Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Sa2VA : Mariage entre SAM2 et LLaVA pour une compréhension dense et ancrée d'images et de vidéos
Sa2VA : Mariage entre SAM2 et LLaVA pour une compréhension dense et ancrée d'images et de vidéos
Haobo Yuan Xiangtai Li Tao Zhang Zilong Huang Shilin Xu Shunping Ji Yunhai Tong Lu Qi Jiashi Feng Ming-Hsuan Yang
Résumé
Ce travail présente Sa2VA, le premier modèle intégré et complet pour une compréhension dense et ancrée à la fois des images et des vidéos. Contrairement aux modèles existants de grands langages multimodaux, souvent limités à des modalités ou tâches spécifiques, Sa2VA prend en charge une large gamme de tâches sur images et vidéos, notamment la segmentation référentielle et les dialogues, avec une adaptation minimale par instruction en une seule occurrence (one-shot instruction tuning). Sa2VA combine SAM-2, un modèle fondamental de segmentation vidéo, avec MLLM, un modèle avancé vision-langage, et unifie le texte, l’image et la vidéo dans un espace commun de jetons de modèle de langage à grande échelle (LLM). Grâce à ce modèle de langage, Sa2VA génère des jetons d'instruction qui guident SAM-2 pour produire des masques précis, permettant ainsi une compréhension multimodale ancrée, tant pour le contenu visuel statique que dynamique. Par ailleurs, nous introduisons Ref-SAV, un jeu de données auto-étiqueté comprenant plus de 72 000 expressions d’objets dans des scènes vidéo complexes, conçu pour améliorer les performances du modèle. Nous avons également validé manuellement 2 000 objets vidéo dans le jeu Ref-SAV afin de constituer une référence (benchmark) pour la segmentation d’objets vidéo référentielle dans des environnements complexes. Les expériences montrent que Sa2VA atteint des performances solides sur plusieurs tâches, en particulier dans la segmentation d’objets vidéo référentielle, soulignant son potentiel pour des applications réelles complexes. En outre, Sa2VA peut être facilement étendu à divers modèles vision-langage (VLM), notamment Qwen-VL et Intern-VL, qui peuvent être mis à jour rapidement grâce aux processus actuellement disponibles dans les VLM open-source. Le code et les modèles ont été rendus disponibles à la communauté.
One-sentence Summary
The authors, from UC Merced, Bytedance Seed, Wuhan University, and Peking University, propose Sa2VA, a unified model that integrates SAM-2 and MLLM to enable dense, grounded understanding of images and videos through a shared LLM token space, using instruction-guided mask generation for tasks like referring segmentation—outperforming prior methods in complex video scenarios and supporting rapid adaptation to other VLMs, with a new Ref-SAV dataset and open-source release.
Key Contributions
-
Sa2VA is the first unified model that integrates SAM-2 and multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) into a single framework, enabling dense, grounded understanding of both images and videos through a shared LLM token space, with support for diverse tasks like referring segmentation, video chat, and grounded captioning using minimal one-shot instruction tuning.
-
The model addresses key challenges in task formulation, performance balance, and knowledge inheritance by employing an end-to-end training approach with frozen SAM-2 components, allowing seamless scalability to advanced VLMs like Qwen-VL and Intern-VL while maintaining strong language and perception capabilities.
-
Sa2VA is evaluated on a new benchmark, Ref-SAV, a large-scale, auto-labeled video dataset with over 72k object expressions and manual validation of 2k examples, where it achieves over 15% improvement over prior methods in zero-shot referring video object segmentation, demonstrating superior performance in complex, real-world scenarios.
Introduction
The authors address the challenge of achieving dense, grounded understanding of images and videos by unifying two powerful foundation models: SAM-2, which excels at promptable segmentation and tracking, and Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), which offer open-ended language comprehension. Prior work either focused on narrow tasks like video segmentation or video QA, or combined models in a modular way that sacrificed end-to-end performance and flexibility. Existing approaches struggle to balance grounding tasks with conversational abilities, often degrading one for the other. To overcome these limitations, the authors introduce Sa2VA, a unified framework that integrates SAM-2 and MLLMs through one-shot visual instruction tuning, enabling end-to-end training across image and video inputs. The model treats visual inputs as tokens, allowing seamless handling of diverse tasks—referring segmentation, visual question answering, and grounded conversation—without architectural specialization. A key innovation is a decoupled design that freezes SAM-2’s encoder and memory, preserving its tracking strength while enabling compatibility with evolving MLLMs. The authors also introduce Ref-SAV, a new benchmark with challenging conditions like long videos, heavy occlusions, and complex text, to better reflect real-world interactive applications. Experiments show Sa2VA achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks, including a 15% gain over prior methods on Ref-SAV under zero-shot settings, establishing a new strong baseline for unified, dense visual understanding.
Dataset
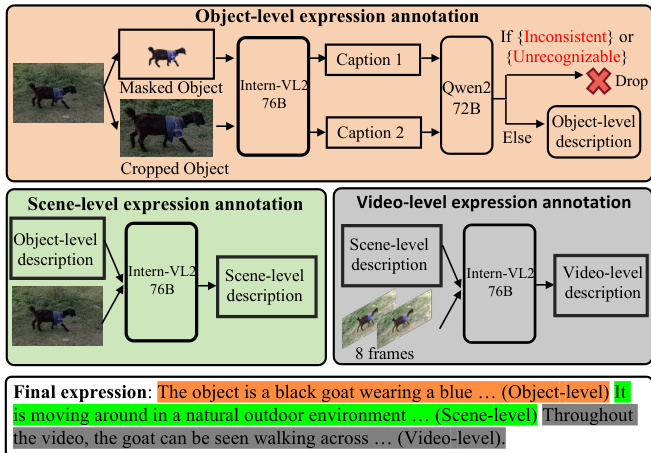
- The Ref-SAV dataset is built from the SA-V dataset using an automated annotation pipeline that generates referring object text expressions without human labeling for the training set.
- The pipeline consists of three stages:
- Object-level annotation: The frame with the largest object area is selected, and the object is cropped and masked. Both versions are processed by InternVL2-76B to generate descriptions, which are then validated and cleaned using Qwen2-72B to remove inconsistent or error-prone outputs.
- Scene-level annotation: The original image and the object-level description are fed into InternVL2-76B to generate context-rich descriptions that include relationships between the object and its surroundings.
- Video-level annotation: Eight uniformly sampled frames from the video are processed with yellow borders highlighting the object. These frames, paired with the scene-level description, are used to generate dynamic video-level descriptions capturing object motion and actions.
- The Ref-SAV training set includes 37,311 videos and 72,509 object expressions, all automatically generated.
- The evaluation benchmark is derived from a separate subset of the SA-V training set, ensuring no overlap with the training data. It contains 1,147 videos and 1,945 expressions: 1,694 long expressions (automatically generated and human-filtered) and 251 short expressions (manually annotated).
- The dataset is used in the paper for training and evaluation, with the training split leveraging the full automated pipeline output. Mixture ratios and processing are applied during training to balance expression length and complexity, while the evaluation benchmark enables assessment of both long and short referring expressions.
- A key processing detail is the use of yellow borders on sampled video frames to emphasize the target object, aiding the model in understanding spatial and temporal context during video-level description generation.
Method
The authors leverage a unified framework to address diverse image and video understanding tasks, integrating a pre-trained multimodal large language model (MLLM) with SAM-2, a foundation video segmentation model. The overall architecture, illustrated in the framework diagram, operates by first encoding textual, visual, and prompt inputs into token embeddings. Text is processed through a tokenizer and language embedding module, while visual inputs—images and videos—are encoded separately using image and video encoders. Visual prompts, such as bounding boxes or points, are encoded via a dedicated prompt encoder. These embeddings are then combined and fed into the large language model (LLM), which generates output tokens that include a special "[SEG]" token. This token serves as a spatial-temporal prompt for the SAM-2 decoder, enabling it to produce precise segmentation masks for both images and videos. The framework supports multiple tasks, including referring segmentation, video object segmentation, image and video chat, and grounded caption generation, by conditioning the output on the specific task requirements.
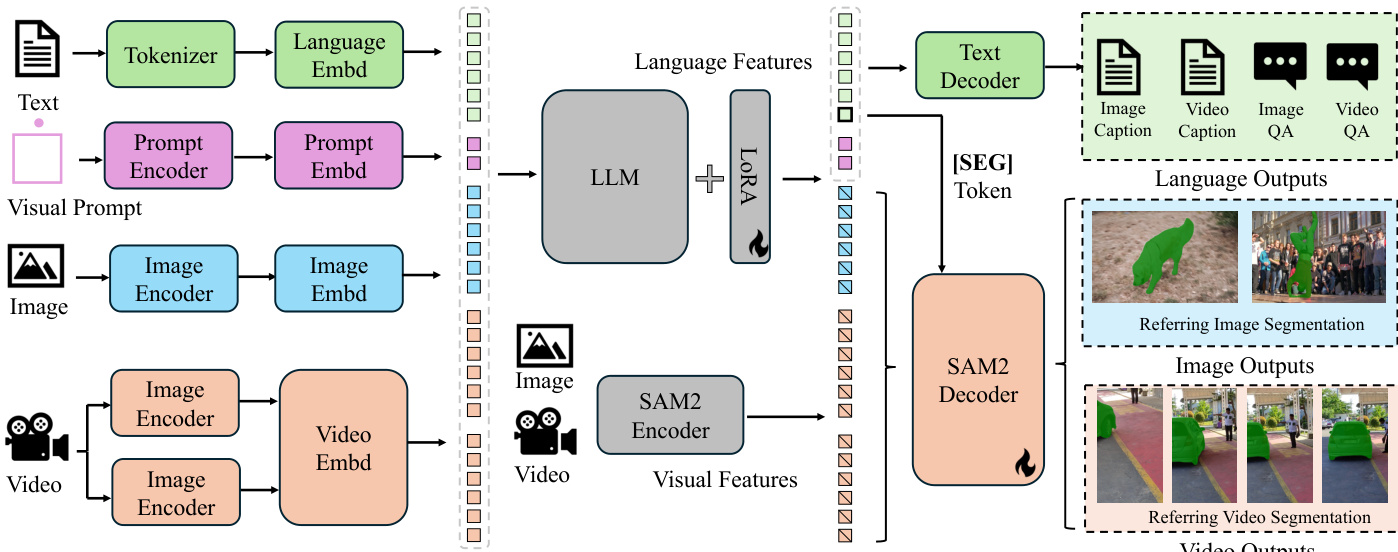
The model employs a decoupled design, where SAM-2 is appended to the pre-trained MLLM without integrating its output tokens into the LLM. This design choice simplifies the architecture, avoids computational overhead, and preserves knowledge inheritance from the MLLM, allowing the system to adapt to evolving MLLM advancements. During training, the SAM-2 decoder is tuned via the "[SEG]" token, which acts as a prompt derived from the LLM's hidden states. Gradients are backpropagated through this token to the MLLM, enabling joint learning. For video tasks, the model uses a memory-based tracking mechanism: key frames are processed to generate initial masks, and the resulting features are used to track objects across subsequent frames, as detailed in the inference algorithm.
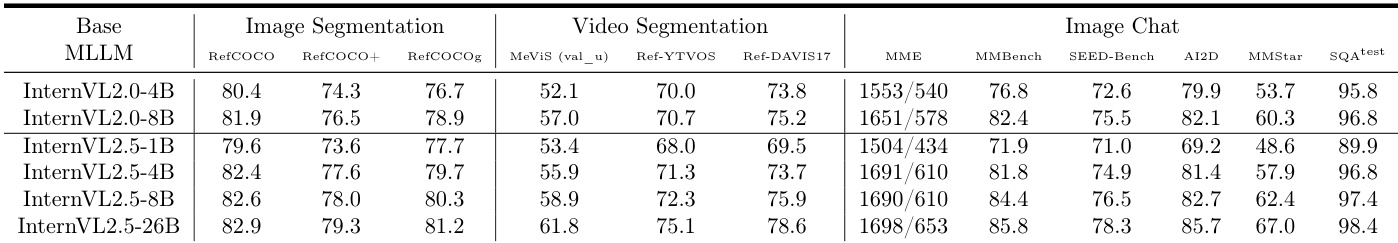
Experiment
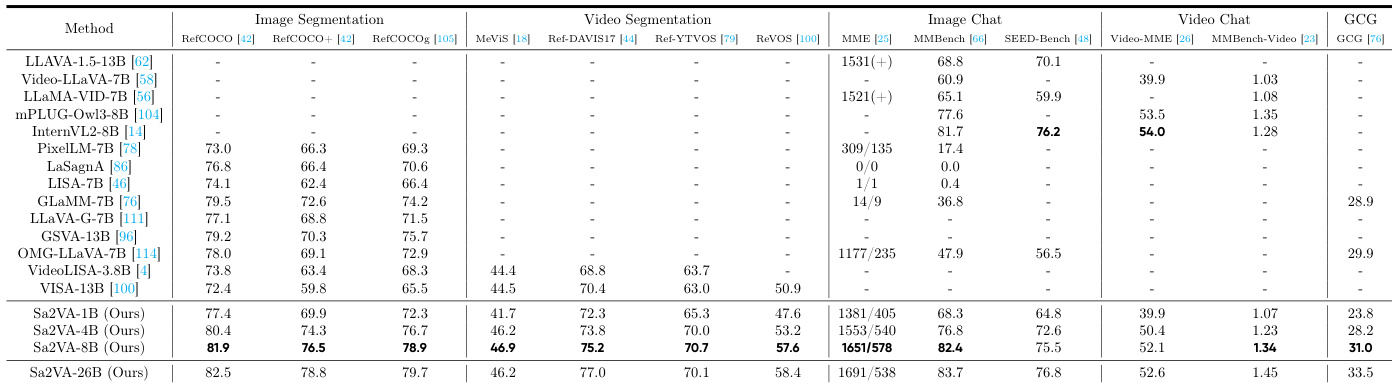
- Sa2VA achieves state-of-the-art performance on image referring segmentation, with cIoU scores of 81.9, 76.5, and 78.9 on RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, and RefCOCOg, surpassing GLaMM-7B by 2.4, 3.9, and 4.7 cIoU, respectively, and outperforming LISA, PixelLLM, PSALM, and OMG-LLaVA.
- On video segmentation benchmarks, Sa2VA-8B achieves 46.9, 75.2, and 57.6 J&F on MeVIS, Ref-DAVIS17, and ReVOS, exceeding VISA-13B by 2.4, 4.8, and 6.7 J&F, and scores 1.34 on MMBench-Video, outperforming InternVL2-8B (1.28).
- Sa2VA maintains strong multimodal chat performance, scoring 2229 (1651/578), 82.4, and 75.5 on MME, MMbench, and SEED-Bench, comparable to InternVL2, demonstrating robustness against catastrophic forgetting.
- Ablation studies confirm that joint co-training across image and video QA, segmentation, and multimodal datasets is critical, with performance drops of up to 129 on MME and 34% on MMBasech-Video when key datasets are omitted.
- The "[SEG]" token design using a single generic token outperforms frame-specific tokens, preserving knowledge transfer from image to video segmentation tasks.
- Training with the proposed Ref-SAV dataset significantly improves performance, with UniRef++ achieving a 4.1 increase in Overall J&F (10.5 to 14.6), validating its value for video referring segmentation.
- Sa2VA-4B achieves the best region caption performance on RefCOCOg with a METEOR score of 17.3, surpassing Osprey (16.6), and Sa2VA-26B outperforms vision expert models across all five Ref-VOS datasets.
- Model scaling with stronger base MLLMs (e.g., InternVL2.5) consistently improves performance across benchmarks, indicating strong scalability.
- Inference is dominated by the auto-regressive MLLM component, with Sa2VA-26B taking 0.463s and Sa2VA-1B taking 0.123s under fixed-length conditions, while SAM-2 remains efficient at 39.5 FPS.
- Uniform keyframe sampling (62.9 J&F) outperforms consecutive first-frame sampling (58.9 J&F) on MeVIS, suggesting advanced sampling strategies can further improve performance.
The authors compare their method with existing Ref-VOS models on the Ref-SAV benchmark, highlighting that previous models fail to handle challenging conditions such as heavy occlusion, long text descriptions, and diverse annotations. Their method, Sa2VA, achieves strong results across all these conditions, demonstrating superior performance and robustness in complex video segmentation tasks.
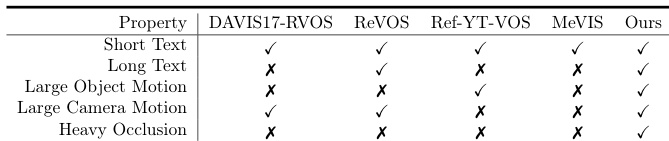
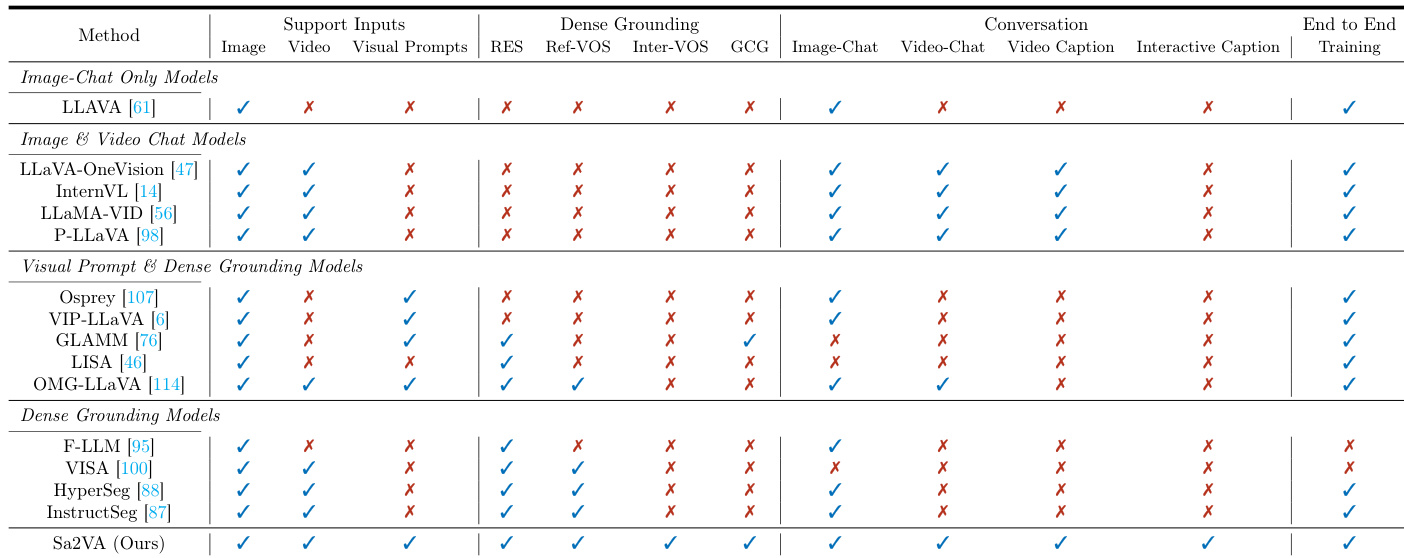
The authors use the table to compare Sa2VA with existing models across multiple capabilities, showing that Sa2VA is the only model that supports all listed tasks, including image and video chat, dense grounding, and visual prompt understanding. Results show that Sa2VA achieves comprehensive performance across all categories, outperforming specialized models that are limited to specific tasks.
Results show that Sa2VA-4B achieves the highest METEOR score of 17.3 on the RefCOCOg dataset, outperforming other recent visual prompt understanding models. This indicates that Sa2VA can generate accurate and context-aware region captions.
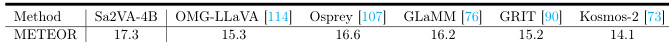
The authors use Sa2VA-8B to achieve state-of-the-art performance on image segmentation benchmarks, scoring 81.9, 76.5, and 78.9 cIoU on RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, and RefCOCOg, respectively, surpassing previous models like GLaMM-7B. The model also demonstrates strong performance across image and video chat tasks, with high scores on MME, MMbench, and SEED-Bench, indicating its versatility in handling both segmentation and conversational capabilities.
The authors use Table 14 to compare the performance of Sa2VA when integrated with different base MLLMs, showing that the choice of base model significantly affects results across tasks. Results show that Sa2VA-InternVL3-14B achieves the highest scores on image and video segmentation benchmarks, while Sa2VA-Qwen3VL-4B performs best on MMBench and other image chat tasks, indicating that model selection is crucial for task-specific optimization.