Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
DenseGRPO : Du récompense épars à dense pour l’alignement des modèles de correspondance de flux
DenseGRPO : Du récompense épars à dense pour l’alignement des modèles de correspondance de flux
Haoyou Deng Keyu Yan Chaojie Mao Xiang Wang Yu Liu Changxin Gao Nong Sang
Résumé
Les approches récentes basées sur GRPO et fondées sur des modèles de matching de flux ont montré des progrès remarquables en matière d’alignement avec les préférences humaines pour la génération d’images à partir de texte. Toutefois, elles souffrent encore du problème des récompenses rares : la récompense terminale de toute la trajectoire de débruitage est appliquée à tous les étapes intermédiaires, entraînant un désalignement entre les signaux de retour globaux et les contributions fines spécifiques à chaque étape de débruitage intermédiaire. Pour résoudre ce problème, nous introduisons DenseGRPO, un cadre novateur qui aligne les préférences humaines avec des récompenses denses, évaluant ainsi la contribution fine de chaque étape de débruitage. Plus précisément, notre approche repose sur deux composants clés : (1) nous proposons de prédire le gain de récompense par étape comme récompense dense de chaque étape de débruitage, en appliquant un modèle de récompense aux images propres intermédiaires via une approche basée sur les équations différentielles ordinaires (ODE). Cette méthode garantit un alignement entre les signaux de retour et les contributions des étapes individuelles, favorisant ainsi une formation efficace ; (2) à partir des récompenses denses estimées, nous mettons en évidence un défaut de désalignement entre le cadre d’exploration uniforme utilisé dans les méthodes GRPO existantes et l’intensité du bruit variant dans le temps, conduisant à un espace d’exploration inapproprié. Par conséquent, nous proposons une stratégie consciente des récompenses pour ajuster l’espace d’exploration en ajustant de manière adaptative l’injection de stochasticité spécifique à chaque instant dans l’échantillonneur SDE, assurant ainsi un espace d’exploration approprié à chaque instant. Des expériences étendues sur plusieurs benchmarks standards démontrent l’efficacité de DenseGRPO et soulignent le rôle crucial des récompenses denses valides dans l’alignement des modèles de matching de flux.
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from Huazhong University of Science and Technology and Tongyi Lab propose DenseGRPO, a framework using dense step-wise rewards to align human preferences in text-to-image generation, overcoming sparse reward issues by calibrating exploration via adaptive stochasticity, significantly improving flow matching model performance.
Key Contributions
- DenseGRPO addresses the sparse reward problem in GRPO-based text-to-image models by introducing step-wise dense rewards estimated via an ODE-based method that evaluates intermediate clean images, aligning feedback with each denoising step’s contribution.
- It reveals and corrects a mismatch between uniform exploration and time-varying noise intensity by proposing a reward-aware SDE sampler that adaptively adjusts stochasticity per timestep, ensuring balanced exploration across the denoising trajectory.
- Experiments on multiple benchmarks confirm DenseGRPO’s state-of-the-art performance, validating the necessity of dense rewards for effective human preference alignment in flow matching models.
Introduction
The authors leverage flow matching models for text-to-image generation and address the persistent challenge of aligning them with human preferences using reinforcement learning. Prior GRPO-based methods suffer from sparse rewards—applying a single terminal reward to all denoising steps—which misaligns feedback with each step’s actual contribution, hindering fine-grained optimization. DenseGRPO introduces dense rewards by estimating step-wise reward gains via ODE-based intermediate image evaluation, ensuring feedback matches individual step contributions. It further calibrates exploration by adaptively adjusting stochasticity in the SDE sampler per timestep, correcting imbalance in reward distribution. Experiments confirm DenseGRPO’s state-of-the-art performance, validating the necessity of dense, step-aware rewards for effective alignment.
Dataset
- The authors use only publicly available datasets, all compliant with their respective licenses, ensuring ethical adherence per the ICLR Code of Ethics.
- No human subjects, sensitive personal data, or proprietary content are involved in the study.
- The methods introduced carry no foreseeable risk of misuse or harm.
- Dataset composition, subset details, training splits, mixture ratios, cropping strategies, or metadata construction are not described in the provided text.
Method
The authors leverage a reformulation of the denoising process in flow matching models as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) to enable reinforcement learning-based alignment. In this formulation, the state at timestep t is defined as st≜(c,t,xt), where c is the prompt, t is the current timestep, and xt is the latent representation. The action corresponds to the predicted prior latent xt−1, and the policy π(at∣st) is modeled as the conditional distribution p(xt−1∣xt,c). The reward is sparse and trajectory-wise, assigned only at the terminal state t=0 as R(x0,c), while intermediate steps receive zero reward. This design leads to a mismatch: the same terminal reward is used to optimize all timesteps, ignoring the distinct contributions of individual denoising steps.
To resolve this, DenseGRPO introduces a step-wise dense reward mechanism. Instead of relying on a single terminal reward, the method estimates a reward Rti for each intermediate latent xti along the trajectory. This is achieved by leveraging the deterministic nature of the ODE denoising process: given xti, the model can deterministically generate the corresponding clean latent x^t,0i via n-step ODE denoising, i.e., x^t,0i=ODEn(xti,c). The reward for xti is then assigned as Rti≜R(x^t,0i,c), where R is a pre-trained reward model. The step-wise dense reward ΔRti is defined as the reward gain between consecutive steps: ΔRti=Rt−1i−Rti. This formulation provides a fine-grained, step-specific feedback signal that reflects the actual contribution of each denoising action.
Refer to the framework diagram illustrating the dense reward estimation process. The diagram shows how, for each latent xti, an ODE denoising trajectory is computed to obtain the clean counterpart x^t,0i, which is then evaluated by the reward model to yield Rti. The dense reward ΔRti is derived from the difference between successive latent rewards, enabling per-timestep credit assignment.
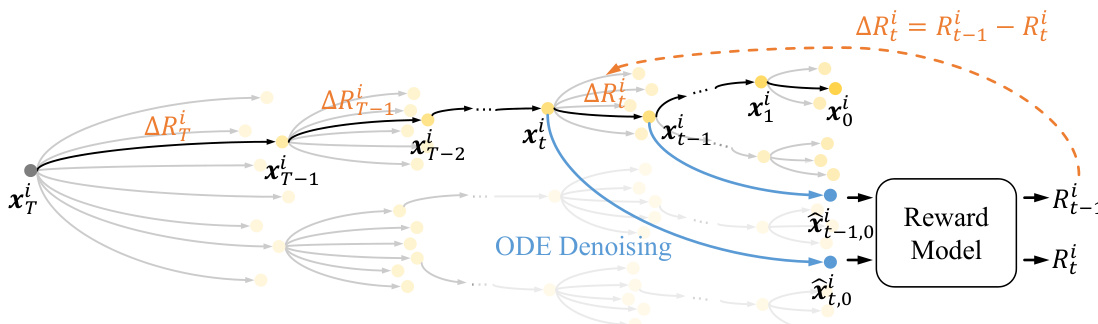
In the GRPO training loop, the dense reward ΔRti replaces the sparse terminal reward in the advantage computation. The advantage for the i-th trajectory at timestep t is recalculated as:
A^ti=std({ΔRti}i=1G)ΔRti−mean({ΔRti}i=1G).This ensures that the policy update at each timestep is guided by a reward signal that reflects the immediate contribution of that step, rather than the global trajectory outcome.
To further enhance exploration during training, DenseGRPO introduces a reward-aware calibration of the SDE sampler’s noise injection. While existing methods use a uniform noise level a across all timesteps, DenseGRPO adapts the noise intensity ψ(t) per timestep to maintain a balanced exploration space. The calibration is performed iteratively: for each timestep t, the algorithm samples trajectories, computes dense rewards ΔRti, and adjusts ψ(t) based on the balance between positive and negative rewards. If the number of positive and negative rewards is approximately equal, ψ(t) is increased to encourage diversity; otherwise, it is decreased to restore balance. The calibrated noise schedule ψ(t) is then used in the SDE sampler, replacing the original σt=at/(1−t) with σt=ψ(t), thereby tailoring the stochasticity to the time-varying nature of the denoising process.
Experiment
- DenseGRPO outperforms Flow-GRPO and Flow-GRPO+CoCA across compositional image generation, human preference alignment, and visual text rendering, demonstrating superior alignment with target preferences through step-wise dense rewards.
- Ablation studies confirm that step-wise dense rewards significantly improve policy optimization over sparse trajectory rewards, and time-specific noise calibration enhances exploration effectiveness.
- Increasing ODE denoising steps improves reward accuracy and model performance, despite higher computational cost, validating that precise reward estimation is critical for alignment.
- DenseGRPO generalizes beyond flow matching models to diffusion models and higher resolutions, maintaining performance gains via deterministic sampling for accurate latent reward prediction.
- While achieving strong alignment, DenseGRPO shows slight susceptibility to reward hacking in specific tasks, suggesting a trade-off between reward precision and robustness that may be mitigated with higher-quality reward models.
The authors use DenseGRPO to introduce step-wise dense rewards in text-to-image generation, achieving consistent improvements over Flow-GRPO and Flow-GRPO+CoCA across compositional, text-rendering, and human preference tasks. Results show that dense reward signals better align feedback with individual denoising steps, enhancing both semantic accuracy and visual quality, while ablation studies confirm the importance of calibrated exploration and multi-step ODE denoising for reward accuracy. Although some reward hacking occurs under specific metrics, DenseGRPO demonstrates robustness and generalizability across model architectures and resolutions.
