Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Au-delà du réel : extension imaginaire des embeddings de position rotatifs pour les LLM à contexte long
Au-delà du réel : extension imaginaire des embeddings de position rotatifs pour les LLM à contexte long
Xiaoran Liu Yuerong Song Zhigeng Liu Zengfeng Huang Qipeng Guo Zhaoxiang Liu Shiguo Lian Ziwei He Xipeng Qiu
Résumé
Les embeddings de position rotationnels (RoPE) sont devenus une norme pour encoder l’ordre des séquences dans les grands modèles linguistiques (LLM), en appliquant des rotations aux vecteurs de requête et de clé dans le plan complexe. Toutefois, les implémentations standards n’utilisent que la composante réelle du produit scalaire à valeurs complexes pour le calcul des scores d’attention. Cette simplification fait abstraction de la composante imaginaire, qui contient des informations de phase précieuses, entraînant ainsi une perte potentielle de détails relationnels essentiels à la modélisation des dépendances à longue portée. Dans cet article, nous proposons une extension qui réintègre cette composante imaginaire abandonnée. Notre méthode exploite la représentation complète à valeurs complexes afin de construire un score d’attention à deux composantes. Nous démontrons théoriquement et empiriquement que cette approche améliore la modélisation des dépendances à longue portée en préservant davantage d’informations positionnelles. En outre, les évaluations sur une série de benchmarks de modélisation linguistique à longue portée montrent que notre méthode améliore de manière cohérente les performances par rapport au RoPE standard, les bénéfices étant d’autant plus marqués que la longueur du contexte augmente. Le code est disponible à l’adresse suivante : https://github.com/OpenMOSS/rope_pp.
Summarization
Researchers from Fudan University, Shanghai Innovation Institute, and China Unicom propose RoPE++, an enhanced rotary position embedding that retains the imaginary component of complex-valued dot products in attention computation. By leveraging full complex information, RoPE++ improves long-context modeling over standard RoPE, demonstrating consistent gains on long-context benchmarks with increasing context lengths.
Key Contributions
- Standard Rotary Position Embeddings (RoPE) discard the imaginary component of complex-valued attention scores, losing phase information that can enhance modeling of long-context dependencies; this work identifies that the imaginary component captures complementary, long-range relational patterns distinct from the local semantics emphasized by real-valued attention.
- The authors propose RoPE++, a method that reintegrates the imaginary component into attention via two configurations: RoPE++EH, which halves KV cache usage while maintaining head count, and RoPE++EC, which doubles the attention heads within the same cache footprint, both preserving RoPE's unified absolute-relative positional encoding structure.
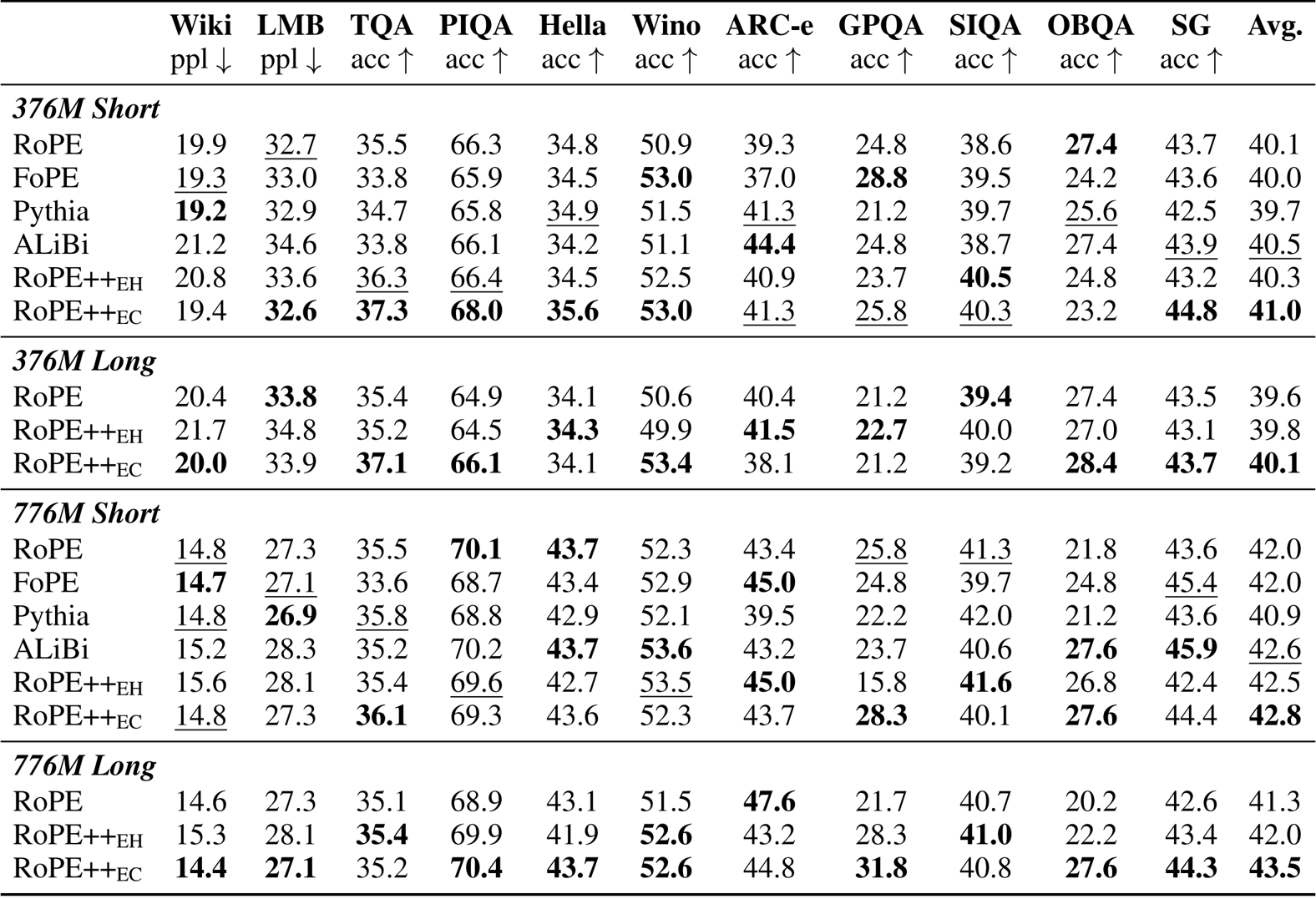
- Evaluations on 376M and 776M-parameter models show RoPE++ consistently outperforms standard RoPE and other position embeddings across short- and long-context benchmarks, with RoPE++EC achieving significant gains in long-context tasks, validating the critical role of imaginary attention in extending effective context length.
Introduction
The authors leverage Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE), a dominant method in modern large language models for encoding positional information, which combines absolute and relative position awareness through complex multiplication. Despite its widespread use, RoPE discards the imaginary component of the resulting complex-valued attention scores, retaining only the real part—an irreversible operation that leads to information loss. Prior work has focused on improving RoPE via interpolation, scaling, or data-aware designs but has largely overlooked this intrinsic computational limitation. The authors’ main contribution is RoPE++, a novel enhancement that reintroduces the discarded imaginary component as functional attention heads, thereby enriching model capacity without disrupting the established RoPE framework.
- RoPE++ recovers the ignored imaginary attention, which exhibits stronger focus on long-range dependencies, enhancing long-context modeling.
- It offers two configurations: RoPE++_EH halves KV cache usage while preserving head count, and RoPE++_EC doubles head count under the same cache footprint, both maintaining compatibility with standard RoPE.
- The method improves performance on both short- and long-context tasks, with ablation studies confirming the critical role of imaginary attention in capturing extended contextual relationships.
Method
The authors leverage the complex-valued formulation of Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE) to design RoPE++, an augmented attention mechanism that reintroduces the previously discarded imaginary component of the attention score. Rather than retaining only the real part as in standard RoPE, RoPE++ computes both real and imaginary attention scores as separate, parallel heads within the same attention layer. This design preserves the core mathematical properties of RoPE—namely, its ability to express relative position information through absolute position embeddings—while expanding the representational capacity of the attention mechanism.
The core innovation lies in the treatment of the imaginary component. The authors recover the negative imaginary part of the complex attention product, which can be expressed as a rotation of the query vector by −π/2 before applying the standard RoPE embedding. As shown in the framework diagram, this operation does not require modifying the key or value projections; only the query is rotated. The resulting imaginary attention score is computed alongside the real one, using the same key and value matrices, and both are treated as independent attention heads. This allows RoPE++ to capture complementary positional semantics: the real attention emphasizes semantic locality and decays with distance, while the imaginary attention exhibits a slower decay and preferentially attends to longer-range dependencies.
Refer to the framework diagram for a visual comparison of the real and imaginary attention pathways, including their respective characteristic curves derived from cosine and sine integral functions. The diagram illustrates how RoPE++ re-incorporates the imaginary component to enhance long-context modeling, cache efficiency, and length extrapolation.
For integration into existing architectures such as Multi-Head Attention (MHA) or Grouped Query Attention (GQA), the authors propose two configurations. In RoPE++EC (equal cache), the total number of attention heads is doubled by interleaving the original query vectors with their −π/2-rotated counterparts, enabling both real and imaginary attention to be computed in a single FlashAttention pass without increasing KV cache size. As shown in the GQA diagram with RoPE++EC, each key is attended to by both the original and rotated queries, effectively doubling the head count while preserving cache efficiency.
In contrast, RoPE++EH (equal head count) maintains the original number of attention heads by halving the number of query, key, and value projections. The rotated queries are still computed, but the total head count remains unchanged, reducing both parameter count and KV cache footprint. As depicted in the GQA diagram with RoPE++EH, this configuration halves the number of key-value pairs while still computing both real and imaginary attention for each query, thereby improving throughput in long-context scenarios.
Importantly, the authors emphasize that real and imaginary attention must share the same query projection matrix. Allocating separate subsets of heads to each component would collapse the architecture back to standard RoPE, since rotating a query by π/2 in the imaginary path recovers the real attention. Thus, RoPE++ is defined as a joint operation: the imaginary attention is not an independent module but a transformation relative to the real attention, and both must be computed together to realize the full benefits of the augmented representation.
Experiment
- Evaluate RoPE++ on 776M and 376M model sizes using DCLM-Baseline-1.0 corpus with 50B training tokens
- Compare RoPE++ against standard RoPE, FoPE, and vanilla attention on 4k, 8k, 16k, and 32k context lengths
- Test on LAMBADA, WikiText, and OpenBookQA with 2k, 4k, 8k, 16k, and 32k context windows
- Achieve best average score of 42.2 on RULER-4k and 41.8 on BABILong with 376M model size
- RoPE++_\\text{EC} outperforms ALiBi, NoPE, and YaRN by 33.9–44.1 in long-context tasks
- On 376M model, RoPE++ achieves 44.3 on short-context and 52.6 on long-context tasks, surpassing prior methods by 18.6–27.2 points
The authors use RoPE++ with two variants, EH and EC, to improve position encoding in transformer models and evaluate them against standard RoPE and other designs on short-context benchmarks. Results show that RoPE++EC consistently achieves the highest average scores across both 376M and 776M model sizes, outperforming all baselines including RoPE, FoPE, Pythia, and ALiBi. RoPE++EH also performs competitively, matching or exceeding RoPE despite using half the KV cache and QKV parameters.
Results show that RoPE++ consistently outperforms standard RoPE on long-context benchmarks RULER and BABILong across both 376M and 776M model sizes, achieving the highest average scores and maintaining stronger performance at 64k context length. RoPE++EC delivers the best overall gains while using the same KV cache size, and RoPE++EH matches or exceeds RoPE’s performance with half the cache and QKV parameters.
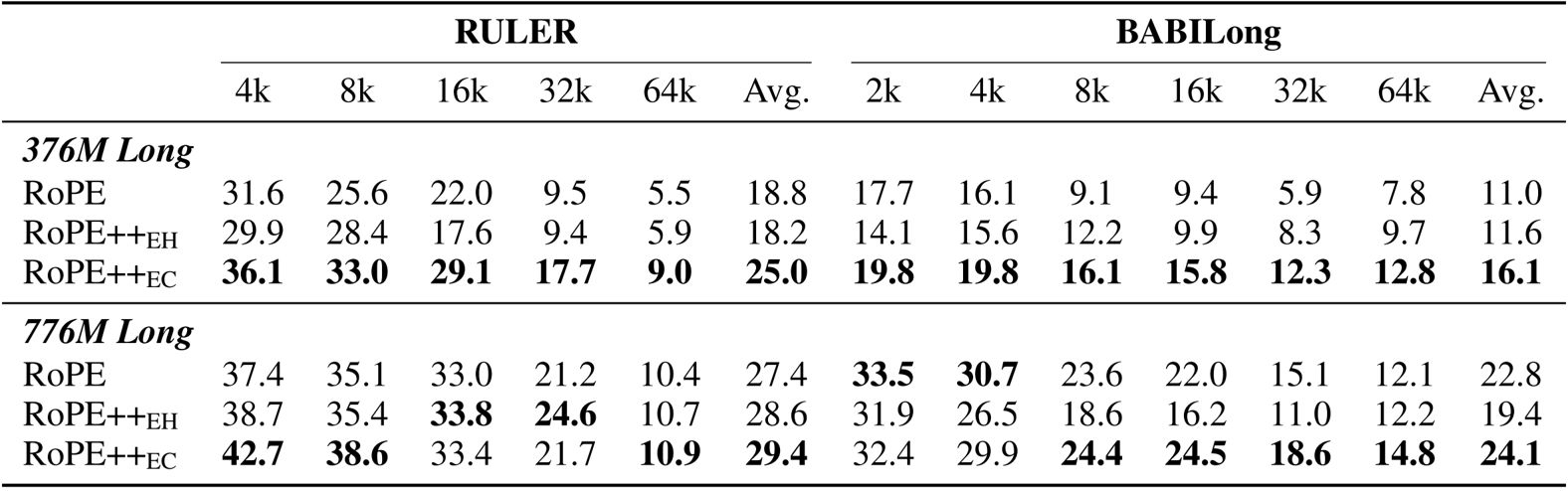
The authors evaluate RoPE++ variants after long-context pre-training using Linear PI and YaRN scaling, showing that RoPE++EC consistently achieves the highest average scores across short-context and long-context benchmarks like RULER and BABILong. RoPE++EH matches or exceeds standard RoPE performance while using half the KV cache, and RoPE++EC delivers further gains at the same cache size, particularly at longer context lengths. Results confirm RoPE++ improves both efficiency and accuracy, with performance advantages widening as context length increases.
