Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
InfiniteVL : Synergie entre l'attention linéaire et l'attention creuse pour des modèles vision-langage à entrée illimitée et très efficaces
InfiniteVL : Synergie entre l'attention linéaire et l'attention creuse pour des modèles vision-langage à entrée illimitée et très efficaces
Hongyuan Tao Bencheng Liao Shaoyu Chen Haoran Yin Qian Zhang Wenyu Liu Xinggang Wang
Résumé
L’attention en fenêtre et l’attention linéaire représentent deux stratégies principales visant à atténuer la complexité quadratique et la croissance continue de la mémoire tampon des paires (KV cache) dans les modèles vision-langage (VLM). Toutefois, nous observons que les VLM basés sur des fenêtres subissent une dégradation des performances lorsque la longueur de la séquence dépasse la taille de la fenêtre, tandis que l’attention linéaire se montre moins efficace sur des tâches riches en informations telles que la reconnaissance optique de caractères (OCR) ou l’analyse de documents. Pour surmonter ces limitations, nous proposons InfiniteVL, une architecture VLM à complexité linéaire qui combine de manière synergique l’attention en fenêtre glissante (SWA) avec un Gated DeltaNet. Afin d’obtenir des performances multimodales compétitives sous contraintes de ressources, nous avons conçu une stratégie d’entraînement en trois étapes : pré-entraînement par distillation, ajustement par instruction et fine-tuning sur séquences longues (SFT). De manière remarquable, en utilisant moins de 2 % des données d’entraînement nécessaires aux VLM leaders, InfiniteVL dépasse non seulement les VLM précédents à complexité linéaire, mais atteint également les performances des meilleurs VLM basés sur les Transformers, tout en démontrant une rétention efficace de la mémoire à long terme. Par rapport aux VLM basés sur les Transformers de taille similaire accélérés par FlashAttention-2, InfiniteVL réalise une accélération d’inférence supérieure à 3,6 fois, tout en maintenant une latence et une empreinte mémoire constantes. Dans les scénarios d’analyse vidéo en flux continu, il maintient une vitesse stable de pré-remplissage en temps réel de 24 FPS tout en préservant la mémoire tampon de mémoire à long terme. Le code et les modèles sont disponibles à l’adresse suivante : https://github.com/hustvl/InfiniteVL.
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from Huazhong University of Science and Technology and Horizon Robotics propose InfiniteVL, a linear-complexity VLM combining sliding window attention with Gated DeltaNet to overcome limitations of prior attention mechanisms. Using a three-stage training strategy, InfiniteVL matches Transformer-based VLM performance with under 2% of their training data, achieves over 3.6× faster inference than FlashAttention-2-accelerated models, and sustains real-time 24 FPS streaming with constant memory, enabling efficient long-sequence and video understanding.
Key Contributions
- We introduce InfiniteVL, a linear-complexity Vision-Language Model that combines sliding window attention with Gated DeltaNet to address the inefficiency of traditional attention mechanisms, enabling efficient long-context modeling without external memory reliance.
- The model leverages distillation pretraining and a three-stage training pipeline involving instruction tuning and long-sequence SFT to achieve strong performance while maintaining efficiency, outperforming existing methods in long-sequence understanding.
- Experiments show that InfiniteVL not only matches but exceeds the performance of state-of-the-art models in long-sequence tasks, achieving real-time performance of 24 FPS in streaming video understanding while preserving memory.
Introduction
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are critical for multimodal applications like autonomous systems and video understanding, but their scalability is limited by the Transformer architecture’s quadratic complexity in attention computation and growing key-value caches during inference. Long input sequences exacerbate computational and memory costs, especially in resource-constrained settings.
Prior approaches to scaling VLMs face trade-offs between fine-grained perception and long-range reasoning. Window-based methods discard global context beyond the window size, while linear attention models suffer from high computational demands when processing global visual contexts.
The authors propose InfiniteVL, a hybrid architecture combining Gated DeltaNet layers for long-term memory with Sliding Window Attention (SWA) to maintain performance on information-intensive tasks like OCR and document understanding, where prior methods struggle with quadratic complexity.
InfiniteVL addresses these challenges by synergizing Gated DeltaNet layers for long-term memory with Sliding Window Attention for fine-grained local modeling. This hybrid design enables efficient long-context processing while maintaining performance on information-intensive tasks.
Method
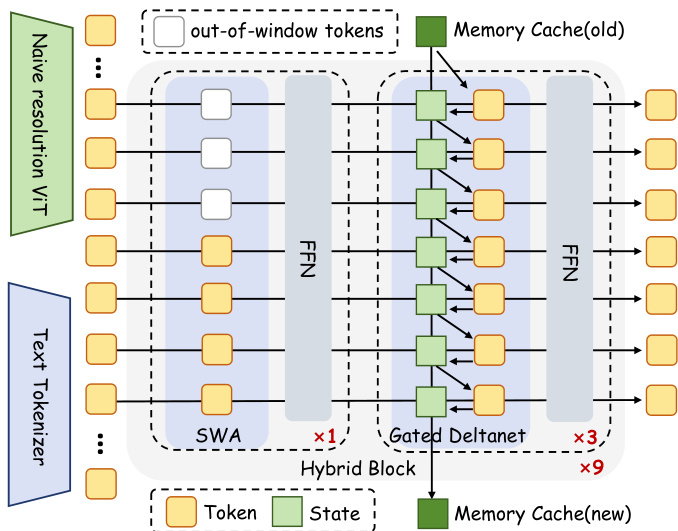
The authors leverage a hybrid architecture that combines local and global token mixing mechanisms to enable efficient, context-length-agnostic inference in multimodal settings. The framework begins by encoding visual inputs via a naïve-resolution ViT and textual inputs via a standard tokenizer, then concatenates and processes them through a stack of nine Hybrid Blocks. Each Hybrid Block is composed of one Sliding Window Attention (SWA) layer followed by three Gated DeltaNet layers, all interleaved with feed-forward networks (FFNs) and connected via residual pathways with layer normalization.
Refer to the framework diagram: the SWA layer employs grouped multi-head attention with 16 query heads and 2 key-value heads, augmented with RoPE for positional encoding. This design ensures efficient local context modeling within a fixed window size of 8192 tokens, preventing instability from long-range position extrapolation. The Gated DeltaNet layers, in contrast, operate without positional encoding or weight bias and maintain a fixed-size memory cache to capture long-range dependencies. This cache is updated via a gated, low-rank transformation that applies a Householder-like rotation to the accumulated state, formulated as:
St=St−1(αt(I−βtktkt⊤))+βtvtkt⊤,where αt and βt are learnable gating parameters that modulate memory retention and update scaling, respectively. The authors further enhance expressiveness by inserting a 1D convolution (window size 4) and an output gate within each Gated DeltaNet layer.
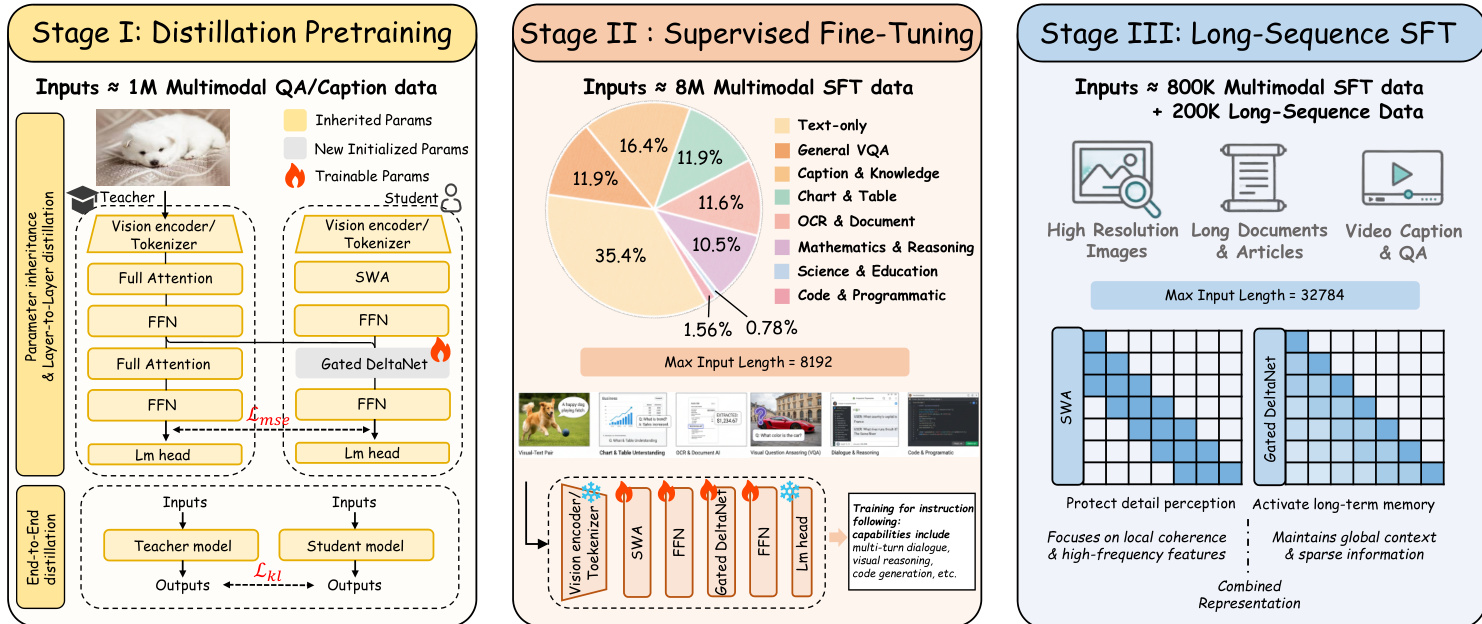
To train this architecture efficiently, the authors implement a three-stage strategy. Stage I performs layer-wise and end-to-end distillation from a full-attention teacher model (Qwen2.5-VL), replacing its attention layers with Gated DeltaNet while inheriting all other parameters. Layer-wise alignment is achieved via an MSE loss between corresponding layer outputs, followed by end-to-end distillation using KL divergence between token-level logits. Stage II applies supervised fine-tuning on a diverse multimodal instruction corpus, enhancing instruction-following and reasoning capabilities while increasing image resolution to 1344×1344. Stage III extends context length to 32,768 tokens and incorporates long-sequence data from video and document sources, trained via LoRA to focus model capacity on robust long-range modeling.
As shown in the figure below: the training pipeline transitions from parameter-efficient distillation to instruction tuning and finally to long-sequence adaptation, each stage progressively exposing the model to more complex multimodal interactions and longer contexts.
Experiment
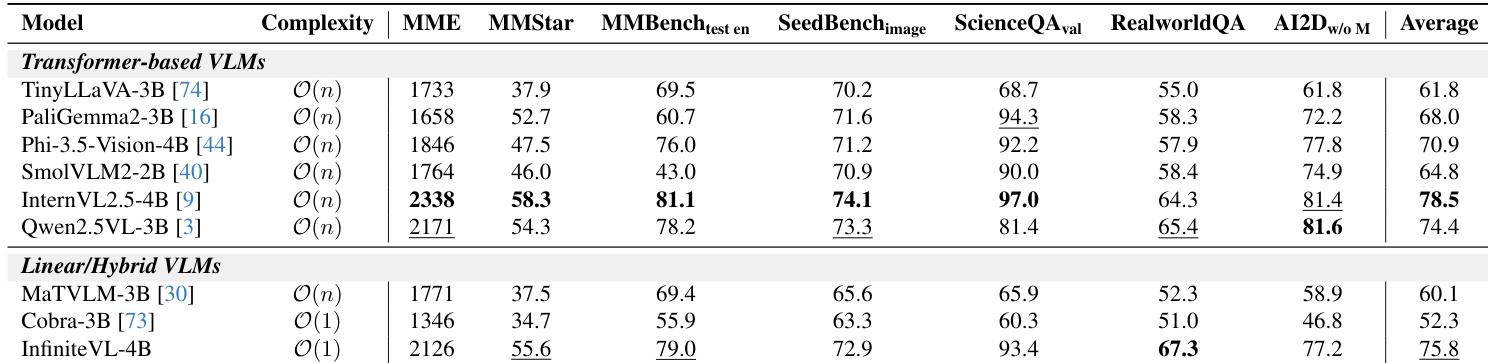
- Evaluated InfiniteVL on public multimodal benchmarks using VLMEvalKit, showing competitive performance against transformer-based and linear/hybrid VLMs. On MMBench_test en achieved 79.0, RealworldQA 67.3, and MMMU_val 44.0, ranking second among linear/hybrid models.
- Demonstrated strong performance on text-rich tasks: achieved 82.0 on ChartQA_test, 78.5 on TextVQA_val, and 91.7 on DocVQA_test, outperforming prior linear models and approaching transformer-based leaders.
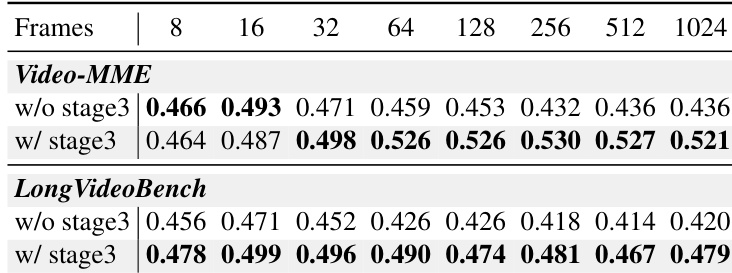
- Validated length generalization on Video-MME and LongVideoBench: at 1024 frames, InfiniteVL maintains stable comprehension and reasoning capabilities, enabling robust performance across diverse scenarios.
Results show that InfiniteVL with Stage III long-sequence fine-tuning maintains or improves performance as input frame count increases beyond 32, while the version without Stage III degrades steadily. This confirms that Stage III enhances long-context generalization, enabling stable comprehension even at ultra-long sequences up to 1024 frames.
InfiniteVL-4B, a linear/hybrid VLM with O(1) complexity, achieves competitive performance on text-rich and reasoning benchmarks, matching or exceeding larger transformer-based models in several categories including ChartQA, TextVQA, and MathVista. While it falls slightly behind Qwen2.5VL-3B in overall average score, it outperforms it in MathVista and OCRBench, demonstrating strong capability in structured and mathematical reasoning tasks despite its constant-complexity design.
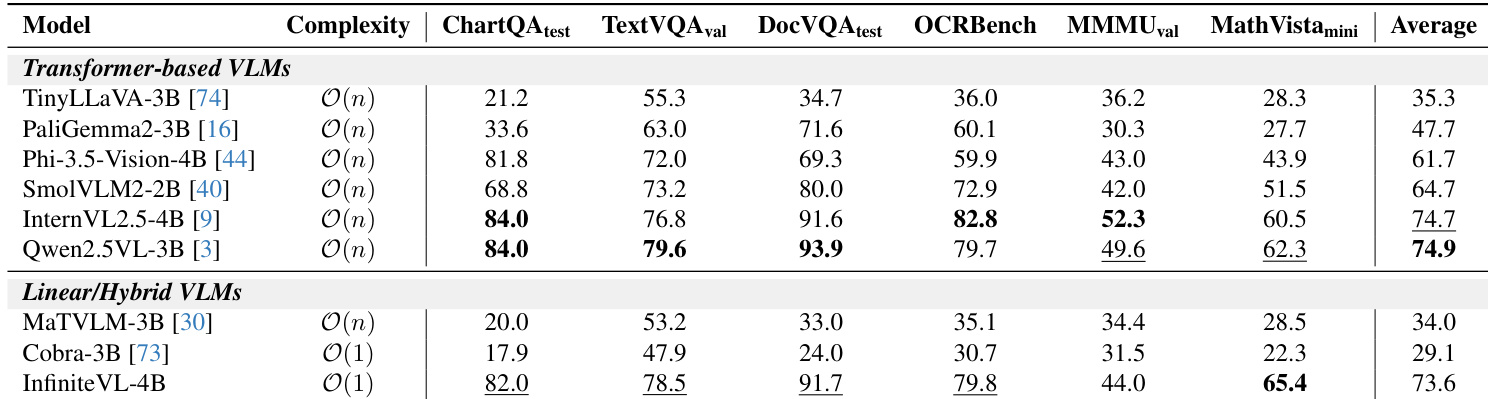
The authors evaluate different linear sequence modeling modules and find that Gated DeltaNet outperforms Mamba and GLA across key text-rich benchmarks, achieving the highest scores on DocVQA, TextVQA, and OCRBench. Linear attention alone fails to converge, while Gated DeltaNet’s state compression mechanism enables stable training and superior performance on fine-grained visual-language tasks.
InfiniteVL-4B, a linear/hybrid VLM with O(1) complexity, achieves an average score of 75.8 across multimodal benchmarks, outperforming other linear/hybrid models and approaching the performance of larger transformer-based models like InternVL2.5-4B and Qwen2.5VL-3B. It excels in RealworldQA and AI2D, demonstrating strong real-world comprehension and visual reasoning despite its constant-complexity design.
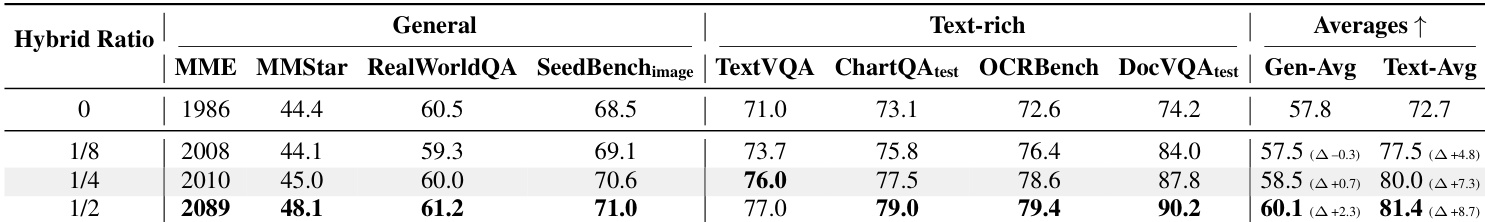
The authors evaluate how varying the proportion of sliding window attention layers affects performance, finding that even a small fraction (1/8) improves text-rich task scores significantly, with further gains at 1/4 and 1/2 ratios, though with diminishing returns. Results show that increasing the hybrid ratio boosts text-intensive benchmarks more than general multimodal ones, with the 1/2 configuration achieving the highest overall averages. The 1/4 ratio is selected as the default, balancing strong text-rich performance with efficient long-range context handling.