Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Agents d'Insight : un système multi-agents basé sur un modèle de langage pour des analyses de données
Agents d'Insight : un système multi-agents basé sur un modèle de langage pour des analyses de données
Jincheng Bai Zhenyu Zhang Jennifer Zhang Zhihuai Zhu
Résumé
Aujourd’hui, les vendeurs de commerce électronique font face à plusieurs défis majeurs, notamment la difficulté à découvrir et à exploiter efficacement les programmes et outils disponibles, ainsi qu’à comprendre et tirer parti des données riches provenant de divers outils. Nous nous proposons donc de développer les Insight Agents (IA), un système conversationnel à agents multiples basé sur l’analyse de données, afin d’offrir aux vendeurs de commerce électronique des informations et des insights personnalisés grâce à une récupération automatisée des données. Nous supposons que les IA agiront comme un amplificateur de performance pour les vendeurs, favorisant ainsi une adoption accrue en réduisant l’effort requis et en accélérant la prise de décisions commerciales pertinentes. Dans cet article, nous présentons un système novateur, entièrement intégré et soutenu par des modèles linguistiques à grande échelle (LLM), fondé sur un paradigme planifier-exécuter, conçu pour une couverture complète, une grande précision et une faible latence. Ce système repose sur une architecture hiérarchique à plusieurs agents, composée d’un agent gestionnaire et de deux agents exécutants : un agent de présentation des données et un agent de génération d’insights, permettant une récupération efficace de l’information et une résolution de problèmes optimisée. Nous avons conçu une solution d’apprentissage automatique simple mais efficace pour l’agent gestionnaire, combinant la détection de données hors domaine (OOD) à l’aide d’un modèle léger encodeur-décodeur et le routage des agents via un classificateur basé sur BERT, afin d’optimiser à la fois la précision et la latence. Dans les deux agents exécutants, une planification stratégique est mise en œuvre pour le modèle de données basé sur les API, qui décompose les requêtes en composants granulaires afin de générer des réponses plus précises, tandis que des connaissances spécifiques au domaine sont injectées dynamiquement pour renforcer le générateur d’insights. Les Insight Agents ont été déployés pour les vendeurs Amazon aux États-Unis, où ils ont atteint une précision élevée de 90 % selon une évaluation humaine, avec une latence au seuil P90 inférieure à 15 secondes.
One-sentence Summary
Amazon researchers propose Insight Agents (IA), an LLM-powered multi-agent system using plan-and-execute architecture with hierarchical agents and OOD-aware routing, enabling US Amazon sellers to rapidly obtain accurate business insights with 90% human-evaluated accuracy and sub-15s latency.
Key Contributions
- Insight Agents (IA) is a novel LLM-backed multi-agent system built on a plan-and-execute paradigm, designed to help e-commerce sellers overcome tool discovery and data utilization barriers by delivering personalized, conversational business insights with high coverage, accuracy, and low latency.
- The system employs a hierarchical architecture with a manager agent that routes queries via OOD detection and BERT-based classification, and two worker agents—data presenter and insight generator—that decompose queries into granular API calls and dynamically inject domain knowledge to improve response accuracy.
- Deployed for Amazon sellers in the US, IA achieves 90% accuracy via human evaluation and maintains P90 latency under 15 seconds, demonstrating practical effectiveness in real-world e-commerce decision support.
Introduction
The authors leverage a hierarchical multi-agent system powered by LLMs to help e-commerce sellers extract actionable business insights from complex, fragmented data tools—addressing a critical need for faster, less cognitively demanding decision-making. Prior systems often struggled with accuracy, latency, or scope when handling open-ended, domain-specific queries across multiple data sources. Their main contribution is Insight Agents, a plan-and-execute architecture with a manager agent routing queries via OOD detection and BERT classification, and two worker agents that decompose queries and inject domain knowledge to boost precision—all achieving 90% accuracy and sub-15s latency in production.
Dataset
The authors use a curated dataset for training and evaluating OOD detection and agent routing models, composed as follows:
-
Dataset Composition:
- 301 total questions: 178 in-domain, 123 out-of-domain.
- In-domain split: 120 for data presenter, 59 for insight generator.
- A separate benchmarking set of 100 popular questions with ground truth for end-to-end evaluation.
-
Data Augmentation:
- Raw in-domain subsets (data presenter and insight generator) are augmented via LLM to reach 300 questions each, introducing semantic variations for balanced training.
- No augmentation applied to out-of-domain or benchmarking sets.
-
Model Usage:
- The augmented 300-question subsets per agent are used to finetune a lightweight BERT model (“bge-small-en-v1.5”).
- OOD detection uses a model with hidden layer dimension 64 and hyperparameter λ = 4.
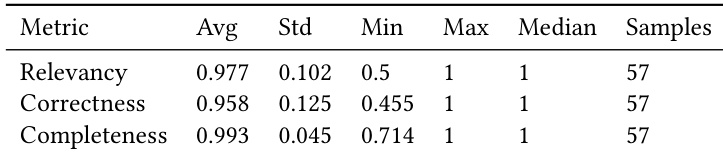
- Final evaluation on the 100-question benchmark is performed by human auditors using three metrics: Relevance, Correctness, and Completeness.
- Question-level accuracy is defined as the percentage of questions scoring above 0.8 on all three metrics.
-
Processing & Evaluation:
- No cropping or metadata construction mentioned.
- LLM used for augmentation: “anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0” via Amazon Bedrock.
- Metrics for OOD and routing models include precision, recall, and accuracy.
Method
The Insight Agents (IA) system employs a hierarchical manager-worker multi-agent architecture designed to deliver accurate, low-latency responses to seller queries through a plan-and-execute paradigm. The overall framework, illustrated in the figure below, begins with a seller query being processed by the manager agent, which acts as the central orchestrator. This agent performs initial validation and routing before delegating the task to one of two specialized worker agents: the data presenter agent or the insight generator agent. The manager agent includes three primary components: Out-of-Domain (OOD) detection, agent routing, and query augmenter. OOD detection filters queries that fall outside the scope of available data insight, ensuring that only relevant requests proceed. Agent routing determines the appropriate resolution path based on the query type, while the query augmenter resolves ambiguities, particularly around time ranges, by enriching the query with contextual information such as the current date. After processing, the system applies response guardrails to prevent the exposure of sensitive or harmful content before returning the final answer to the seller.

The low-level architecture of the two worker agents, the data presenter and the insight generator, is detailed in the figure below. Both agents share a common data workflow planning and execution pipeline but diverge in their generation strategies. The data presenter agent focuses on retrieving and aggregating tabular data based on the query. Its data workflow planner decomposes the query into executable steps using a chain-of-thought approach, selecting appropriate APIs or functions and generating the necessary input payloads. This process is grounded in a robust data model that leverages the company's internal data APIs, ensuring high accuracy through structured retrieval. The data workflow executor then retrieves the data via the selected APIs, performs any required transformations, and applies post-processing steps such as column renaming and semantic filtering. The final response is generated through standard prompting, guided by few-shot examples to ensure the correct format.
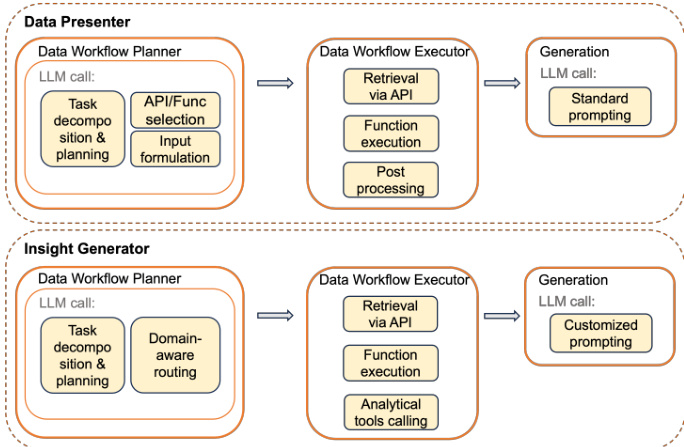
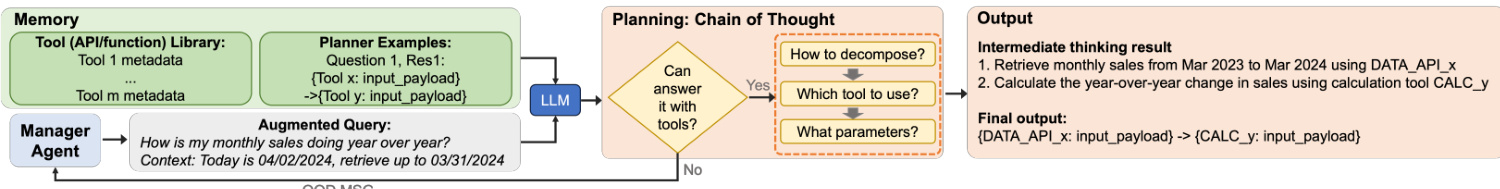
The insight generator agent follows a similar planning and execution structure but is designed to produce analytical insights rather than raw data. Its data workflow planner also performs task decomposition and planning, but it includes an additional step of domain-aware routing to select the appropriate analytical technique—such as benchmarking, trend analysis, or seasonal analysis—based on the query's intent. The planner uses few-shot learning to guide the LLM in selecting the correct resolution path. The data workflow executor retrieves data and may invoke analytical tools for transformation. The generation process for the insight generator is more complex, utilizing customized prompting that incorporates domain-specific knowledge, prompt templates, and few-shot examples provided by domain experts. This ensures that the generated insights are not only accurate but also contextually relevant and actionable. The entire process is supported by a memory system that stores tool metadata and planner examples, enabling the LLM to effectively plan and execute tasks. The figure below illustrates the planning phase, where the LLM evaluates the query, determines if it can be answered using available tools, and decomposes the task into a sequence of steps, ultimately producing an intermediate thought process and a final output that includes the necessary API calls and calculations.
Experiment
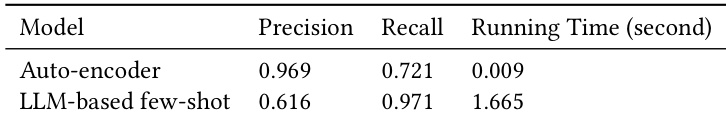
- AE-based OOD detection is highly efficient, processing samples in under 0.01s and achieving higher precision than LLM-based methods; recall can be improved by expanding the in-domain training set.
- Branch routing achieves 83% accuracy with 0.3s latency per case, significantly outperforming LLM-based classification in both speed and accuracy.
- Human evaluation of end-to-end IA responses shows 89.5% overall accuracy across 100 questions, with 57 deemed in-scope; system latency averages 13.56s at P90.
The authors use a finetuned BERT model for branch routing, achieving higher accuracy and significantly lower latency compared to an LLM-based approach. Results show that the BERT model provides a more efficient and effective solution for routing decisions in the system.
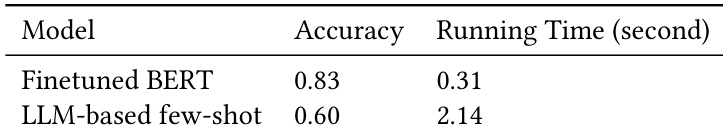
Results show that the auto-encoder-based method achieves higher precision and significantly faster running time compared to the LLM-based few-shot approach, while the LLM method demonstrates better recall. The overall performance indicates a trade-off between speed and accuracy, with the auto-encoder method being more efficient for real-time applications.
Results show that the system achieves high question-level accuracy, with 89.5% of responses correctly classified as true. The evaluation indicates strong performance in identifying in-scope questions, with a low error rate of 10.5% for false classifications.

Results show that the system achieves high average scores across relevance, correctness, and completeness, with strong consistency indicated by low standard deviations and a high number of samples. The evaluation demonstrates reliable performance in generating accurate and comprehensive responses, supported by robust metrics across key dimensions.