navigation success by 9.5% over Gemini-2.5-Flash.
Key Contributions
- Code2World introduces a vision-language model that predicts next GUI states by generating renderable HTML code, addressing the limitations of text- and pixel-based methods by combining high visual fidelity with fine-grained structural control.
- To overcome data scarcity, the authors construct AndroidCode, a dataset of 80K+ high-quality screen-action pairs, synthesized from GUI trajectories and refined via a visual-feedback mechanism to ensure code-to-render alignment.
- The model is trained with Render-Aware Reinforcement Learning that uses rendered visuals as reward signals, achieving top-tier next UI prediction performance and boosting downstream agent navigation success by +9.5% on AndroidWorld.
Introduction
The authors leverage structured HTML code as a native representation to build Code2World, a GUI world model that predicts next interface states by generating renderable code—enabling both high visual fidelity and fine-grained structural control, which prior text- and pixel-based methods fail to achieve simultaneously. Existing approaches either lose spatial detail (text-based) or struggle with discrete GUI transitions and layout precision (pixel-based), limiting their use in safety-critical or text-heavy interfaces. To overcome data scarcity and alignment challenges, they construct AndroidCode—a dataset of 80K+ screen-action pairs refined via visual feedback—and train their model using Supervised Fine-Tuning followed by Render-Aware Reinforcement Learning, which uses rendered visuals and action consistency as reward signals. Code2World-8B outperforms leading models in next UI prediction and boosts downstream agent navigation success by +9.5% when integrated as a plug-and-play simulator.
Dataset
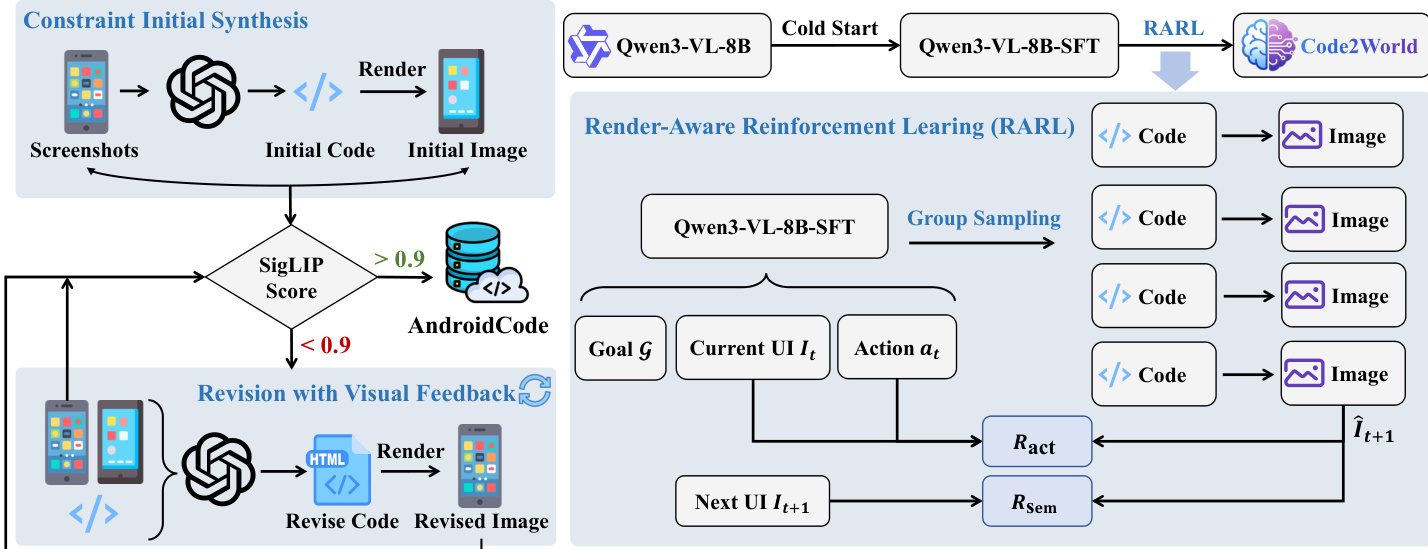
- The authors synthesize AndroidCode, a large-scale dataset of paired GUI screenshots and clean HTML representations, derived from the Android Control corpus to address the scarcity of such paired data in existing benchmarks.
- The dataset is built using a two-stage automated pipeline: first, GPT-5 generates constrained HTML from screenshots using fixed root containers and semantic placeholders (e.g., [IMG: Red Shoe]) to ensure self-contained, dependency-free code; second, a visual feedback loop revises low-fidelity outputs using SigLIP similarity scores (threshold τ = 0.9) and limits revisions to one iteration per sample.
- Samples failing to meet the visual fidelity threshold after one revision are discarded, ensuring only high-quality (I, C) pairs are retained in the final corpus.
- For instruction tuning, the authors augment visual inputs by overlaying red circles (for clicks) or directional arrows (for swipes) to ground spatial attention, and expand sparse action logs into natural language instructions that describe intent, causality, and expected outcomes.
- All augmented visuals and expanded instructions are formatted into a standardized prompt template to guide the model’s simulation of interface dynamics during training.
Method
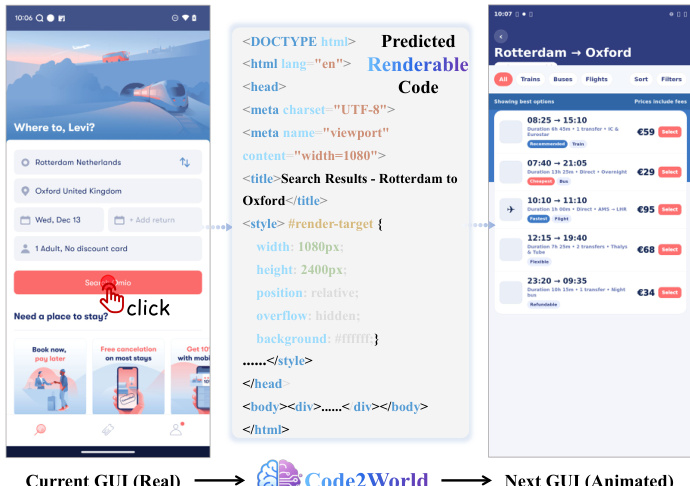
The authors leverage a renderable code generation paradigm to model the deterministic state transition of a digital environment, framing the problem as Next UI Prediction. Instead of operating directly in pixel space, the method targets the underlying structural representation of the interface by generating executable HTML code, which is then deterministically rendered into a visual state. The core state transition is formalized as a two-step conditional generation process: given a visual observation It, a user action at, and a task goal G, the multimodal generator Mθ produces a predicted HTML code C^t+1, which is subsequently rendered into the predicted visual state I^t+1 via a browser engine R. This approach decouples structural reasoning from pixel-level rendering, enabling precise control over UI layout while abstracting away asset generation.
To train the multimodal generator Mθ, the authors employ a two-stage optimization strategy. The first stage, Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT), initializes the model using the Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct backbone and trains it on multimodal triplets (It,at,G) to predict the ground-truth HTML code C∗. This phase instills syntactic and structural knowledge but remains agnostic to the rendered visual outcome. The second stage, Render-Aware Reinforcement Learning (RARL), refines the policy by incorporating feedback from the rendered visual state I^t+1. This stage introduces a composite reward function Rtotal=λ1Rsem+λ2Ract, where Rsem evaluates semantic alignment between the rendered prediction and ground truth using a VLM-as-a-Judge, and Ract verifies whether the state transition logically follows from the executed action at, also assessed via a VLM judge. The model is optimized using Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), which computes advantages relative to a group of sampled outputs and updates parameters while penalizing deviation from the SFT policy via a KL-divergence term.
During inference, Code2World functions as a plug-and-play simulator for GUI agents via a “Propose, Simulate, Select” pattern. The agent first generates K candidate actions with associated reasoning and confidence scores. For each candidate, Code2World simulates the resulting UI state by generating HTML code and rendering it. A scorer then evaluates the simulated outcomes against the task goal, selecting the action that best advances progress. This mechanism enables the agent to detect and rectify hallucinations or illogical plans by grounding decisions in rendered visual consequences.

The training data, AndroidCode, is synthesized through a constrained initial generation phase followed by a visual-feedback revision loop. Initial HTML is generated from screenshots and rendered; if the SigLIP score between the rendered and target image falls below 0.9, the code is revised iteratively until alignment is achieved. This ensures strict structural fidelity while tolerating semantic placeholders for images and icons, which are represented as styled divs with text labels (e.g., [IMG: Avatar]) to avoid hallucinating external assets. The model’s architecture enforces strict structural rules: all content is wrapped in a #render-target div with exact pixel dimensions, the body is reset with zero margin/padding and transparent background, and styling is applied to the container rather than the body to ensure consistent rendering.

The training hyperparameters are tuned to accommodate high-resolution screenshots and verbose HTML: the model uses a 24,576-token context window, DeepSpeed ZeRO-2 for memory efficiency, and Flash Attention for throughput. In Stage 1, the vision encoder and projector are frozen while the language model is fully fine-tuned for two epochs. In Stage 2, GRPO samples four outputs per prompt with temperature 1.0, and the KL penalty coefficient is set to 0.01 to balance exploration and policy stability. The visual and action rewards are weighted equally to ensure both structural and logical fidelity.
Experiment
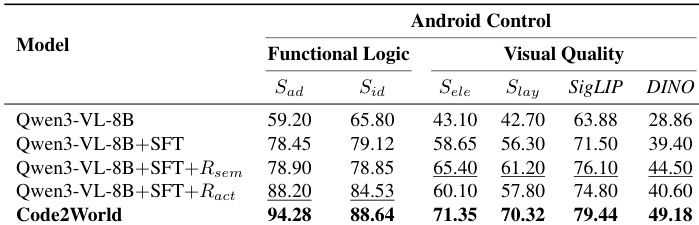
- Code2World excels at predicting next UI states by combining functional logic (action adherence and identifiability) with visual fidelity (element alignment and layout integrity), outperforming larger models despite its compact size.
- It generalizes robustly across in-domain and out-of-distribution GUI environments, maintaining high dynamic logic scores even when visual similarity declines, indicating internalized interaction rules rather than layout memorization.
- As a plug-and-play simulator, it significantly boosts GUI agent performance in both offline and online settings by enabling foresight into action consequences, improving decision-making and task success rates.
- Ablation studies confirm that combining supervised fine-tuning with dual reinforcement learning rewards (semantic and action-based) is essential for achieving balanced logic and visual accuracy.
- Qualitative examples show Code2World helps agents avoid redundant actions, discover more efficient strategies, and make contextually appropriate decisions by simulating future UI states accurately.
The authors use Code2World to enhance GUI agents by enabling them to simulate future interface states, which improves decision-making accuracy and task success rates. Results show that integrating Code2World with both general and specialized agents consistently boosts grounding accuracy and success rates, demonstrating its plug-and-play effectiveness across models. This improvement stems from the model’s ability to provide reliable foresight into action consequences, helping agents avoid redundant or inefficient steps.

Code2World demonstrates superior performance in predicting next UI states by effectively balancing functional logic and visual quality, outperforming both larger open-source models and proprietary image generation systems across in-domain and out-of-distribution benchmarks. Its renderable code generation approach enables accurate simulation of interaction dynamics and structural fidelity, allowing it to maintain high performance even when generalizing to unseen applications and device interfaces. The model’s ability to internalize GUI interaction rules rather than rely on pixel-level matching makes it a robust foundation for enhancing agent navigation in real-world scenarios.
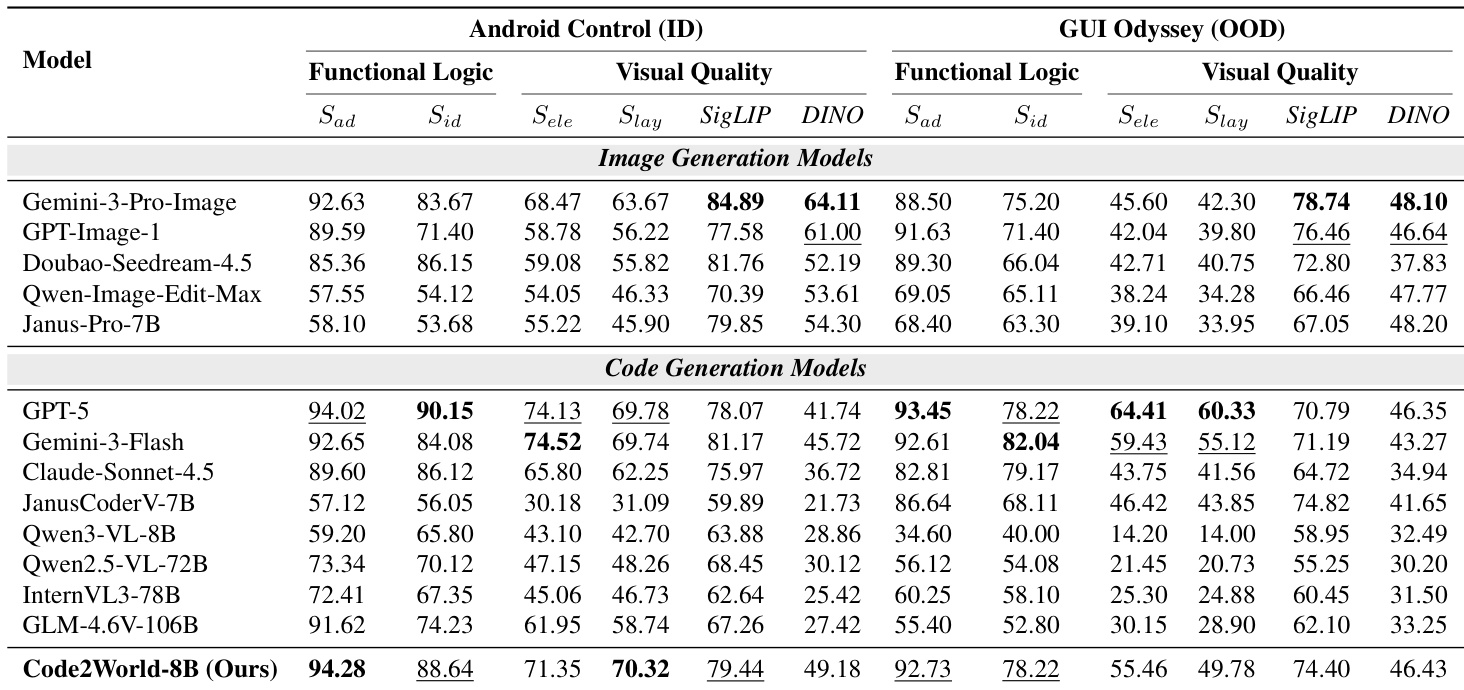
The authors use a specialized evaluation framework to assess next UI prediction models across functional logic and visual quality dimensions. Results show that Code2World significantly outperforms both open-source and proprietary baselines in both dimensions, achieving the highest scores in action adherence, identifiability, element alignment, and layout integrity. This demonstrates its ability to generate structurally accurate and interactionally coherent GUI states, even with a compact 8B parameter footprint.