Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
WeDLM : Réconcilier les modèles de langage par diffusion avec l'attention causale standard pour une inférence rapide
WeDLM : Réconcilier les modèles de langage par diffusion avec l'attention causale standard pour une inférence rapide
Aiwei Liu Minghua He Shaoxun Zeng Sijun Zhang Linhao Zhang Chuhan Wu Wei Jia Yuan Liu Xiao Zhou Jie Zhou
Résumé
La génération autoregressive (AR) constitue le paradigme standard de décodage pour les grands modèles linguistiques (LLM), mais sa nature token par token limite la parallélisation au moment de l’inférence. Les modèles linguistiques à diffusion (DLLM) permettent un décodage parallèle en récupérant plusieurs tokens masqués à chaque étape ; toutefois, en pratique, ils peinent souvent à transformer cette parallélisation en gains de vitesse réels par rapport aux moteurs AR optimisés (par exemple, vLLM). Une cause majeure réside dans le fait que de nombreux DLLM reposent sur une attention bidirectionnelle, qui rompt le mécanisme classique de mise en cache préfixe des vecteurs KV et contraint une contextualisation répétée, compromettant ainsi l’efficacité. Nous proposons WeDLM, un cadre de décodage par diffusion entièrement fondé sur une attention causale standard, afin de rendre la génération parallèle compatible avec le cache préfixe. L'idée centrale consiste à permettre à chaque position masquée de conditionner sur tous les tokens actuellement observés, tout en maintenant un masque causal strict, grâce à une réorganisation topologique qui déplace les tokens observés vers la partie physique du préfixe tout en préservant leurs positions logiques. En s'appuyant sur cette propriété, nous introduisons une procédure de décodage en flux (streaming) qui intègre continuellement les tokens les plus fiables à un préfixe croissant de gauche à droite, tout en maintenant une charge de travail parallèle fixe, évitant ainsi le comportement « stop-and-wait » fréquent dans les méthodes de diffusion par blocs. Les expériences montrent que WeDLM préserve la qualité des modèles AR de référence performants tout en offrant des accélérations substantielles, atteignant près de 3× sur des benchmarks exigeants en raisonnement et jusqu’à 10× dans des régimes de génération à faible entropie ; de manière cruciale, nos comparaisons sont effectuées contre des baselines AR servies par vLLM dans des conditions de déploiement identiques, démontrant ainsi que le décodage de type diffusion peut surpasser en pratique un moteur AR optimisé.
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from WeChat AI, Tencent, Peking University, and Tsinghua University propose WeDLM, a diffusion-based decoder using causal attention and topological reordering to enable prefix-caching and streaming decoding, achieving up to 10× speedups over vLLM-optimized AR models while preserving quality.
Key Contributions
- WeDLM introduces a diffusion decoding framework using only causal attention, enabling prefix KV caching by reordering observed tokens to the physical prefix while preserving their logical positions via Topological Reordering, thus avoiding the repeated contextualization that plagues bidirectional diffusion models.
- It implements a streaming decoding procedure that incrementally commits confident tokens into a growing left-to-right prefix and maintains fixed parallel workload per step, eliminating the stop-and-wait inefficiency common in block diffusion methods and aligning with optimized AR inference engines.
- Experiments show WeDLM matches strong AR baselines in quality while achieving up to 3× speedup on reasoning tasks and 10× in low-entropy regimes, with direct comparisons against vLLM-optimized AR models under identical deployment conditions, proving practical gains over state-of-the-art AR serving.
Introduction
The authors leverage diffusion language models to enable fast, parallel inference while preserving standard causal attention—avoiding the bidirectional attention typically used in masked diffusion models. Prior work relied on bidirectional context for mask recovery, which impedes efficient decoding and complicates integration with existing autoregressive infrastructure. The authors’ main contribution is a novel framework, WeDLM, that achieves parallel decoding under causal attention by enforcing two algorithmic principles: topological reordering of tokens and position-aware masking, enabling compatibility with KV caching and existing AR systems without architectural overhaul.
Method
The authors leverage a novel diffusion decoding framework called WeDLM, which is designed to reconcile parallel token generation with the efficiency constraints of industrial-grade autoregressive inference engines. The core innovation lies in enforcing strict causal attention throughout both training and inference, thereby enabling seamless integration with standard KV caching mechanisms such as FlashAttention and PagedAttention. This is achieved through two key components: Topological Reordering for training and Streaming Parallel Decoding for inference.
During training, WeDLM employs Topological Reordering to ensure that masked tokens can access the full context of observed tokens while operating under a standard causal mask. As shown in the figure below, the input sequence is first masked at random positions. Then, all observed tokens are physically moved to the front of the sequence, while masked tokens are placed at the end. Crucially, logical position IDs (e.g., via RoPE) are preserved, allowing attention scores to reflect true positional relationships rather than physical indices. This reordering enables each masked token to attend to all observed tokens under a causal mask, satisfying the requirement for global context visibility without bidirectional attention.

To bridge the training-inference gap induced by prefix-conditioned decoding, the authors introduce Dual-Stream Masking. This strategy constructs two parallel streams: a clean Memory Stream and a masked Prediction Stream, both sharing the same logical position IDs. The Prediction Stream is partitioned into blocks, each of which undergoes intra-block topological reordering. The attention mask is carefully designed so that tokens in the Prediction Stream can attend to clean context from the Memory Stream for preceding blocks, while within a block, attention follows standard causal masking. This mimics the inference setting where earlier tokens are already committed and serve as clean context, reducing distributional mismatch.
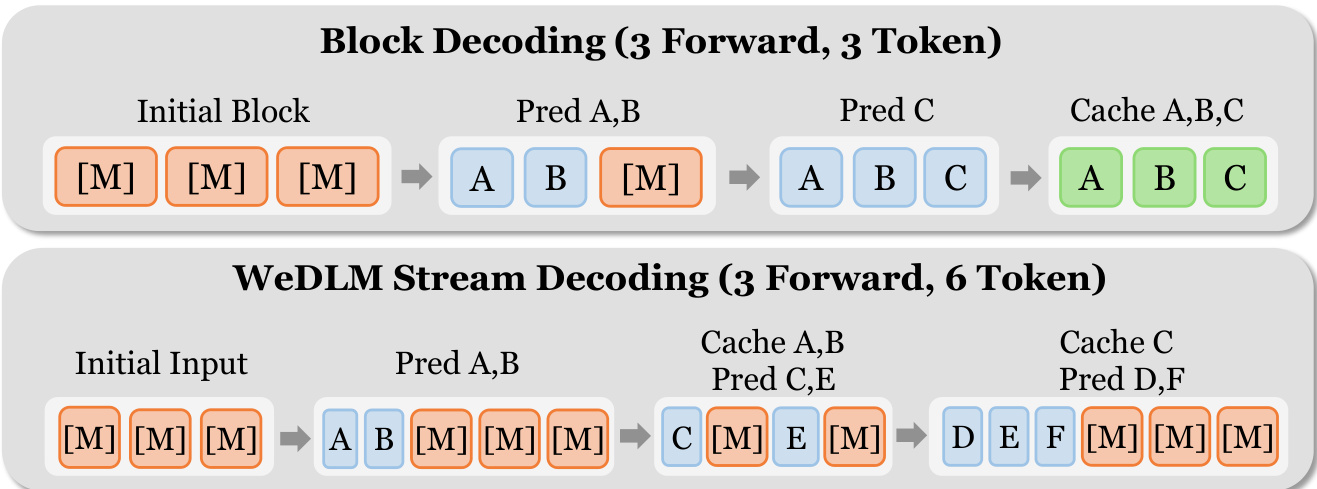
For inference, WeDLM implements Streaming Parallel Decoding, a procedure that continuously commits confident tokens into a growing left-to-right prefix while maintaining a fixed parallel workload. The algorithm operates on a sliding window of fixed size W, containing a mix of filled (predicted) and masked tokens. At each step, the window is reordered to place filled tokens before masks, preserving logical positions. A causal forward pass is then executed over the window, conditioned on the persistent KV cache. The leftmost contiguous filled prefix is immediately committed to the cache, as its KV states depend only on earlier tokens under the causal mask. New mask tokens are appended to refill the window, avoiding the stop-and-wait behavior of block-wise methods.
Refer to the framework diagram comparing block decoding with WeDLM’s streaming approach. Block decoding requires the entire block to be finalized before any token can be cached, leading to pipeline bubbles. In contrast, WeDLM’s streaming method commits tokens as soon as they are resolved, enabling continuous parallel prediction. The authors further enhance left-to-right growth by applying a distance-penalized entropy selection rule, which prioritizes earlier positions for prediction, thereby maximizing prefix cacheability pcache.
Experiment
- WeDLM consistently matches or exceeds its autoregressive base models in generation quality, especially on reasoning and code tasks, while significantly outperforming prior diffusion language models.
- Instruct-tuned WeDLM models show strong gains over AR baselines on complex reasoning and coding benchmarks, confirming compatibility with instruction tuning and potential for performance amplification.
- Inference efficiency is highly tunable: streaming decoding and left-position biasing improve speed via better prefix caching, with flexible trade-offs between accuracy and throughput.
- Ablation studies reveal robustness to block size, superiority of causal intra-block attention for caching and performance, and stronger adaptation gains in larger base models.
- Generation speed varies sharply by task entropy: deterministic or structured tasks enable 8x+ speedups, while high-entropy open-ended generation shows limited acceleration, highlighting a key area for future improvement.
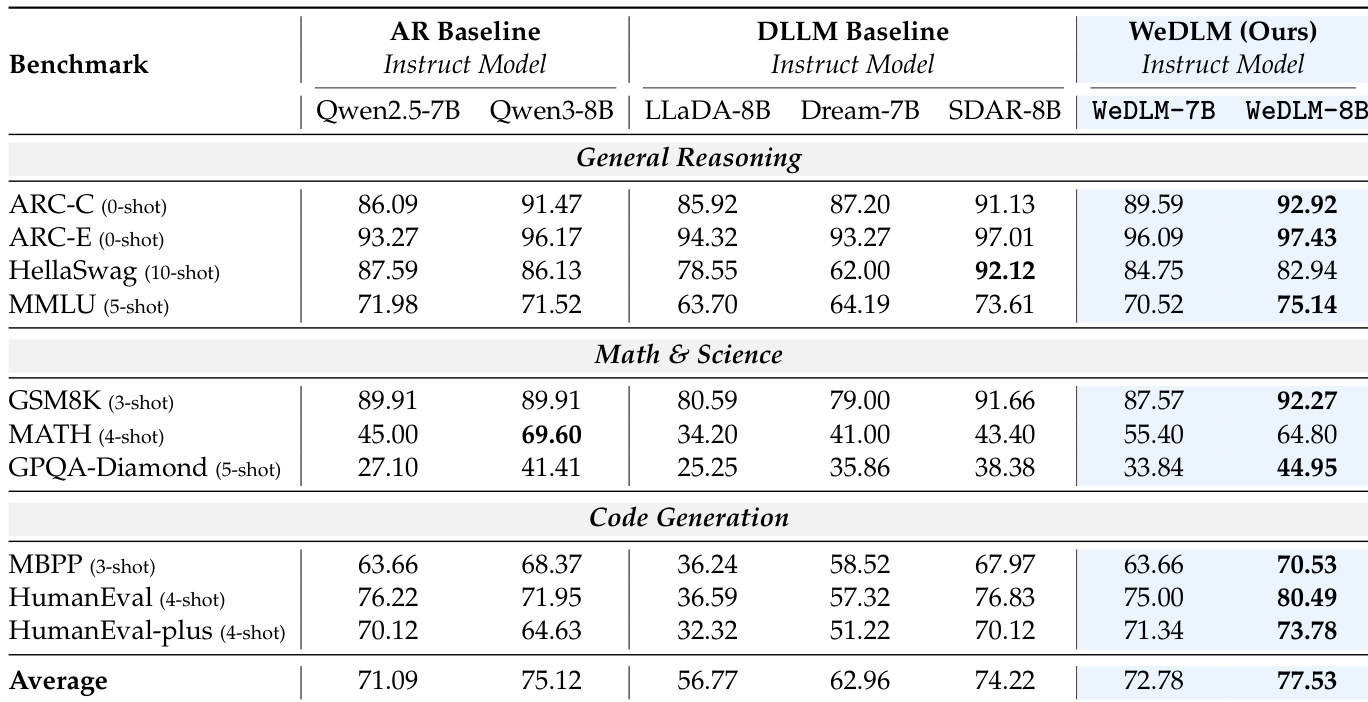
The authors use WeDLM to enhance base autoregressive models, achieving higher average scores than both their AR counterparts and prior diffusion language models across reasoning, math, and code benchmarks. Results show consistent gains in math and code tasks, with WeDLM-8B outperforming all compared models in several high-difficulty categories, while maintaining competitive performance in general reasoning. The method demonstrates that diffusion-style training can preserve and even improve upon the capabilities of strong AR checkpoints without compromising inference efficiency.

The authors use WeDLM to enhance autoregressive base models through diffusion-style training and parallel decoding, achieving consistent gains over both AR and diffusion baselines on reasoning and code generation tasks. Results show that WeDLM-8B-Instruct outperforms its AR counterpart and all compared diffusion models, particularly on challenging benchmarks like GPQA-Diamond and HumanEval, while maintaining flexibility in speed-accuracy trade-offs during inference. The method demonstrates that diffusion objectives can complement instruction tuning without compromising performance, especially when starting from strong base models.