Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
SmartSnap : Recherche proactive de preuves pour des agents auto-vérifiants
SmartSnap : Recherche proactive de preuves pour des agents auto-vérifiants
Résumé
L'apprentissage par renforcement agencent (agentic RL) présente un potentiel considérable pour le développement d'agents autonomes dans des tâches complexes sur des interfaces graphiques utilisateur (GUI), mais sa scalabilité est fortement freinée par le problème de vérification de la réussite des tâches. La vérification des tâches existante est actuellement traitée comme un processus passif et post-hoc : un vérificateur (c’est-à-dire un script de notation basé sur des règles, une fonction de récompense ou un modèle critique, ou encore un LLM en tant que juge) analyse l’ensemble de la trajectoire d’interaction de l’agent afin de déterminer s’il a réussi. Ce traitement d’un contexte verbeux, contenant des historiques irrélevants et bruités, pose de sérieux défis aux protocoles de vérification, entraînant des coûts prohibitifs et une fiabilité faible. Pour surmonter ce goulot d’étranglement, nous proposons SmartSnap, un changement de paradigme qui passe d’une vérification passive et post-hoc à une auto-vérification proactive et en temps réel, effectuée directement par l’agent lui-même. Nous introduisons l’agent auto-vérifiant, un nouveau type d’agent conçu avec deux missions : non seulement accomplir une tâche, mais aussi prouver sa réussite à l’aide de preuves ciblées sous forme de captures d’écran (snapshots). Guidé par nos principes 3C (Complétude, Concision, Créativité), l’agent exploite son accès à l’environnement en ligne pour effectuer une auto-vérification sur un ensemble minimal et décisif de captures. Ces preuves servent de matériel exclusif à un vérificateur LLM généraliste (LLM en tant que juge) pour évaluer leur validité et leur pertinence. Des expériences menées sur des tâches mobiles, sur plusieurs familles et tailles de modèles, démontrent que notre paradigme SmartSnap permet d’entraîner des agents pilotés par LLM de manière scalable, offrant des gains de performance allant jusqu’à 26,08 % et 16,66 % respectivement pour les modèles de 8B et 30B de paramètres. La synergie entre la recherche de solutions et la collecte de preuves favorise ainsi le développement d’agents efficaces, capables d’auto-vérification, dont les performances sont compétitives par rapport à DeepSeek V3.1 et Qwen3-235B-A22B.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Tencent Youtu Lab and Peking University propose SmartSnap, a paradigm shift in agentic reinforcement learning that enables LLM-driven agents to proactively curate minimal, decisive snapshot evidences—guided by Completeness, Conciseness, and Creativity principles—enabling efficient, reliable self-verification and achieving up to 26.08% performance gains over 8B models on Android tasks, with competitive results against larger models like Qwen3-235B-A22B.
Key Contributions
-
We introduce SmartSnap, a paradigm shift from passive, post-hoc verification to proactive, in-situ self-verification, where the agent autonomously curates minimal, decisive evidence snapshots to prove task completion, significantly improving scalability and reliability in GUI-based agentic reinforcement learning.
-
Guided by the 3C Principles—Completeness, Conciseness, and Creativity—the Self-Verifying Agent learns to generate high-quality evidence sets that are both sufficient and compact, enabling efficient evaluation by a general LLM-as-a-Judge verifier without relying on verbose or noisy full trajectories.
-
Experiments on the AndroidLab benchmark show that SmartSnap boosts task success rates by up to 26.08% and 16.66% for 8B and 30B models respectively, outperforming strong baselines like DeepSeek V3.1 and Qwen3-235B-A22B, while reducing verification costs through intrinsic reward shaping and structured feedback.
Introduction
The authors address a critical challenge in agentic reinforcement learning: the scalability bottleneck caused by inefficient and unreliable post-hoc verification of task completion in complex GUI environments. Prior approaches rely on passive verification, where a verifier—such as a rule-based system, reward model, or LLM-as-a-Judge—analyzes full interaction trajectories, leading to high computational costs and reduced reliability due to noisy, irrelevant context. To overcome this, the authors introduce SmartSnap, a paradigm shift toward proactive, in-situ self-verification by the agent itself. The core contribution is the Self-Verifying Agent, which operates under the 3C Principles—Completeness, Conciseness, and Creativity—to autonomously collect minimal, decisive snapshot evidence during task execution. This curated evidence is then used by a general LLM-as-a-Judge for fast, reliable validation. Experiments on mobile tasks show significant performance gains—up to 26.08% and 16.66% for 8B and 30B models—demonstrating scalable, efficient training with improved success rates and competitive performance against large models like DeepSeek V3.1 and Qwen3-235B-A22B.
Dataset
- The dataset is derived from AndroidLab, a reproducible benchmark with 138 tasks across nine Android apps, each running on predefined Android Virtual Devices (AVDs).
- Only the predefined tasks and their initial environments are used, excluding AndroidLab’s rule-based evaluation system to enable the Self-Verifying paradigm.
- The observation space uses compressed XML tree representations instead of screenshots, emphasizing planning and decision-making over visual perception.
- The action space includes native AndroidLab actions: Tap, Swipe, Type, Long Press, Home, Back, plus a custom submit tool for evidence snapshots.
- For training, the authors replicate the 726 tasks from the Android Instruct dataset to ensure comparability across experiments.
- The supervised fine-tuning (SFT) dataset is built using a rollout framework based on the VeRL agent loop, with two large language models—DeepSeek V3.1 and Qwen3-235B-A22B—generating trajectories across all 726 tasks.
- Trajectories are collected with both task completion and evidence submission, ensuring diverse and high-quality data.
- Original Android Instruct responses are updated with outputs from the two LLM agents, resulting in approximately 550K trainable QA pairs from 30K trajectories.
- A random subset of 100K QA pairs is selected as the cold-start dataset for initial training.
- Task distribution statistics are detailed in Table 1, which provides breakdowns across apps and task types.
Method
The authors leverage a self-verifying agent framework, formalized as an augmented Markov Decision Process, to address the challenge of reliable task completion in interactive environments. The agent operates within an environment modeled as a tuple M=(S,A′,P), where the augmented action space A′ is the union of execution actions Aexec (e.g., click, type) and curation actions Acurate (e.g., submit). The agent's policy πθ maps the history of observations, actions, and the task instruction I to a probability distribution over A′. The agent's trajectory terminates when it selects a terminal action from Acurate, such as submit('text', E), where text is a final message and E is the curated evidence set. This evidence is not a self-declared summary but a set of integer indices pointing to critical interaction pairs from the agent's history. 
The core of the SmartSnap framework lies in the grounding of evidence in tool interactions. The authors define a single piece of evidence, an exhibit, as an atomic tuple (at,st+1), representing a direct cause-and-effect event between a tool call at and its immediate observation st+1. This definition ensures the evidence is an objective, unalterable fact, contrasting with the untrustworthy nature of self-declared summaries. The agent's learning objective is to select a minimal yet decisive evidence set E from its full interaction history. This curated evidence is then programmatically formatted using the OpenAI chat template, resulting in a string representation that is fed to the verifier. 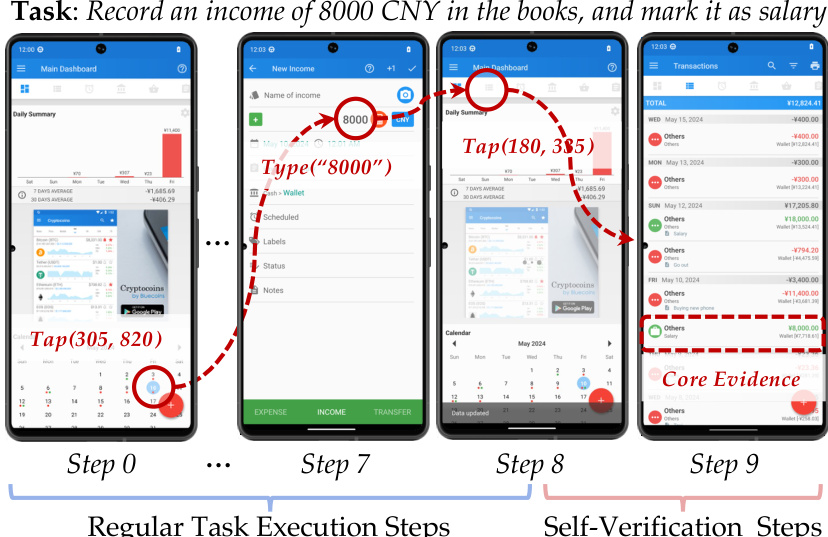
To guide the agent's evidence curation behavior, the authors formalize the 3C Principles: Completeness, Conciseness, and Creativity. These principles are embedded as meta-instructions in the agent's system prompt. Completeness requires the agent to include all pivotal tool interactions to maximize the True Positive rate of the verifier, ensuring a correctly executed task is not penalized. Conciseness aims to minimize the False Positive rate by reducing redundant information, which is crucial for the verifier's efficiency and robustness, mitigating risks like context rot. Creativity encourages the agent to take additional, evidence-oriented actions if necessary, transforming it from a passive historian into a proactive investigator. This principle allows the agent to create evidence by inspecting the environment for indirect consequences of its actions, thereby achieving a more robust and comprehensive proof of task completion. 
The evidence verification and reward shaping process is designed to provide dense, structured feedback. A multi-component reward function Rtotal is constructed from four components: Rformat penalizes formatting errors; Rvalidity rewards relevant evidence; Rcomplete is a binary reward based on a rigorous "success only upon unequivocal proof" rule, which includes checks for zero assumptions and traceable reasoning; and Rconcise penalizes the size of the evidence set. This composite reward function guides the agent's end-to-end learning. The authors adopt Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) as the learning algorithm, which eliminates the need for a separate critic network by computing the advantage function relative to a group of trajectories sampled from the same policy. This approach reduces training cost and memory overhead. 
Experiment
- SmartSnap introduces a self-verifying agent paradigm that integrates task execution and evidence curation, significantly improving performance on AndroidLab across model families and scales without relying on rule-based verifiers or task-specific reward models.
- On AndroidLab with XML mode, SmartSnap (Qwen3-8B-Instruct) and SmartSnap (Qwen3-32B-Instruct) achieve on-par success rates with DeepSeek-V3.1 and Qwen3-235B-A22B, respectively, demonstrating strong generalization across model sizes.
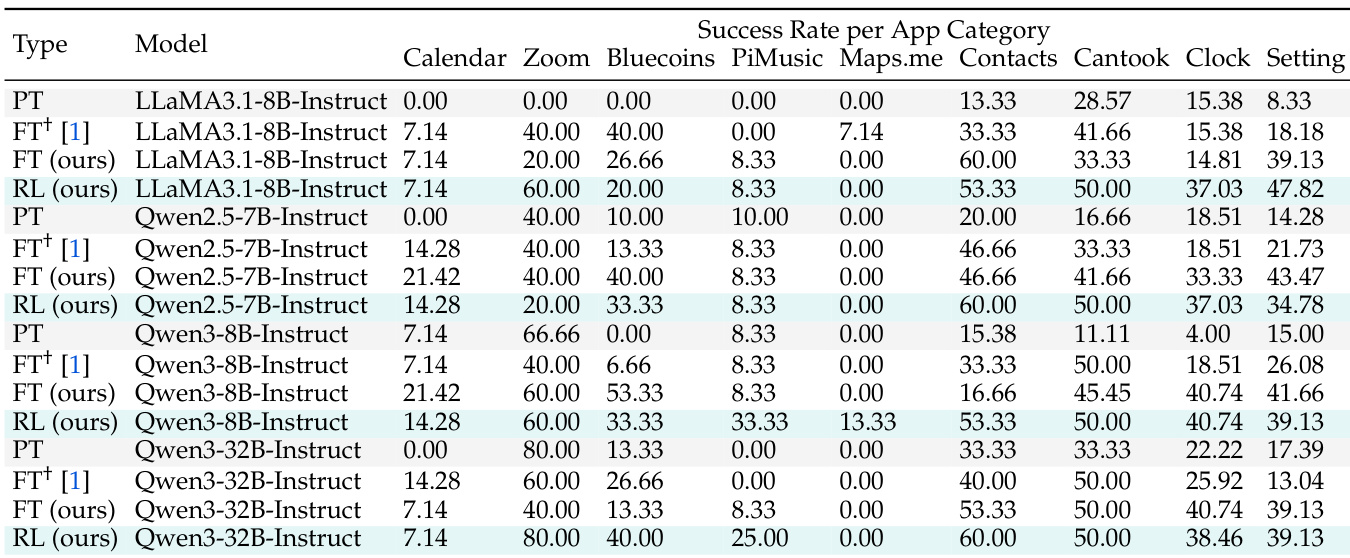
- All models under investigation show performance gains exceeding 16% over vanilla prompting and fine-tuning, with consistent improvements across most app categories except Maps.me, where a knowledge gap limits progress.
- Self-verification enables agents to curate minimal, high-quality evidence sets—averaging 1.5 evidences per task—leading to more efficient, compact interactions and reduced reliance on trial-and-error.
- Reinforcement learning under SmartSnap consistently increases training rewards and validation accuracy, with decreasing interaction turns and response lengths, indicating improved task efficiency and policy refinement.
- Case studies show agents learn to correct misinterpretations of UI elements, discover optimal paths (e.g., using floating buttons or search), and submit decisive evidence, demonstrating enhanced problem decomposition and self-verification capabilities.
- Performance stagnation on complex domains like Calendar, Maps.me, and Zoom highlights the need for domain-specific knowledge injection via continual pre-training and larger, balanced training datasets.
The authors use SmartSnap to enhance the performance of LLM-driven agents on AndroidLab, achieving significant improvements in success rate across various app categories and model scales. Results show that the proposed self-verifying paradigm, particularly through reinforcement learning, enables agents to complete tasks more efficiently and generate concise, relevant evidence, leading to higher success rates compared to vanilla prompting and fine-tuning methods.
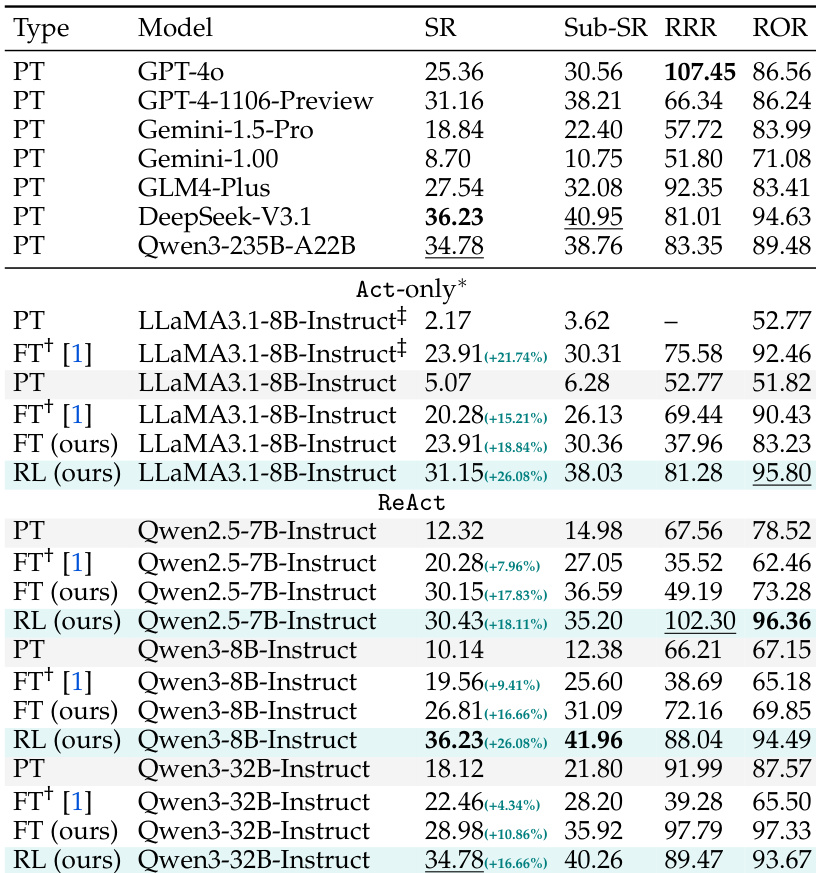
The authors use SmartSnap to enhance the performance of LLM-driven agents on AndroidLab, achieving significant improvements in success rate and evidence curation through reinforcement learning. Results show that the proposed method consistently outperforms vanilla prompting and fine-tuning across various model families and scales, with the best results obtained using the ReAct mode and Qwen3-32B-Instruct.
The authors analyze the distribution of tasks across app categories in the AndroidLab benchmark, showing that the training set is heavily dominated by tasks from the Settings app (31.26%), while the Validation set includes a more balanced distribution with notable representation from Calendar, Bluecoins, and Contacts. This imbalance suggests that model performance may be particularly influenced by the overrepresentation of certain app domains in the training data.

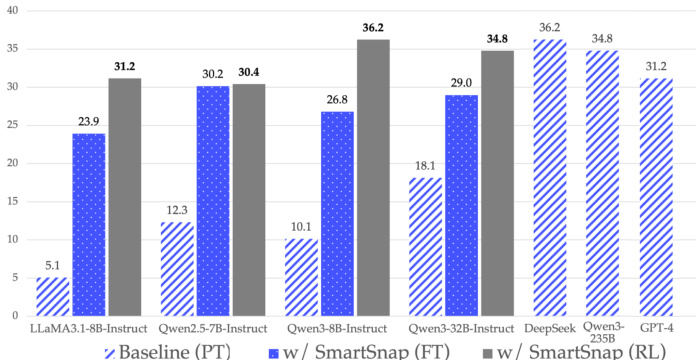
The authors use SmartSnap to enhance the performance of LLM-driven agents on AndroidLab, achieving significant improvements in success rate across various model families and scales. Results show that both fine-tuning and reinforcement learning with SmartSnap lead to substantial gains, with models like Qwen3-32B-Instruct and Qwen3-235B-A22B reaching performance comparable to larger models such as DeepSeek-V3.1 and GPT-4.