Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Hunyuan3D 2.0 : Extension des modèles de diffusion pour la génération d'actifs 3D texturés à haute résolution
Hunyuan3D 2.0 : Extension des modèles de diffusion pour la génération d'actifs 3D texturés à haute résolution
Résumé
Nous présentons Hunyuan3D 2.0, un système avancé de synthèse 3D à grande échelle permettant de générer des actifs 3D haute résolution avec textures. Ce système repose sur deux composants fondamentaux : un modèle de génération de formes à grande échelle — Hunyuan3D-DiT — et un modèle de synthèse de textures à grande échelle — Hunyuan3D-Paint. Le modèle de génération de géométrie, basé sur un transformateur à diffusion à flux évolutif, vise à produire des formes géométriques correctement alignées avec une image conditionnelle donnée, établissant ainsi une base solide pour les applications ultérieures. Le modèle de synthèse de textures, bénéficiant de priorités géométriques et de diffusion puissantes, génère des cartes de textures haute résolution et vibrantes pour des maillages soit générés automatiquement, soit conçus manuellement. Par ailleurs, nous avons développé Hunyuan3D-Studio — une plateforme de production polyvalente et intuitive qui simplifie considérablement le processus de re-création d’actifs 3D. Cette plateforme permet aux utilisateurs professionnels comme aux amateurs de manipuler, voire d’animer, leurs maillages de manière efficace. Nous avons mené une évaluation systématique de nos modèles, démontrant que Hunyuan3D 2.0 surpassait les modèles précédents de pointe, tant dans les modèles open-source que fermés, en termes de détails géométriques, d’alignement conditionnel, de qualité des textures, etc. Hunyuan3D 2.0 est désormais publié publiquement afin de combler les lacunes du domaine open-source en matière de modèles fondamentaux de génération à grande échelle pour la 3D. Le code source et les poids pré-entraînés de nos modèles sont disponibles à l’adresse suivante : https://github.com/Tencent/Hunyuan3D-2
One-sentence Summary
The Hunyuan3D Team presents Hunyuan3D 2.0, a large-scale 3D synthesis system featuring Hunyuan3D-DiT for condition-aligned shape generation via a flow-based diffusion transformer and Hunyuan3D-Paint for high-fidelity texture synthesis, enabling high-quality, user-friendly 3D asset creation and animation through Hunyuan3D-Studio, with open-source release to advance the 3D generative modeling community.
Key Contributions
-
Hunyuan3D 2.0 addresses the challenge of high-cost, expertise-intensive 3D asset creation by introducing a scalable two-stage pipeline that decouples shape and texture generation, enabling efficient and high-fidelity synthesis of detailed 3D assets from conditional images or sketches.
-
The system introduces Hunyuan3D-DiT, a large-scale flow-based diffusion transformer built on a vector-set representation of 3D shapes via a specialized VAE, and Hunyuan3D-Paint, a mesh-conditioned multi-view diffusion model that generates high-resolution, multi-view-consistent texture maps with strong geometric priors.
-
Extensive evaluations on multiple benchmarks and a user study with 50 participants demonstrate that Hunyuan3D 2.0 outperforms state-of-the-art open-source and closed-source models in geometry detail, condition alignment, texture quality, and user preference, with the full code and pre-trained models publicly released.
Introduction
Digital 3D asset creation is critical for industries like gaming, film, and embodied AI, yet remains labor-intensive and expertise-heavy due to complex pipelines involving modeling, texturing, and simulation. Despite rapid advances in image and video generation via diffusion models, 3D generation has lagged, largely due to the lack of scalable, open-source foundational models and the inherent challenges of representing 3D geometry. Prior methods either relied on small-scale models with limited generalization or suffered from poor multi-view consistency and geometric alignment, especially in texture synthesis. The authors introduce Hunyuan3D 2.0, a two-stage open-source system featuring Hunyuan3D-DiT—a large-scale flow-based diffusion model using vector-set representations for efficient, high-fidelity shape generation—and Hunyuan3D-Paint, a mesh-conditioned multi-view diffusion model with a novel multi-task attention mechanism that ensures high-resolution, detail-preserving texture synthesis with strong alignment to input images. This work advances the state of the art by enabling end-to-end, high-quality 3D asset generation with strong semantic and geometric fidelity, supported by large-scale 3D datasets and a flexible architecture suitable for both generated and handcrafted meshes.
Method
The Hunyuan3D 2.0 system is structured around two primary foundation models: a shape generation model, Hunyuan3D-DiT, and a texture synthesis model, Hunyuan3D-Paint, which together form a pipeline for creating high-resolution textured 3D assets from a single input image. The overall framework, as illustrated in the figure below, begins with the shape generation model, which produces a bare mesh. This mesh is then processed by the texture synthesis model to generate high-fidelity texture maps, which are subsequently baked onto the geometry. The system is further supported by Hunyuan3D-Studio, a production platform that provides tools for downstream applications such as low-polygon stylization and character animation.

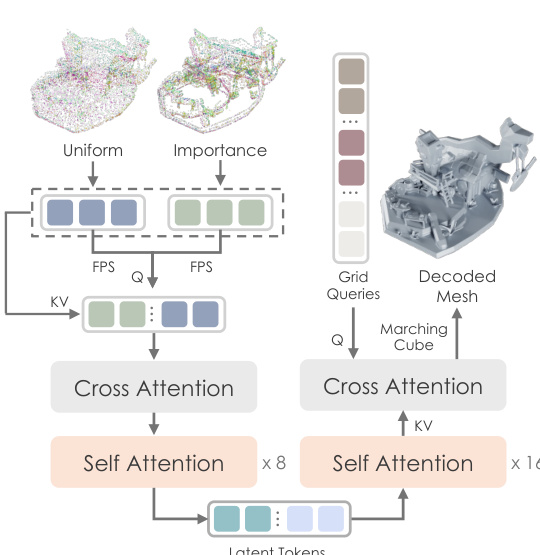
The shape generation model, Hunyuan3D-DiT, is built upon a latent diffusion framework and consists of two key components: the Hunyuan3D-ShapeVAE and the diffusion transformer itself. The ShapeVAE acts as a compressor, transforming a 3D polygon mesh into a sequence of continuous latent tokens. This process begins with the input mesh, from which both uniformly sampled and importance-sampled point clouds are extracted. The importance sampling strategy focuses on capturing high-frequency details, such as edges and corners, by concentrating samples on these complex regions. These point clouds are then encoded into latent tokens using a transformer-based architecture that employs cross-attention and self-attention layers. The encoder's output is a latent shape embedding, which is decoded by a variational decoder to reconstruct the 3D shape as a Signed Distance Function (SDF). This SDF is then converted into a triangle mesh using the marching cube algorithm. The training of the ShapeVAE is supervised by a combination of a reconstruction loss, which measures the mean squared error between the predicted and ground truth SDF, and a KL-divergence loss to ensure a compact and continuous latent space.
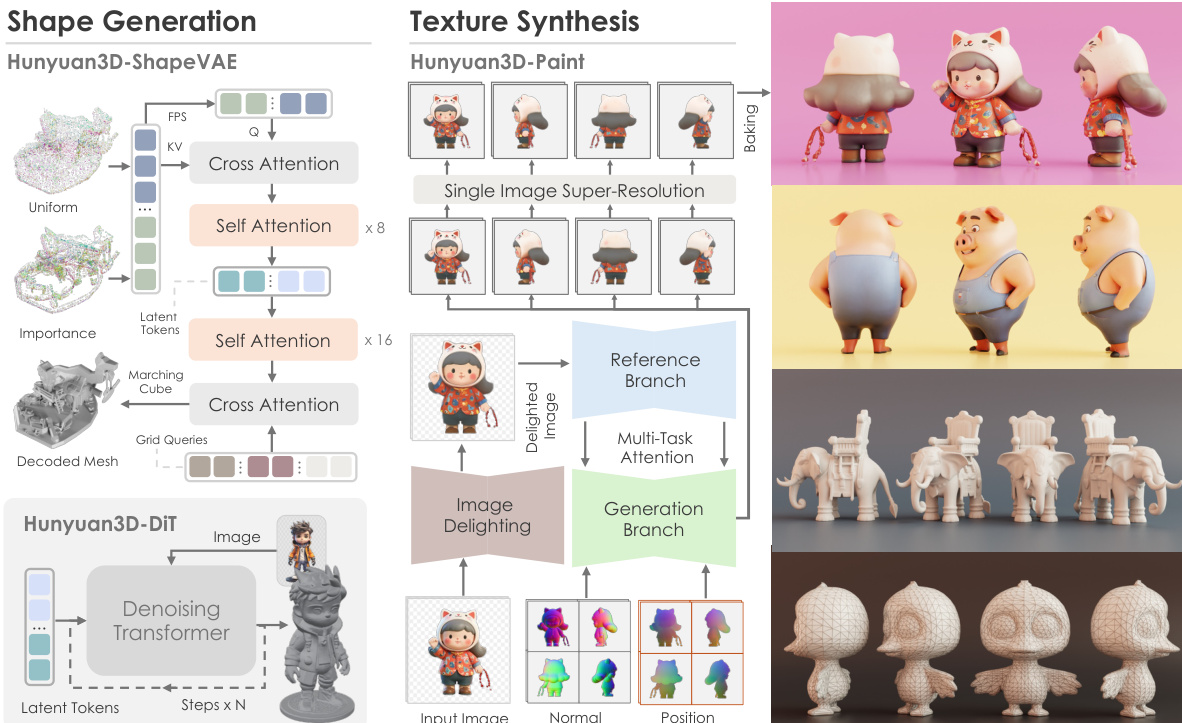
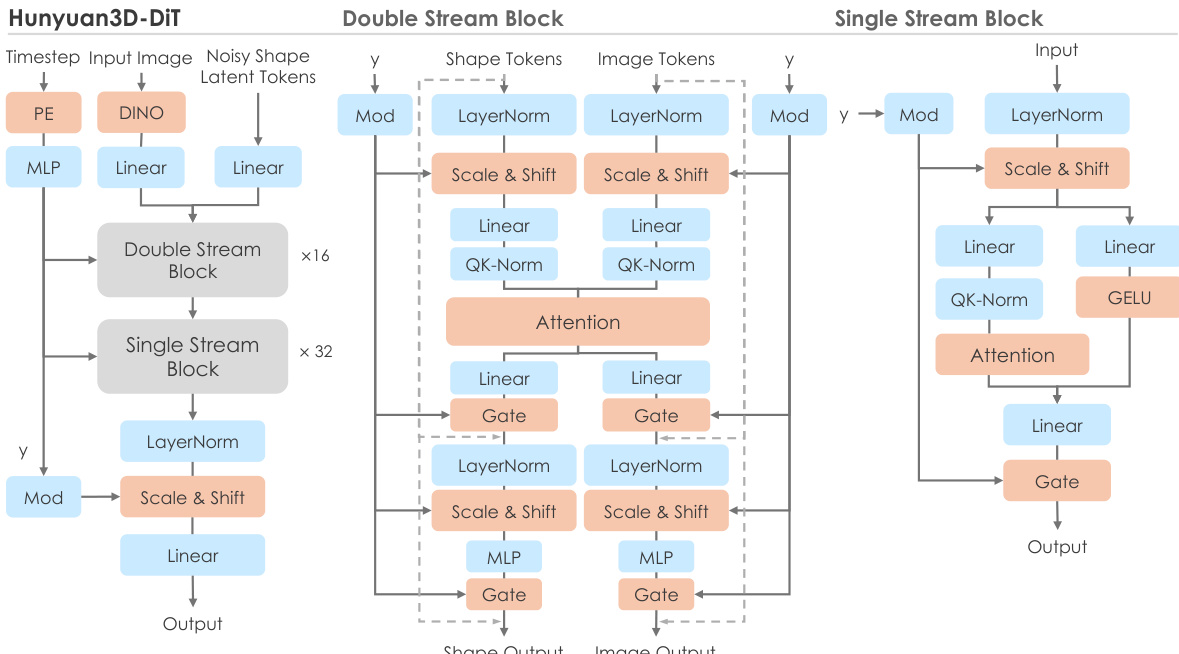
The Hunyuan3D-DiT model, which operates on the latent space defined by the ShapeVAE, is a flow-based diffusion transformer designed to generate high-fidelity 3D shapes conditioned on an input image. The model's architecture, shown in the figure below, employs a dual- and single-stream network structure. The dual-stream blocks process latent tokens (representing the 3D shape) and condition tokens (representing the input image) separately but allow them to interact through attention mechanisms. The single-stream blocks process the concatenated latent and condition tokens in parallel, using spatial and channel attention. The model is conditioned on a pre-trained image encoder, DINOv2, which extracts high-resolution image tokens from the input. To ensure the model focuses on the object of interest, the input image is pre-processed by removing the background, resizing, and centering the object. The training objective is based on flow matching, where the model learns to predict the velocity field that guides a sample from a Gaussian distribution to the data distribution. During inference, the model uses a first-order Euler ODE solver to generate the final shape.
The texture synthesis model, Hunyuan3D-Paint, is a multi-view image generation framework that produces high-resolution, self-consistent texture maps for a given 3D mesh. The process is divided into three stages: pre-processing, multi-view image synthesis, and texture baking. The pre-processing stage includes an image delighting module that converts the input image to an unlit state, removing illumination and shadows to ensure the texture maps are light-invariant. A geometry-aware viewpoint selection strategy is used to determine the optimal number of viewpoints for inference, ensuring efficient coverage of the mesh surface. The core of the model, the multi-view image synthesis stage, is a diffusion model that generates images from multiple viewpoints. This model uses a double-stream image conditioning reference-net to faithfully capture the details of the input image, with a fixed-weight reference branch to prevent style drift. To ensure consistency across all generated views, a multi-task attention mechanism is employed, which integrates a reference attention module and a multi-view attention module in parallel. The model is also conditioned on the geometry of the mesh, using canonical normal and position maps, and a learnable camera embedding to provide viewpoint information. The training and inference pipeline, illustrated in the figure below, involves dense-view inference, where a view dropout strategy is used during training to enhance the model's 3D perception. After generating the multi-view images, a single-image super-resolution model is applied to enhance texture quality, and a texture inpainting method is used to fill any uncovered regions in the UV map.
Experiment
- Hunyuan3D-ShapeVAE achieves superior 3D shape reconstruction, outperforming baselines (3DShape2VecSet, Michelangelo, Direct3D) on V-IoU and S-IoU metrics, with fine-grained detail recovery and no floating artifacts.
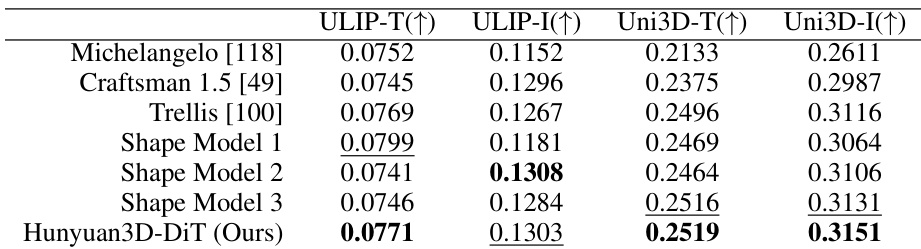
- Hunyuan3D-DiT generates high-fidelity 3D shapes with strong condition-following ability, surpassing open-source (Michelangelo, Craftsman 1.5, Trellis) and closed-source baselines on ULIP-T/I and Uni3D-T/I metrics, producing holeless meshes with detailed surface features.
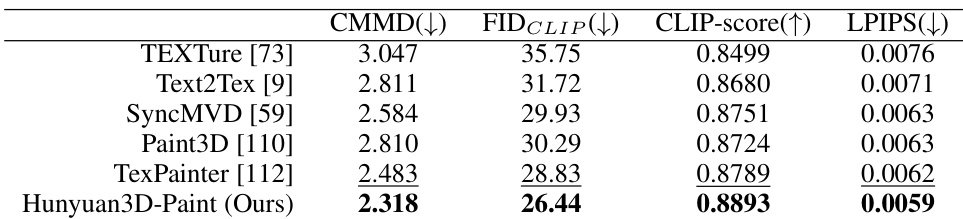
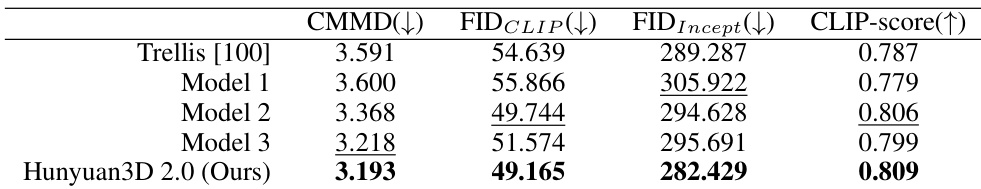
- Hunyuan3D-Paint generates high-quality, condition-conforming texture maps, achieving the best performance on FID_CLIP, CMMD, CLIP-score, and LPIPS metrics compared to TEXture, Text2Tex, SyncMVD, Paint3D, and TexPainter, with seamless, lighting-invariant results and rich detail synthesis.
- Hunyuan3D 2.0 excels in end-to-end textured 3D asset generation, outperforming Trellis and closed-source models on FID_CLIP, CMMD, CLIP-score, and LPIPS, producing high-resolution, high-fidelity assets with accurate texture and surface bump mapping.
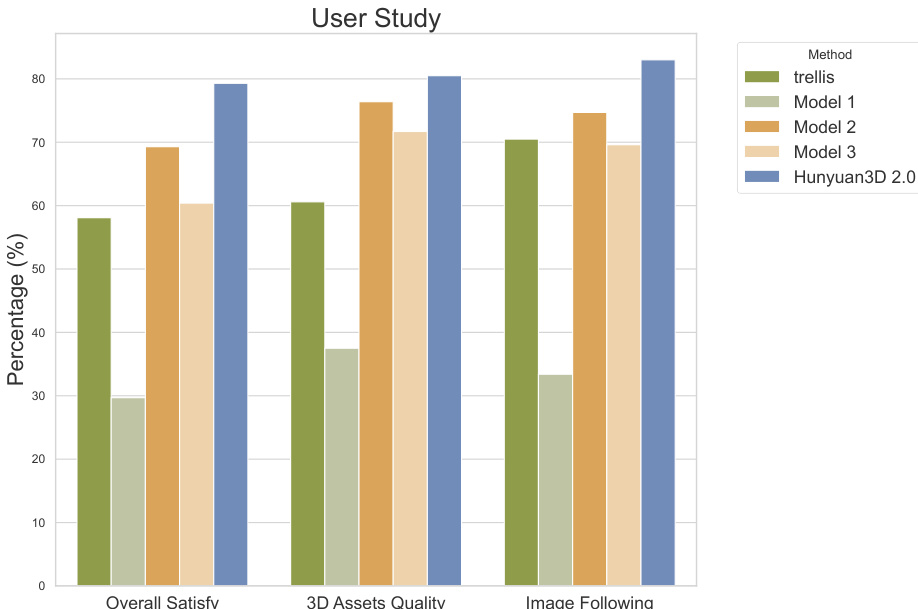
- User study with 50 participants confirms Hunyuan3D 2.0's strong adherence to image conditions and overall visual quality, significantly outperforming baselines in subjective evaluation.
The authors use Hunyuan3D 2.0 to generate textured 3D assets and compare its performance against several baselines using metrics such as CMMD, FIDCLIP, FIDIncept, and CLIP-score. Results show that Hunyuan3D 2.0 outperforms all baselines, achieving the best scores across all metrics, particularly in semantic alignment and detail preservation.
The authors conduct a user study involving 50 volunteers to evaluate the quality of textured 3D assets generated by Hunyuan3D 2.0 and compare it with baselines. Results show that Hunyuan3D 2.0 achieves the highest scores across all evaluation criteria, including overall satisfaction, 3D assets quality, and image following, outperforming all compared methods.
The authors use Table 1 to evaluate the reconstruction performance of Hunyuan3D-ShapeVAE against several baselines using volume IoU (V-IoU) and surface IoU (S-IoU) metrics. Results show that Hunyuan3D-ShapeVAE outperforms all compared methods, achieving the highest scores in both V-IoU and S-IoU, indicating superior shape reconstruction quality.
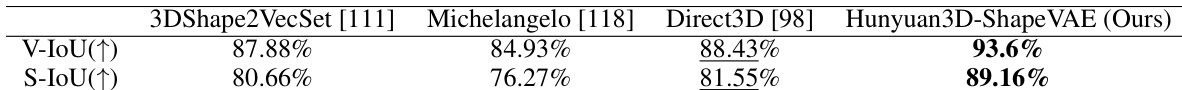
The authors use Table 2 to evaluate the shape generation performance of Hunyuan3D-DiT against several baselines using ULIP-T/I and Uni3D-T/I metrics. Results show that Hunyuan3D-DiT achieves the highest scores across all metrics, indicating it produces the most condition-following results compared to other methods.
Results show that Hunyuan3D-Paint outperforms all baselines across multiple metrics, achieving the lowest CMMD and FIDCLIP values and the highest CLIP-score and LPIPS scores, indicating superior generative quality, semantic alignment, and detail preservation in texture map synthesis.