Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Rapport technique Gemma
Rapport technique Gemma
Abstract
Nous présentons TranslateGemma, une suite de modèles open source de traduction automatique fondés sur les modèles fondamentaux Gemma 3. Pour renforcer les capacités intrinsèques multilingues de Gemma 3 dans le cadre de la traduction, nous mettons en œuvre un processus de fine-tuning en deux étapes. Tout d’abord, un fine-tuning supervisé est effectué à l’aide d’un mélange riche de données parallèles synthétiques à grande échelle de haute qualité, générées à l’aide de modèles de pointe, combinées à des données parallèles traduites par des humains. Cette phase est suivie d’une étape d’apprentissage par renforcement, durant laquelle nous optimisons la qualité de traduction à l’aide d’un ensemble de modèles de récompense, incluant MetricX-QE et AutoMQM, en ciblant spécifiquement la qualité de la traduction. Nous démontrons l’efficacité de TranslateGemma à travers une évaluation humaine sur le jeu de test WMT25 pour 10 paires de langues, ainsi qu’une évaluation automatique sur le benchmark WMT24++ pour 55 paires de langues. Les métriques automatiques montrent des gains constants et significatifs par rapport aux modèles de base Gemma 3, sur toutes les tailles de modèles. Notamment, les modèles TranslateGemma plus petits atteignent souvent des performances comparables à celles des modèles de base plus volumineux, offrant ainsi une meilleure efficacité. Nous montrons également que les modèles TranslateGemma conservent de fortes capacités multimodales, avec une performance améliorée sur le benchmark de traduction d’images Vistra. La mise à disposition open source des modèles TranslateGemma vise à fournir à la communauté scientifique des outils puissants et adaptables pour la traduction automatique.
One-sentence Summary
The Google Translate Research Team presents TranslateGemma, an open machine translation system built upon Gemma 3 through a two-stage fine-tuning process: supervised training on a mixture of human and high-quality synthetic parallel data, followed by reinforcement learning using an ensemble of reward models including MetricX-QE and AutoMQM, which significantly improves translation quality across 55 language pairs—especially for low-resource languages—while enabling smaller models to match or exceed larger baseline performance, and retaining strong multimodal capabilities for image-based translation without additional training.
Key Contributions
-
TranslateGemma is an open machine translation model built upon Gemma 3, enhanced through a two-stage fine-tuning process: supervised fine-tuning on a diverse mix of human-translated and high-quality synthetic parallel data, followed by reinforcement learning using an ensemble of reward models including MetricX-QE and AutoMQM to optimize translation quality.
-
The model demonstrates substantial improvements across 55 language pairs on the WMT24++ benchmark, with consistent gains in automatic metrics like MetricX and CoMET22, and smaller TranslateGemma variants (4B, 12B) often matching or exceeding the performance of larger baseline Gemma 3 models, offering better efficiency.
-
TranslateGemma retains the multimodal capabilities of Gemma 3, showing enhanced performance on the Vistra image translation benchmark without additional multimodal training, indicating that text translation improvements generalize to cross-modal tasks.
Introduction
Machine translation (MT) is critical for global communication, and recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have significantly improved translation quality. However, progress has been limited by the lack of strong, open-source models that enable transparency, reproducibility, and collaborative innovation. Prior approaches often relied on limited or static training data and struggled to balance translation accuracy with broader linguistic capabilities. The authors introduce TranslateGemma, an open-source variant of Gemma 3 specifically optimized for MT through a two-stage process: supervised fine-tuning on a diverse mix of human and synthetic parallel data, followed by reinforcement learning using human and model-based feedback. This approach yields substantial improvements across 55 language pairs on WMT25 and WMT24++ benchmarks, while preserving the original model’s multimodal abilities—demonstrated by enhanced performance on image translation tasks. The release of TranslateGemma aims to accelerate research and application in open, high-quality machine translation.
Dataset
- The dataset for TranslateGemma consists of two main types of data used across both supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL) phases, with most data shared between them.
- For lower-resource languages, the authors include human-generated parallel data from SMOL (123 languages) and GATITOS (170 languages), enhancing script diversity and coverage.
- The SFT phase uses a mixture of data, with 30% drawn from the original Gemma 3 generic instruction-following dataset to prevent overfitting to translation and preserve general instruction-following abilities.
- In addition to WMT24++ data, synthetic data was created for 30 specific language pairs involving English (e.g., English–Armenian, English–Hawaiian, English–Maltese), expanding coverage beyond existing sources.
- The RL phase uses the same translation data as SFT, except for GATITOS and SMOL, which are used only in SFT.
- Language distribution across SFT and RL is detailed in Figure 1, with full language pairings provided in Appendix C across three tables: bidirectional English pairs (Table 5), English-to-other language pairs (Table 6), and non-English language pairs (Table 7).
- No explicit cropping strategy is mentioned, but data filtering and selection are guided by language coverage, resource availability, and task relevance.
- Metadata for language pairs and data sources is constructed to support balanced training and clear tracking of language-specific contributions.
Method
The authors leverage a two-stage fine-tuning framework to enhance the multilingual translation capabilities of the Gemma 3 foundation models, resulting in the TranslateGemma suite. The overall approach begins with supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on a diverse mix of parallel data, followed by a reinforcement learning phase that optimizes translation quality using an ensemble of reward models. This framework is designed to improve translation performance across a broad range of language pairs while maintaining efficiency and multimodal capabilities.
For the supervised fine-tuning stage, the authors start with the publicly released Gemma 3 27B, 12B, and 4B checkpoints. They fine-tune these models using a combination of human-translated parallel data and high-quality synthetic data generated via Gemini 2.5 Flash. The synthetic data is produced by first selecting source segments from the MADLAD-400 corpus based on length buckets, then filtering them using a preliminary quality estimation step that compares greedy and sampled decoding outputs from Gemini 2.5 Flash. This filtering ensures that only source segments likely to benefit from further refinement are selected. For each selected source, 128 translations are generated and filtered using MetricX 24-QE to retain the highest quality examples. The synthetic data includes both individual sentence translations and longer text blobs up to 512 tokens, enabling support for both short and extended text translation. In addition to parallel data, generic instruction-following data is also incorporated to improve general language understanding. The fine-tuning process employs the AdaFactor optimizer with a learning rate of 0.0001 and a batch size of 64, running for 200k steps. All model parameters are updated except for the embedding parameters, which are frozen to preserve translation performance for languages and scripts not present in the SFT data mix.
Experiment
- Reinforcement learning was applied to the SFT checkpoint using an ensemble of reward models, including MetricX-24-XXL-QE, Gemma-AutoMQM-QE, ChrF, a custom Naturalness Autorater, and a generalist reward model, with token-level advantages enabling fine-grained credit assignment.
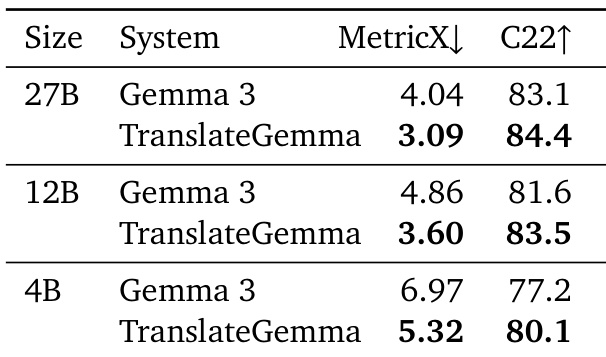
- On the WMT24++ dataset, TranslateGemma achieved significant improvements over baseline Gemma 3 models: the 27B model reduced MetricX score from 4.04 to 3.09 (23.5% relative decrease), the 12B model from 4.86 to 3.60 (25.9% decrease), and the 4B model from 6.97 to 5.32 (23.6% decrease), with consistent gains across all 55 language pairs.
- COMET22 results confirmed improvements, with the 12B TranslateGemma scoring 83.5 (up from 81.6) and the 4B model reaching 80.1 (up from 77.2), demonstrating generalization beyond optimized metrics.
- TranslateGemma models achieved performance comparable to or exceeding larger baseline models—e.g., 12B TranslateGemma outperformed 27B baseline Gemma 3, and 4B TranslateGemma matched 12B baseline performance—indicating improved efficiency.
- On the Vistra benchmark for image translation, TranslateGemma retained multimodal capabilities, with the 27B model improving MetricX by nearly 0.5 points and the 12B model by 0.25 points, despite no multimodal training during SFT or RL.
- Human evaluation on 10 language pairs using MQM confirmed TranslateGemma’s superiority in most cases, with notable gains in low-resource pairs (e.g., +1.6 for English→Marathi, +1.0 for English→Swahili), though a regression was observed in Japanese→English due to named entity errors.
Results show that TranslateGemma models consistently outperform the baseline Gemma 3 models across all sizes on both MetricX and CoMET22 metrics, with the 27B TranslateGemma achieving a 23.5% relative reduction in MetricX score compared to the 27B baseline. The improvements are consistent across model sizes, with smaller TranslateGemma models achieving performance comparable to or exceeding larger baseline models, indicating enhanced efficiency and translation quality.
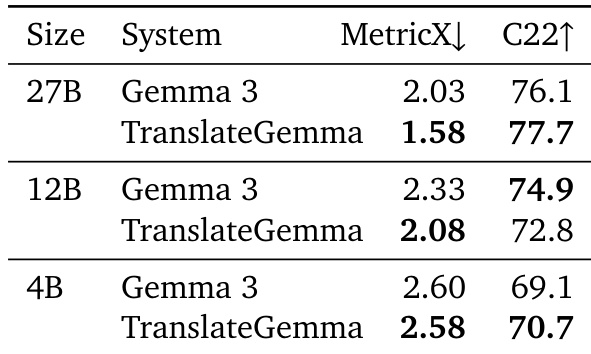
Results show that TranslateGemma models consistently outperform the baseline Gemma 3 models across all evaluated sizes and metrics, with significant improvements in both MetricX and COMET22 scores. The 27B TranslateGemma model achieves a MetricX score of 1.58, a substantial reduction from the baseline Gemma 3's score of 2.03, while the 12B and 4B TranslateGemma models also show notable improvements over their respective baselines.
The authors use the TranslateGemma models to evaluate translation quality across multiple language pairs, comparing them against baseline Gemma 3 models using MetricX scores. Results show that TranslateGemma consistently achieves lower MetricX scores than the baseline models across all sizes and language pairs, indicating improved translation quality, with the 12B TranslateGemma model outperforming the larger 27B Gemma 3 model in several cases.
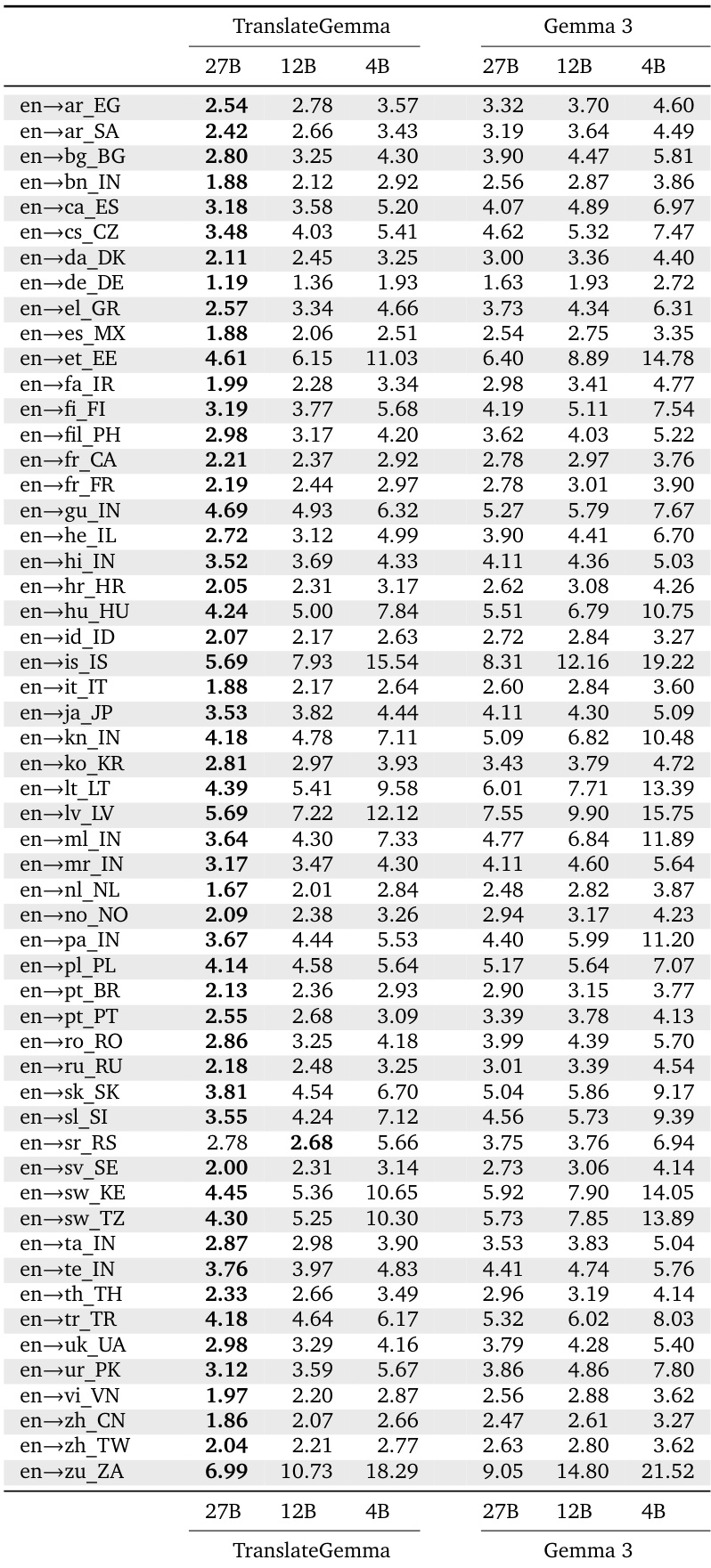
Results show that TranslateGemma models achieve lower MetricX scores than the baseline Gemma 3 models across all evaluated language pairs, indicating improved translation quality. The 27B TranslateGemma model consistently outperforms the 27B Gemma 3 model, with notable reductions in scores such as 1.8 compared to 2.2 for English→German and 6.3 compared to 7.4 for English→Chinese.