Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Rapport technique HY-MT1.5
Rapport technique HY-MT1.5
Mao Zheng Zheng Li Tao Chen Mingyang Song Di Wang
Résumé
Dans ce rapport, nous présentons nos derniers modèles de traduction, HY-MT1.5-1.8B et HY-MT1.5-7B, une nouvelle famille de modèles de traduction automatique développés grâce à un cadre d'entraînement holistique spécifiquement conçu pour assurer des performances élevées. Notre approche repose sur une pipeline multi-étapes intégrant l'entraînement préalable général et orienté traduction, le fine-tuning supervisé, la distillation en politique (on-policy distillation) et l'apprentissage par renforcement. Le modèle HY-MT1.5-1.8B, doté de 1,8 milliard de paramètres, démontre une efficacité remarquable en termes de paramètres, surpassant de manière globale des modèles open-source bien plus volumineux (tels que Tower-Plus-72B et Qwen3-32B) ainsi que des APIs commerciales majeures (comme Microsoft Translator et Doubao Translator) sur des tâches standard de traduction chinois-étranger et anglais-étranger. Il atteint environ 90 % des performances des modèles propriétaires ultra-élevés comme Gemini-3.0-Pro, tout en étant légèrement en retrait sur les benchmarks WMT25 et langues minoritaires en chinois mandarin, tout en conservant une avance significative sur les autres modèles concurrents. Par ailleurs, HY-MT1.5-7B établit une nouvelle référence (state-of-the-art) pour sa catégorie en termes de taille, atteignant 95 % des performances de Gemini-3.0-Pro sur Flores-200, et dépassant ce dernier sur les jeux de test exigeants de WMT25 et des langues minoritaires en chinois mandarin. Au-delà des tâches de traduction standard, la série HY-MT1.5 prend en charge des contraintes avancées, notamment l’intervention terminologique, la traduction contextuelle et la préservation du format. Des évaluations empiriques étendues confirment que ces deux modèles offrent des solutions hautement compétitives et robustes pour les tâches de traduction générale et spécialisée, dans leur gamme respective de paramètres.
One-sentence Summary
Tencent Hunyuan Team introduces HY-MT1.5-1.8B and HY-MT1.5-7B, efficient translation models trained via multi-stage pipeline, outperforming larger open-source and commercial systems while supporting advanced constraints like terminology control and format preservation for real-world deployment.
Key Contributions
- HY-MT1.5-1.8B and HY-MT1.5-7B achieve state-of-the-art translation quality for their parameter scales, with the 1.8B model matching ~90% of Gemini-3.0-Pro’s performance and the 7B model reaching 95% on Flores-200 while surpassing it on WMT25 and Mandarin-minority benchmarks, all while maintaining deployment efficiency.
- The models are trained via a holistic multi-stage pipeline combining general and MT-specific pre-training, supervised fine-tuning, on-policy distillation, and reinforcement learning with a rubrics-based evaluator, enabling strong performance across both high- and low-resource language pairs.
- Beyond standard translation, HY-MT1.5 supports practical customization features including terminology control, context-aware translation, and format preservation, allowing prompt-driven adaptation to specialized industrial use cases.
Introduction
The authors leverage recent advances in large language models to address two persistent bottlenecks in machine translation: the tradeoff between translation quality and inference efficiency, and the lack of support for customized translation tasks. Prior work either relies on massive closed-source models that are too costly to deploy or lightweight open-source models that sacrifice quality, while also failing to handle contextual coherence, document formatting, or terminology control. To bridge this gap, they introduce HY-MT1.5 — a family of efficient, high-performing models (1.8B and 7B parameters) that match or exceed top closed-source models in quality while enabling practical deployment. Their contribution includes a tailored training pipeline combining pretraining, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, plus built-in features for prompt-driven customization such as terminology control, contextual translation, and formatted output preservation.
Method
The authors leverage a multi-stage training pipeline to develop the HY-MT1.5-1.8B and HY-MT1.5-7B models, designed to enhance multilingual translation performance through knowledge transfer and alignment. The overall framework begins with base models HY-1.8B-Base and HY-7B-Base, which undergo a sequence of five distinct stages. As shown in the figure below, the process initiates with MT-oriented Pretraining (Stage 1), followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning (Stage 2), and then Reinforcement Learning (Stage 3), producing the HY-MT1.5-1.8B-preview and HY-MT1.5-7B models. 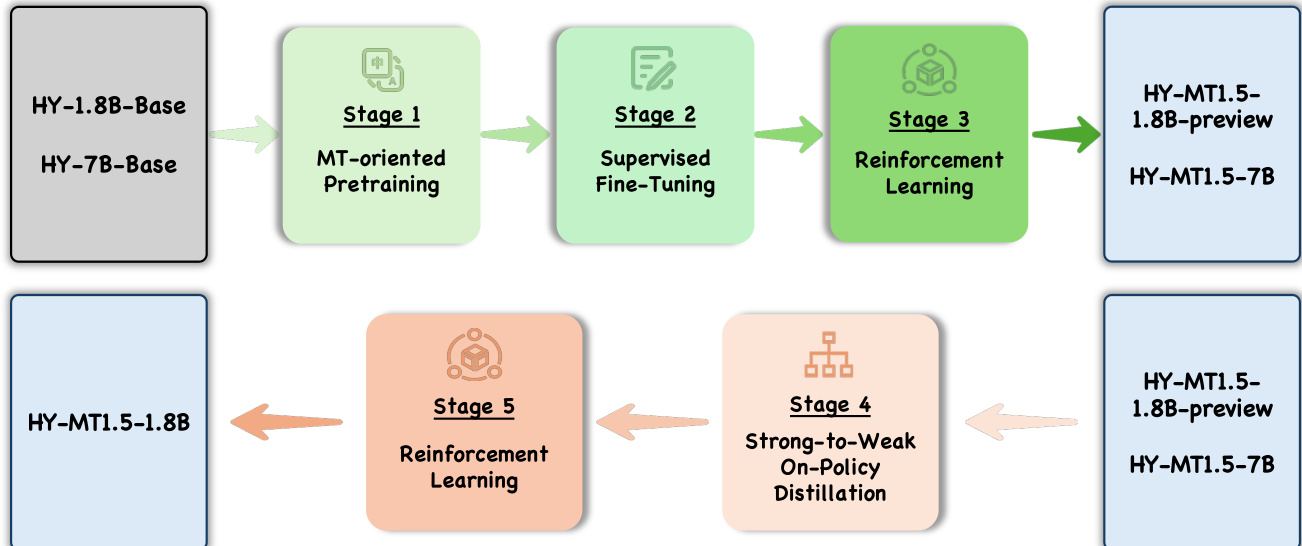
Following the initial stages, the framework proceeds to Stage 4, Strong-to-Weak On-Policy Distillation, where the fully trained HY-MT1.5-7B model serves as the teacher to guide the smaller HY-MT1.5-1.8B-preview model. This stage employs per-token reverse KL divergence to align the student’s output distribution with that of the teacher, enabling the 1.8B model to inherit the superior translation capabilities of the 7B model. The distillation process utilizes approximately one million monolingual samples across 33 supported languages, including minority languages and dialects. After distillation, the model undergoes a final Reinforcement Learning (Stage 5) phase, which further refines translation quality by aligning the model with human preferences.
The Reinforcement Learning stage employs the GRPO (Group Relative Policy Optimization) algorithm, which updates the policy based on relative comparisons within groups of outputs, enhancing training stability. To improve reward modeling, a Rubrics-based Evaluation System is introduced, where an LLM-based evaluator scores translations across five dimensions: Accuracy, Fluency, Consistency, Cultural Appropriateness, and Readability. Each dimension is assigned specific scoring standards and weights, and the aggregated scores form the final reward signal, providing fine-grained feedback to guide the model’s optimization. This multi-dimensional evaluation enables the model to improve across multiple facets simultaneously, resulting in translations that are accurate, natural, coherent, and culturally appropriate.
Experiment
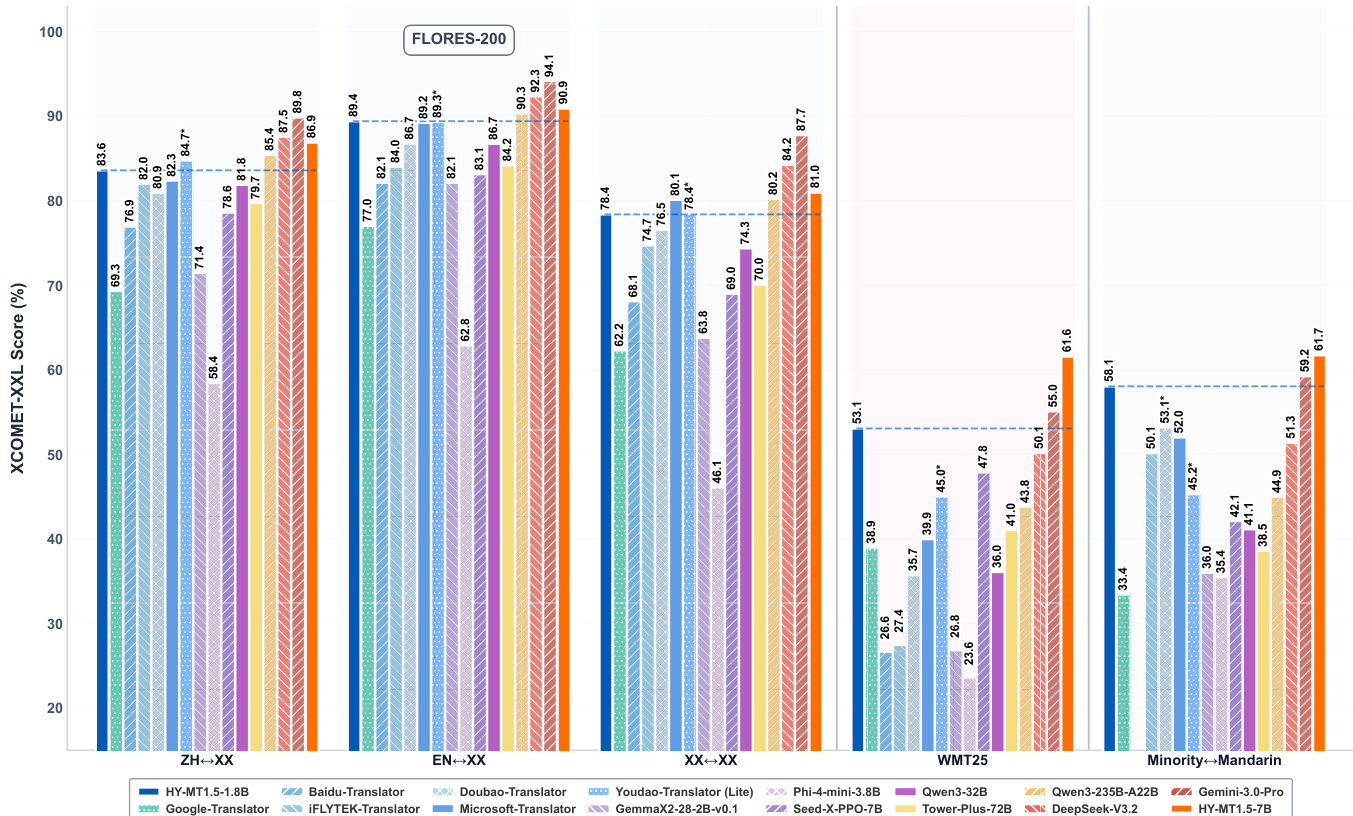
- HY-MT1.5-1.8B and HY-MT1.5-7B validated via Flores-200, WMT25, and Mandarin-minority benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art performance for their sizes; HY-MT1.5-7B surpasses Gemini-3.0-Pro on WMT25 (XCOMET-XXL 0.6159 vs 0.5505) and Mandarin-minority translation (0.6174 vs 0.5921), while HY-MT1.5-1.8B outperforms larger open-source and commercial models like Tower-Plus-72B and Doubao Translator.
- Human evaluation confirms HY-MT1.5-1.8B leads commercial systems in Chinese-English translation (avg. score 2.74), aligning with automatic metrics.
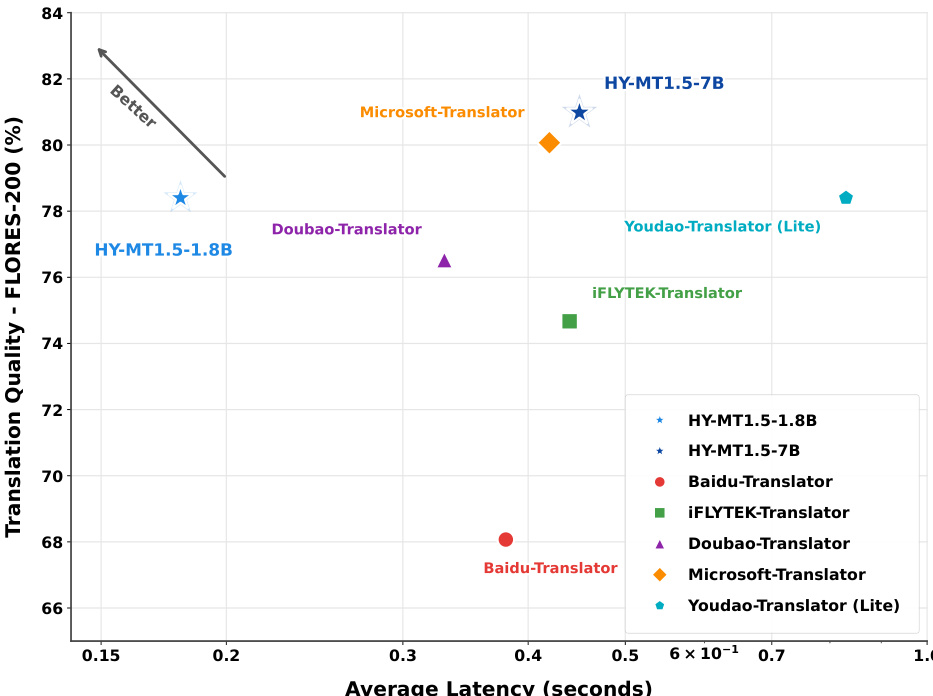
- Efficiency tests show HY-MT1.5-1.8B delivers 78% Flores-200 quality in 0.18s, ideal for real-time use; HY-MT1.5-7B offers >80% quality in 0.45s, outperforming Microsoft Translator in quality at similar speed.
- Quantization experiments reveal FP8 preserves near-original accuracy (e.g., ZH↔XX XCOMET-XXL 0.8379 vs 0.8361), while Int4 incurs noticeable degradation, supporting edge deployment via FP8.
The authors use the HY-MT1.5-1.8B and HY-MT1.5-7B models to evaluate translation performance across multiple benchmarks, including Flores-200, WMT25, and Mandarin-minority language pairs. Results show that HY-MT1.5-7B achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models on WMT25 and Mandarin-minority translation, outperforming larger models like Tower-Plus-72B and Gemini 3.0 Pro, while HY-MT1.5-1.8B demonstrates strong efficiency with competitive quality and fast inference speeds.
The authors use the HY-MT1.5-1.8B and HY-MT1.5-7B models to evaluate translation quality and efficiency, with results showing that HY-MT1.5-1.8B achieves high translation quality at low latency, while HY-MT1.5-7B offers superior quality with a moderate increase in response time. The models outperform several commercial and open-source baselines, demonstrating a strong balance between performance and speed.
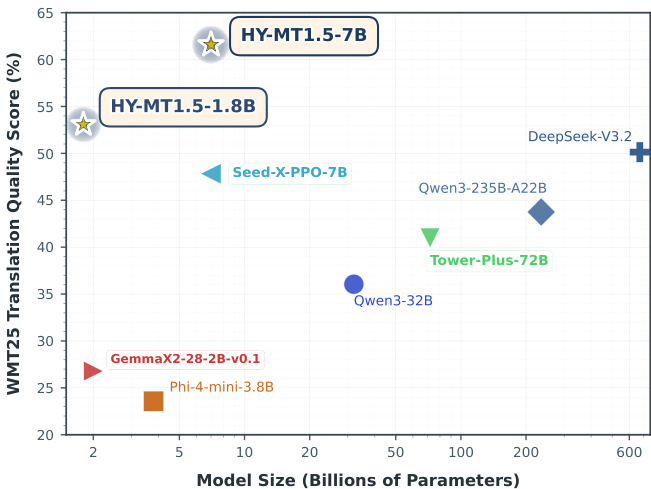
Results show that HY-MT1.5-7B achieves a WMT25 translation quality score of 61.59%, significantly outperforming all compared models across all baseline categories, including ultra-large general models like Gemini 3.0 Pro and translation-specialized models such as Tower-Plus-72B. The smaller HY-MT1.5-1.8B model also demonstrates strong performance with a WMT25 score of 53.08%, surpassing many medium to small-sized general and translation-specialized models.
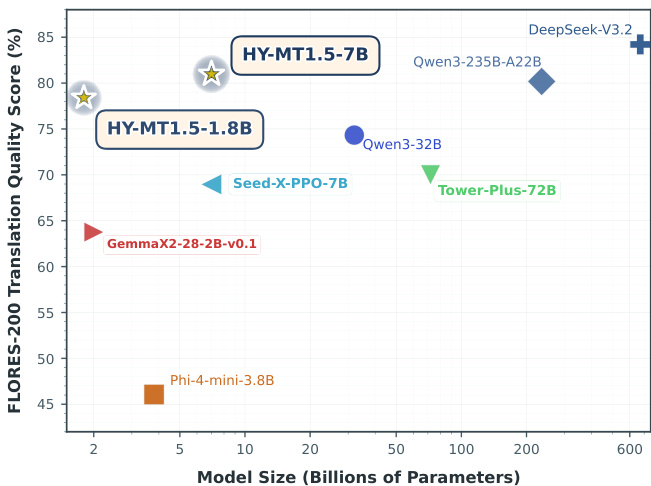
Results show that HY-MT1.5-1.8B achieves a FLORES-200 translation quality score of approximately 78% with a model size of 1.8 billion parameters, demonstrating high parameter efficiency. HY-MT1.5-7B achieves a higher score of around 86% with 7 billion parameters, outperforming larger models such as Qwen3-32B and Tower-Plus-72B while maintaining competitive performance relative to ultra-large models like DeepSeek-V3.2.
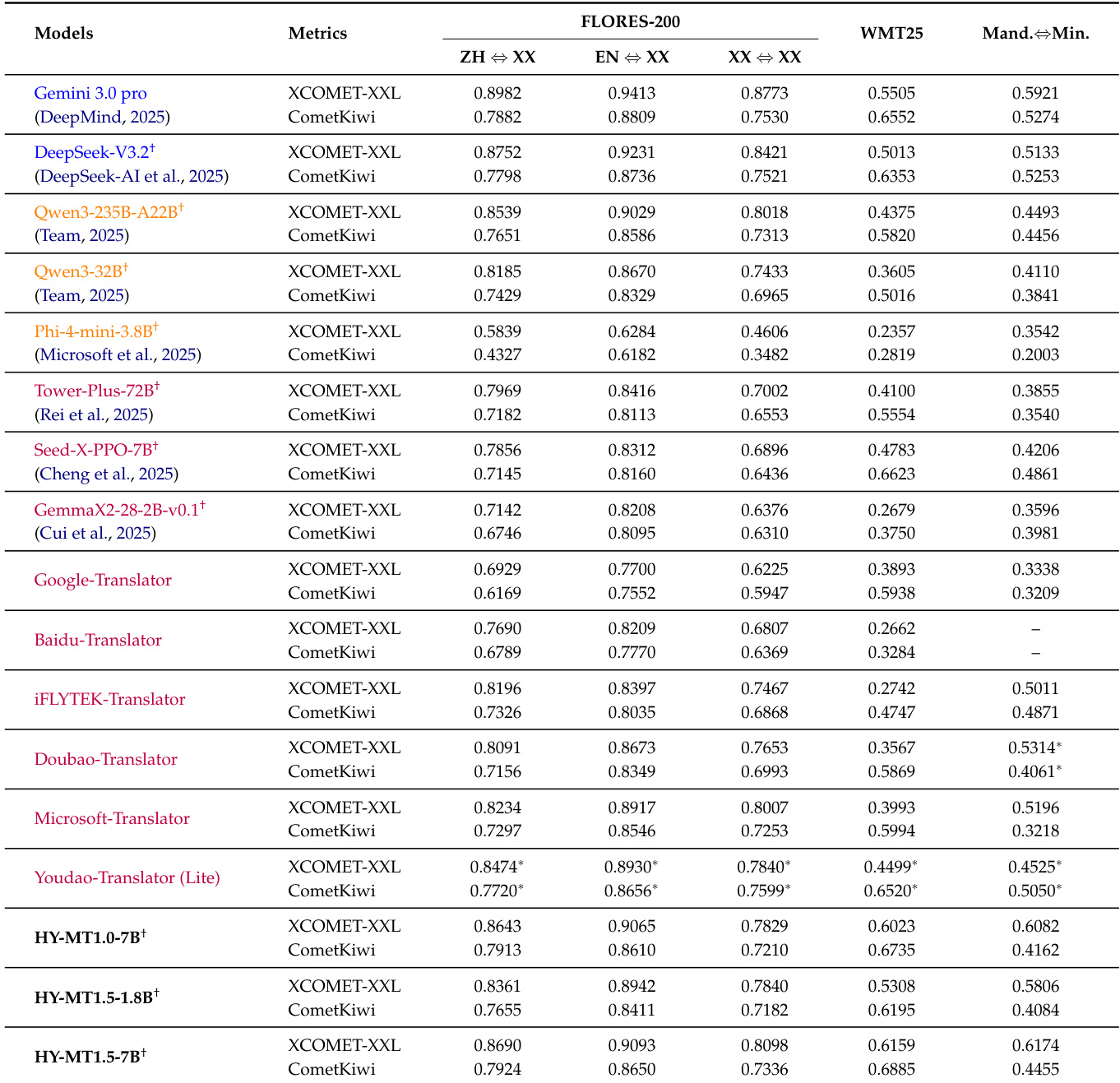
The authors use the table to compare the performance of HY-MT1.5 models against various baselines on Flores-200 and WMT25 benchmarks, showing that HY-MT1.5-7B achieves high scores across all translation directions, outperforming most models including larger ones like Tower-Plus-72B and Gemini 3.0 Pro. Results show that HY-MT1.5-1.8B also performs competitively, particularly on WMT25, where it surpasses many medium and small-sized models despite its smaller size.