Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
VAR RL Fait Correctement : Affronter les Conflits de Politiques Asynchrones dans la Génération Autoregressive Visuelle
VAR RL Fait Correctement : Affronter les Conflits de Politiques Asynchrones dans la Génération Autoregressive Visuelle
Résumé
La génération visuelle est dominée par trois paradigmes : les modèles AutoRegressive (AR), les modèles à diffusion et les modèles Visual AutoRegressive (VAR). Contrairement aux modèles AR et à diffusion, les VAR opèrent sur des structures d'entrée hétérogènes au cours de leurs étapes de génération, ce qui engendre des conflits politiques asynchrones sévères. Ce problème devient particulièrement critique dans les scénarios d'apprentissage par renforcement (RL), entraînant une instabilité d'entraînement et un alignement sous-optimal. Pour résoudre ce défi, nous proposons un cadre novateur visant à améliorer l'optimisation politique relative par groupe (Group Relative Policy Optimization, GRPO) en gérant explicitement ces conflits. Notre méthode intègre trois composants synergiques : 1) une récompense intermédiaire stabilisante pour guider la génération en phase précoce ; 2) un schéma dynamique de réévaluation des pas de temps pour une attribution précise des mérites ; et 3) un nouvel algorithme de propagation de masque, dérivé des principes de l'apprentissage par rétroaction de récompense (Reward Feedback Learning, ReFL), conçu pour isoler les effets d'optimisation à la fois dans l'espace et dans le temps. Notre approche montre des améliorations significatives en termes de qualité des échantillons et d'alignement objectif par rapport à la version de base de GRPO, permettant une optimisation robuste et efficace pour les modèles VAR.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Tsinghua University and ByteDance propose NextFlow, a novel framework that enhances Group Relative Policy Optimization for Visual AutoRegressive models by introducing a stabilizing intermediate reward, dynamic time-step reweighting, and a mask propagation algorithm inspired by Reward Feedback Learning, effectively resolving asynchronous policy conflicts to improve sample quality and alignment in reinforcement learning settings.
Key Contributions
- Visual autoregressive (VAR) models, which generate images through a coarse-to-fine, multi-scale token prediction process, face severe asynchronous policy conflicts during reinforcement learning due to highly heterogeneous input structures across generation steps, leading to unstable training and poor alignment compared to autoregressive and diffusion models.
- The proposed framework enhances Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with three key components: a stabilizing intermediate reward (VMR) for early-stage guidance, dynamic time-step reweighting (PANW) to balance gradient contributions across scales, and a mask propagation (MP) algorithm inspired by Reward Feedback Learning to spatially and temporally isolate optimization effects.
- Experiments demonstrate that the method significantly improves sample quality and objective alignment over vanilla GRPO, with stable training curves across varying prefix scales and superior performance in text-to-image generation tasks, establishing a practical and effective RL recipe for VAR models.
Introduction
The authors leverage reinforcement learning to improve visual autoregressive (VAR) image generation, a paradigm that generates images by predicting tokens across progressively finer spatial scales, offering better inference efficiency and fidelity than traditional raster-scan methods. While reinforcement learning has shown success in enhancing text-to-image alignment and controllability in other generative models, its application to VAR architectures remains underexplored due to unique challenges arising from asynchronous, multi-scale, and parallel token generation. Prior work fails to address policy conflicts caused by differing temporal dependencies across scales, leading to unstable training and suboptimal performance. The authors’ main contribution is a novel framework that resolves these asynchronous policy conflicts through a tailored reward mechanism and optimization strategy, enabling stable and effective reinforcement learning in VAR models.
Dataset
- The dataset comprises an in-house training corpus and a curated evaluation set, with the training data exhibiting a significant imbalance in text-rendering regions per image—dominated by single-region samples and a long tail of images with more than five regions.
- To address this imbalance, the authors apply a region-count-based filtering strategy to the training data, categorizing samples into six bins: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and >5 regions, with the >5 bin used to aggregate the long tail for analysis.
- The evaluation set is designed to follow a target distribution across bins 2 to 5, with probabilities set at 0.2, 0.3, 0.3, and 0.2, respectively, ensuring a balanced representation of moderate region counts.
- The filtered training set and evaluation set are used to train and assess the model, with the filtering strategy explicitly intended to align the training distribution with the desired task difficulty, not to leak evaluation information.
- No cropping is applied to the images; instead, metadata is constructed based on region counts and their distribution across the defined bins, enabling precise control over training and evaluation conditions.
Method
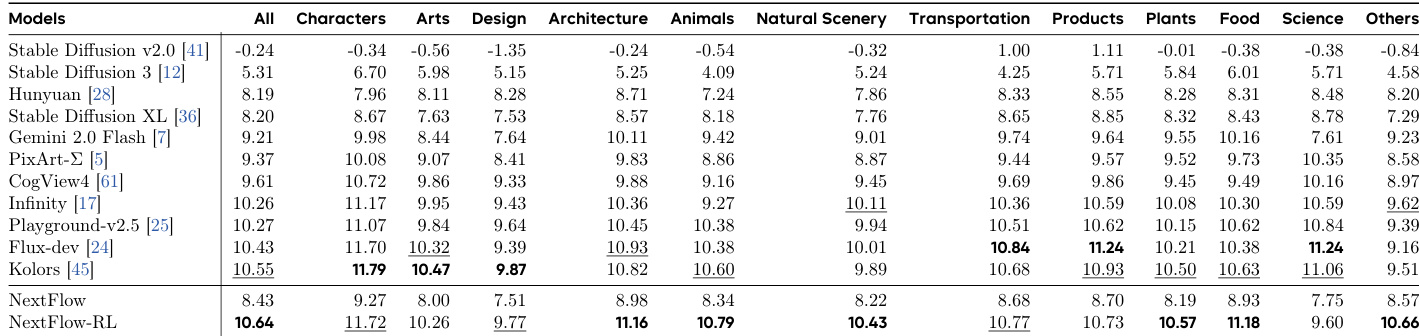
The authors leverage a hierarchical reinforcement learning framework to address asynchronous policy conflicts in Visual AutoRegressive (VAR) models, which arise due to the heterogeneous, parallel action spaces across generation steps. The core of the method involves a two-stage optimization process that decomposes the full-horizon reinforcement learning objective into prefix and suffix subtasks, thereby mitigating multi-step conflicts and enabling more stable training. This decomposition is achieved through the Value-as-Middle-Return (VMR) mechanism, which introduces an intermediate soft return at a middle timestep m. The framework computes the reward for the prefix policy π1:m−1θ using Monte Carlo estimation and then applies Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to both the prefix and suffix segments independently, each with a local KL penalty. This stage-wise approach stabilizes training by ensuring that per-stage token lengths remain comparable, while preserving the global objective value. The detailed algorithm is illustrated in the framework diagram, which shows the flow of policy updates, reference models, and reward computation across the two stages.
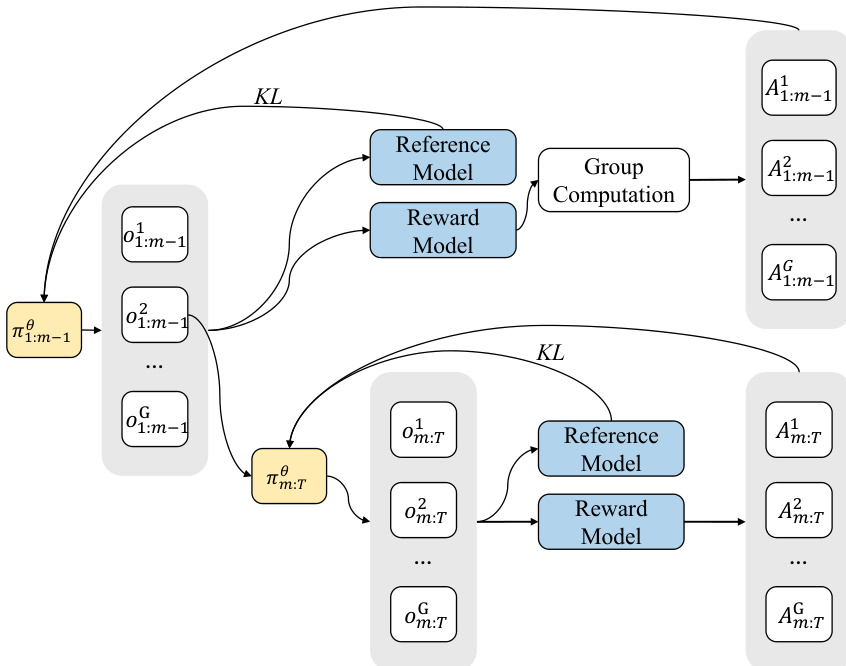
To balance the contributions of different timesteps and counteract the step-wise heterogeneity caused by varying token-grid sizes, the authors propose Per-Action Normalization Weighting (PANW). This technique normalizes the loss associated with each action mathbfat by a weight k_t = 1/(h_t w_t)^\\alpha, where ht and wt are the height and width of the token grid at timestep t, and alpha is a decay exponent. By weighting the loss in this manner, PANW ensures that timesteps with a larger number of query tokens do not disproportionately influence the learning process, thereby promoting a more balanced optimization across all timesteps. This normalization is crucial for stabilizing the training dynamics, especially given the significant variation in task similarity across different timesteps, as highlighted in the analysis of token grid sizes.
Finally, the authors introduce a novel Mask Propagation (MP) algorithm to precisely identify and prioritize updates on the tokens most responsible for the final return. This mechanism is inspired by principles of Reward Feedback Learning (ReFL) and operates by first constructing an initial mask from the output components that directly determine the reward, such as predicted bounding boxes. This mask is then propagated backward through the model's multi-scale hierarchy, moving from finer to coarser feature scales. The propagation process directs updates toward the most relevant tokens, effectively isolating optimization effects both spatially and temporally. This spatiotemporal masking reduces variance across both space and time, sharpens credit assignment, and improves cross-scale balance, leading to more effective and efficient optimization of the VAR model.
Experiment
- Conducted experiments on text rendering (CVTG-2K) and HPS refine (HPSv3) tasks using NextFlow-RL with a two-stage RL framework optimizing prefix tokens via VMR-based rewards and alternating GRPO updates.
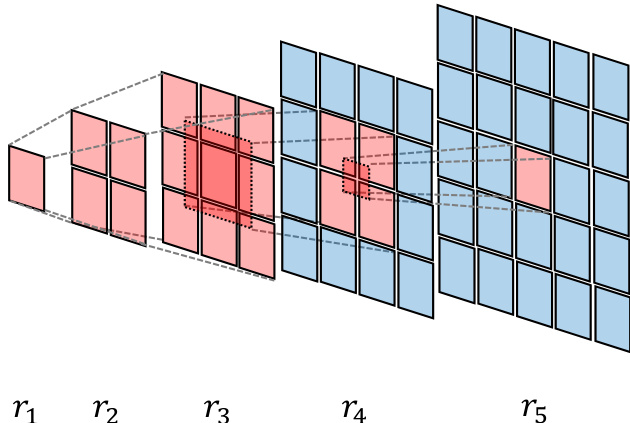
- On CVTG-2K, NextFlow-RL achieved Word Accuracy of 0.7841 and NED of 0.9081, surpassing NextFlow by +0.2305 and +0.1265 respectively, with improved CLIPScore (0.8224 vs. 0.8068), validating enhanced text fidelity and visual quality.
- On HPSv3, NextFlow-RL achieved an overall score of 10.64, ranking first across multiple categories including Animals (10.79), Natural Scenery (10.43), Plants (10.57), Food (11.18), and Architecture (11.16), establishing SOTA performance among diffusion models.
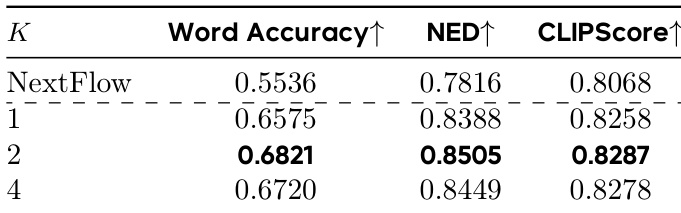
- Ablations confirmed optimal design choices: m=m256 (128×128 to 256×256 resolution) for balanced performance and efficiency, α=0.6 to 0.8 for decay exponent, K=2 samples for VMR estimation, and fine-grained alternating training for better credit assignment.
- Mask Propagation (MP) improved text fidelity (Word Acc. 0.7071 vs. 0.6855, NED 0.8699 vs. 0.8601) with minimal impact on CLIPScore, confirming its benefit in spatiotemporal credit assignment.
The authors use NextFlow-RL, a reinforcement learning-enhanced version of NextFlow, to improve text rendering performance. Results show that NextFlow-RL achieves the highest Word Accuracy (0.7841), NED (0.9081), and CLIPScore (0.8224) among all compared models, significantly outperforming the base NextFlow and setting a new state-of-the-art on the CVTG-2K dataset.
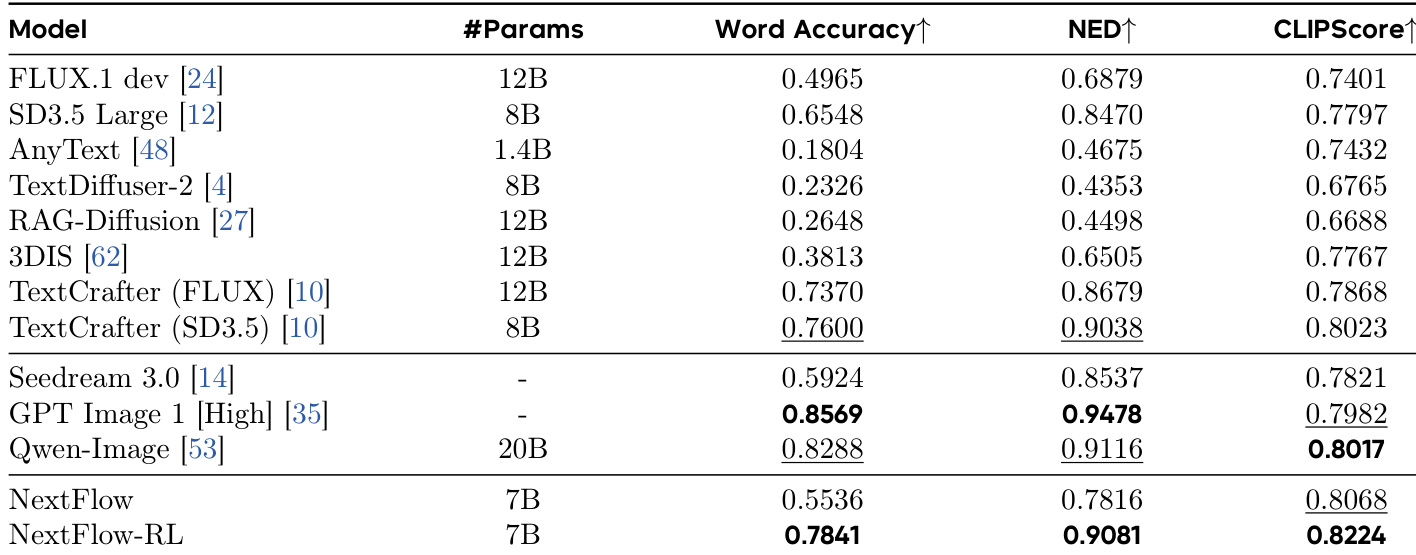
The authors use a two-stage reinforcement learning approach to optimize text rendering in images, with results showing that selecting the middle-stage value at m=128 (corresponding to 128×128 resolution) yields the best performance across Word Accuracy, NED, and CLIPScore. This configuration achieves a Word Accuracy of 0.6677, NED of 0.8501, and CLIPScore of 0.8142, outperforming other values of m and the baseline NextFlow model.
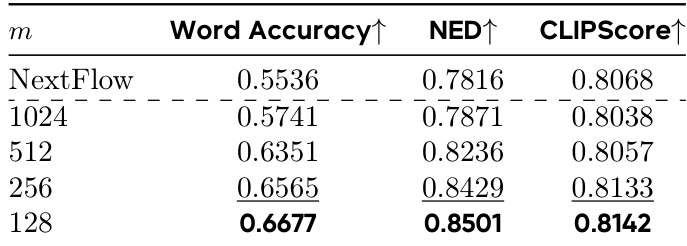
Results show that varying the decay exponent α in the reward function affects model performance, with α = 0.6 achieving the highest Word Accuracy, NED, and CLIPScore, indicating optimal gradient normalization and performance across metrics.
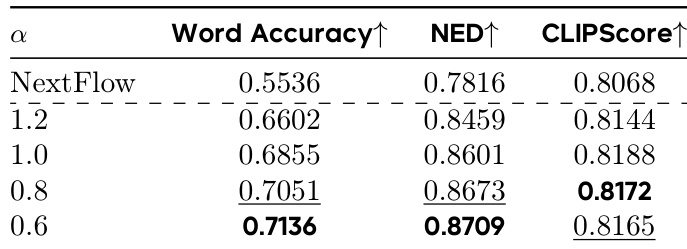
Results show that increasing the number of on-policy samples K for VMR estimation improves text rendering performance, with K=2 achieving the best Word Accuracy (0.6821), NED (0.8505), and CLIPScore (0.8287) compared to K=1 and K=4. The authors use this configuration as the default, noting that K=2 offers the best balance of stability and performance.
Results show that NextFlow-RL achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple categories on the HPSv3 benchmark, outperforming all other diffusion-based models in key metrics such as All, Animals, Natural Scenery, Plants, and Food, while also ranking second in Characters and Design. The improvements demonstrate the effectiveness of the two-stage RL scheme, which optimizes early-token decisions using OCR-guided rewards and enhances text fidelity and visual quality across diverse domains.