Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Avatar Forcing : Génération en temps réel d'avatar de tête pour des conversations naturelles
Avatar Forcing : Génération en temps réel d'avatar de tête pour des conversations naturelles
Taekyung Ki Sangwon Jang Jaehyeong Jo Jaehong Yoon Sung Ju Hwang
Résumé
La génération d’avatars parlants permet de créer des avatars réalistes à partir de portraits statiques, destinés à la communication virtuelle et à la création de contenu. Toutefois, les modèles actuels ne parviennent pas encore à transmettre l’impression d’une interaction véritablement interactive, produisant souvent des réponses unidirectionnelles dépourvues d’engagement émotionnel. Nous identifions deux défis clés pour atteindre des avatars véritablement interactifs : la génération de mouvements en temps réel sous contraintes causales, et l’apprentissage de réactions expressives et dynamiques sans données étiquetées supplémentaires. Pour relever ces défis, nous proposons Avatar Forcing, un nouveau cadre pour la génération d’avatars de tête interactifs, qui modélise les interactions temps réel entre l’utilisateur et l’avatar grâce à une force de diffusion. Ce design permet à l’avatar de traiter des entrées multimodales en temps réel, notamment le son et les mouvements de l’utilisateur, avec une latence faible, garantissant des réactions instantanées aux indices verbaux et non verbaux tels que la parole, les hochements de tête ou les rires. Par ailleurs, nous introduisons une méthode d’optimisation directe des préférences qui exploite des échantillons synthétiques perdants construits en supprimant les conditions utilisateur, permettant ainsi un apprentissage expressif sans étiquetage. Les résultats expérimentaux montrent que notre cadre permet une interaction en temps réel avec une latence réduite (environ 500 ms), offrant une accélération de 6,8 fois par rapport à la méthode de référence, tout en produisant des mouvements d’avatar réactifs et expressifs, préférés dans plus de 80 % des cas par rapport à la référence.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from KAIST, NTU Singapore, and DeepAuto.ai propose Avatar Forcing, a diffusion-based framework enabling real-time, expressive interactive head avatars that react to multimodal user inputs—audio and motion—with low latency (~500ms) and 6.8× speedup over baselines, using a novel label-free preference optimization via synthetic condition-dropping to learn vibrant, emotionally responsive behaviors without labeled data, significantly enhancing engagement in virtual communication.
Key Contributions
- Existing talking head generation models fail to enable truly interactive communication, often producing one-way, non-reactive avatars that lack emotional engagement due to high latency and insufficient modeling of bidirectional verbal and non-verbal cues.
- The proposed Avatar Forcing framework addresses real-time interaction by employing causal diffusion forcing with key-value caching, enabling low-latency (≈500ms) generation of expressive avatar motion in response to live multimodal inputs such as audio and user motion.
- A novel label-free preference optimization method uses synthetic losing samples—created by dropping user conditions— to train expressive, reactive avatar behavior, resulting in 80% human preference over the baseline and a 6.8× speedup in inference.
Introduction
The authors address the challenge of creating truly interactive head avatars for natural conversation, where avatars must react in real time to both verbal and non-verbal user cues—such as speech, laughter, and head movements—while maintaining expressive, lifelike motion. Prior work in talking head generation often focuses on audio-driven lip sync or one-way response generation, lacking bidirectional interaction and suffering from high latency due to reliance on future context. Additionally, expressive listening behaviors like nodding or empathetic expressions are difficult to learn without labeled data, leading to stiff, unresponsive avatars. To overcome these limitations, the authors propose Avatar Forcing, a diffusion-forcing framework that enables causal, real-time generation by processing multimodal inputs (audio and motion) with low latency—achieving ~500ms response time and a 6.8× speedup over baselines. The key innovation lies in a label-free preference optimization method that synthesizes under-expressive motion samples by dropping user conditions, allowing the model to learn richer, more reactive behaviors without human annotations. This results in avatars that not only respond instantly but also exhibit natural, engaging expressions, outperforming baselines in human evaluations by 80%.
Dataset
- The dataset comprises dyadic conversation videos from RealTalk [16] and ViCo [67], selected for their natural, interactive speaker-listener dynamics.
- Videos are preprocessed by detecting scene changes using PySceneDetect [44], splitting them into individual clips for focused analysis.
- Each face is detected and tracked using Face-Alignment [4], then cropped and resized to 512×512 pixels to standardize visual input.
- Speaker and listener audio are separated using a visual-grounded speech separation model [30], leveraging visual cues for accurate audio assignment.
- All video content is converted to 25 frames per second, and audio is resampled to 16 kHz to ensure consistent temporal and spectral alignment.
- A subset of 50 videos from the HDTF [66] dataset is randomly selected for evaluating talking-head generation performance.
- The data is used in training with a mixture of RealTalk and ViCo subsets, where each subset contributes to the overall training split based on predefined ratios.
- Metadata is constructed during preprocessing to associate speaker and listener roles, clip boundaries, and audio-visual alignment, supporting interactive avatar generation.
- No explicit cropping beyond face-centered 512×512 crops is applied, and all processing is designed to preserve natural conversational context and visual fidelity.
Method
The authors leverage diffusion forcing as the core generative mechanism for real-time interactive head avatar generation, operating within a motion latent space. The overall framework, illustrated in the figure below, consists of two primary stages: encoding multimodal user and avatar signals, and causal inference of avatar motion. The motion latent auto-encoder, detailed in the accompanying figure, maps an input image S to a latent z that is explicitly decomposable into an identity latent zS and a motion latent mS. This decomposition allows the model to capture holistic head motion and fine-grained facial expressions, which are essential for realistic avatar generation. The motion generation process is formulated as an autoregressive model, where each motion latent mi is predicted conditioned on past motion latents and a condition triplet ci comprising user audio aui, user motion mui, and avatar audio ai.
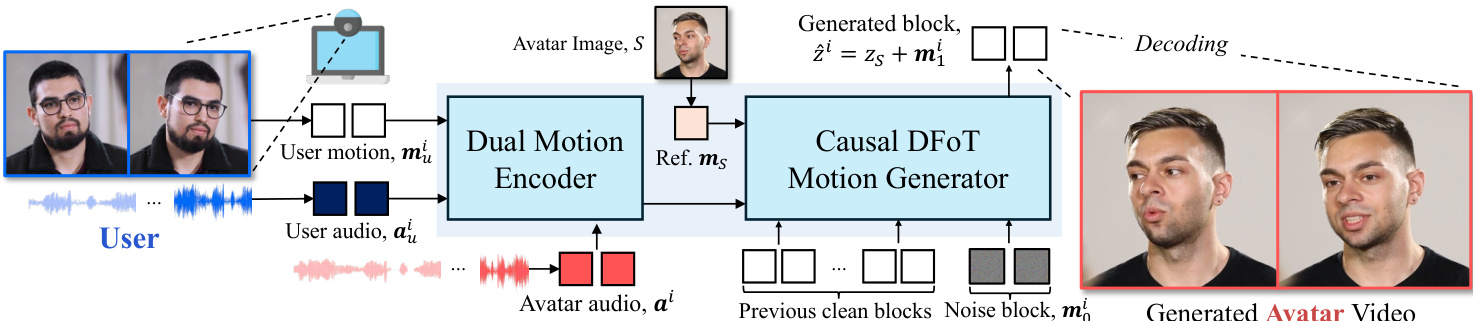
The core of the motion generation is a diffusion forcing-based causal motion generator, modeled as a vector field vθ. As shown in the figure below, this model is composed of two main components: a Dual Motion Encoder and a Causal DFoT Motion Generator. The Dual Motion Encoder first processes the user motion mui and user audio aui through a cross-attention layer to capture holistic user motion. This representation is then integrated with the avatar audio ai using another cross-attention layer, which learns the causal relationship between the user and the avatar, producing a unified condition. The Causal DFoT Motion Generator, detailed in the figure below, operates on the motion latent space using a blockwise causal structure. The latent frames are divided into blocks to capture local bidirectional dependencies within each block while maintaining causal dependencies across blocks. For each block, a shared noise timestep is applied, and an attention mask prevents the current block from attending to any future blocks, enabling stepwise motion generation under causal constraints.
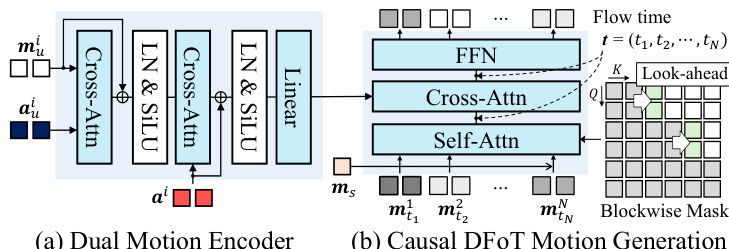
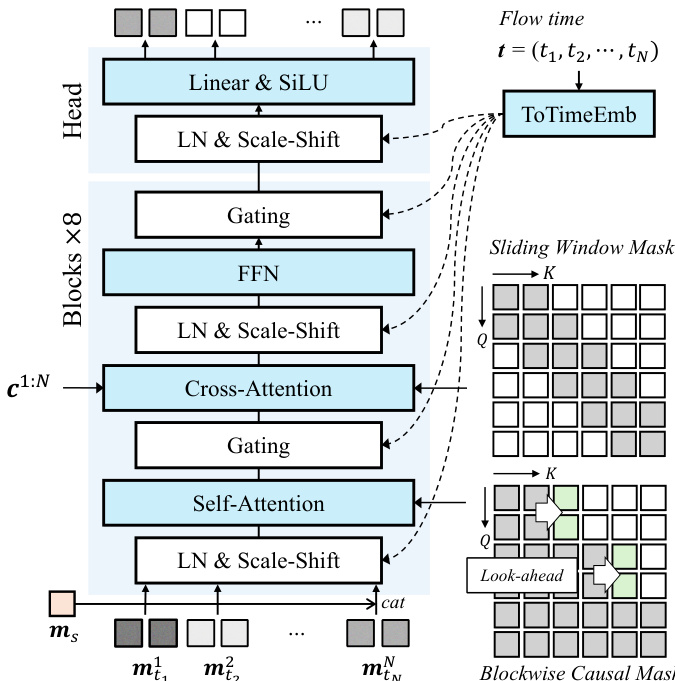
To address the issue of temporal jittering caused by the strict causal mask, the authors introduce a look-ahead mechanism in the causal mask. This allows each block to attend to a limited number of future frames, ensuring a smooth transition across blocks while preserving overall causality. The blockwise look-ahead causal mask M is defined such that a frame i can attend to frame j if ∣j/B∣≤∣i/B∣+l, where B is the block size and l is the look-ahead frame size. The model vθ is trained using a diffusion forcing objective that regresses the vector field vθ towards the target vector field (m1n−m0n), where m0n is the clean motion latent and m1n is the noisy motion latent. During inference, the model generates motion latents in a blockwise manner, utilizing a rolling key-value (KV) cache to maintain context and achieve low-latency real-time interaction. The figure below provides a detailed architecture of the Causal DFoT Motion Generator, which consists of eight DFoT transformer blocks followed by a transformer head. Each DFoT block modulates the noisy latents by the flow time t through a shared AdaLN scale-shift coefficients layer. The attention modules use the blockwise causal look-ahead mask for self-attention and a sliding-window attention mask to align the driving signal c1:N to the noisy latents.
Experiment
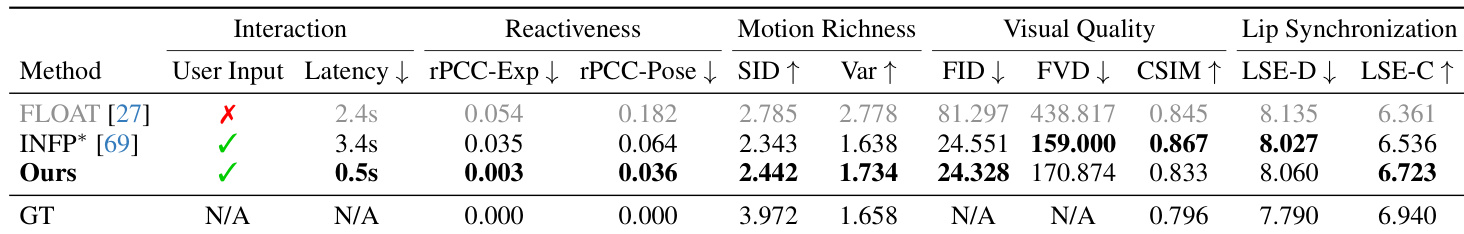
- Evaluates interactive avatar generation across latency, reactiveness, motion richness, visual quality, and lip synchronization using metrics including rPCC, SID, Var, FID, FVD, CSIM, LSE-D, and LSE-C.
- On the RealTalk dataset, Avatar Forcing achieves 0.5s latency, outperforms INFP* in reactiveness and motion richness, and maintains comparable visual quality and lip synchronization, enabling real-time interaction.
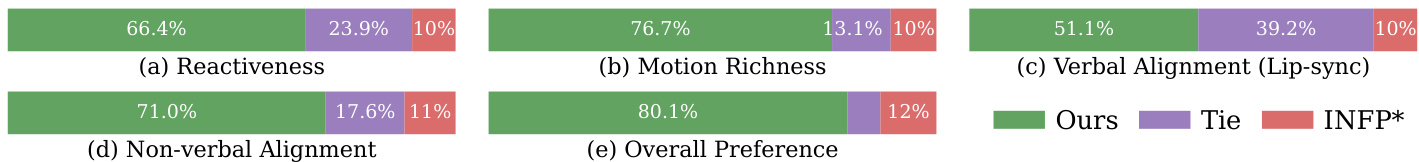
- Human preference study with 22 participants shows over 80% preference for Avatar Forcing across all metrics, particularly in reactivity, motion richness, and non-verbal alignment.
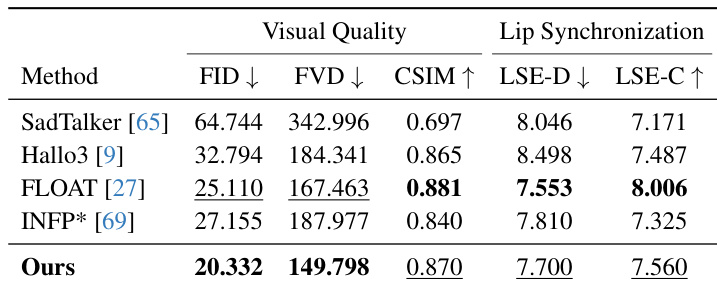
- On the HDTF dataset, Avatar Forcing achieves competitive performance with the best image and video quality (FID, FVD) and strong lip synchronization (LSE-D, LSE-C) compared to SadTalker, Hallo3, FLOAT, and INFP*.
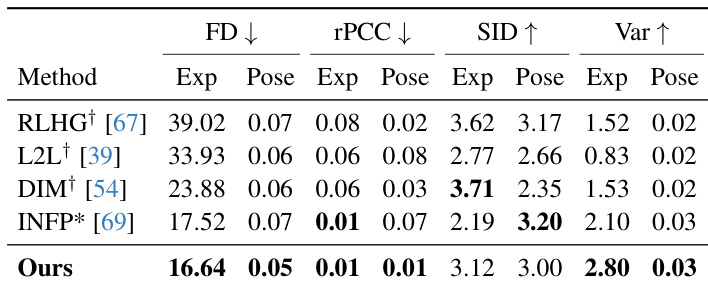
- On the ViCo dataset, Avatar Forcing outperforms listening head avatar models (RLHG, L2L, DIM, INFP*) in user-avatar motion synchronization (rPCC), expression and pose diversity (SID, Var), and distributional similarity (FD).
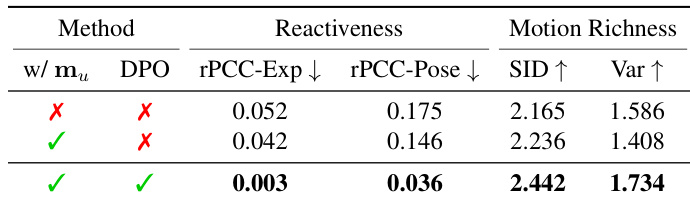
- Ablation studies confirm that user motion input is essential for reactivity and expressiveness, with removal leading to static behavior during silent audio.
- Preference optimization via DPO significantly improves rPCC, SID, and Var, resulting in more expressive and reactive avatar motion, as validated by both quantitative metrics and qualitative visualizations.
The authors use an ablation study to evaluate the impact of user motion input and preference optimization on avatar generation. Results show that including both user motion and preference optimization significantly improves reactivity and motion richness, with the best performance achieved when both components are present.
Results show that the proposed model achieves the lowest latency of 0.5s, significantly outperforming baselines in reactivity and motion richness while maintaining competitive visual quality and lip synchronization. The model's superior performance in reactivity and motion richness metrics indicates more expressive and synchronized avatar behavior compared to existing methods.
Results show that the proposed method achieves superior visual quality, as indicated by lower FID and FVD scores, and better identity preservation with a higher CSIM value compared to SadTalker, Hallo3, FLOAT, and INFP*. The model also maintains competitive lip synchronization performance, with lower LSE-D and higher LSE-C scores, demonstrating effective alignment between generated lip motion and audio.
Results show that the proposed model achieves higher reactivity, motion richness, verbal alignment, non-verbal alignment, and overall preference compared to the baselines INFP* and Tie. The model demonstrates superior performance in generating expressive and synchronized avatar motions, with significant improvements in user-avatar interaction metrics.
Results show that the proposed model achieves the best performance across all metrics compared to the baselines, with the lowest Frechet distance (FD) for expression and pose, the highest similarity index for diversity (SID), and the highest variance (Var) for both expression and pose. The model also demonstrates superior motion synchronization, as indicated by the lowest residual Pearson correlation coefficients (rPCC) for expression and pose, indicating more reactive and expressive avatar motion.