Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Deploy GLM-4-32B Using vLLM and Open-WebUI



1. Tutorial Introduction
The GLM4 project was launched by the THUDM organization in 2025, and the relevant technical report is "ChatGLM: A Family of Large Language Models from GLM-130B to GLM-4 All Tools".
The GLM family welcomes a new member, the GLM-4-32B-0414 series model, which has 32 billion parameters, comparable performance to OpenAI's GPT series and DeepSeek's V3/R1 series, and supports very friendly local deployment functions. GLM-4-32B-Base-0414 has been pre-trained on 15T high-quality data, including a large amount of synthetic data for reasoning, laying the foundation for subsequent reinforcement learning expansion. In the post-training stage, the research team introduced human-machine preference alignment for dialogue scenarios. In addition, the research team used techniques such as rejection sampling and reinforcement learning to improve the model's performance in instruction following, code engineering, and function calling, thereby enhancing the atomic capabilities required for agent tasks. GLM-4-32B-0414 has achieved good results in code engineering, artifact generation, function calling, search-based question and answer, and report generation. In particular, on several benchmarks such as code generation or specific question answering tasks, GLM-4-32B-Base-0414 achieves comparable performance to larger models such as GPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3-0324(671B).
This tutorial uses the resources for the dual-SIM A6000.
👉 This project provides a model of:
- GLM-4-32B-0414 Model
Project Examples
Animation drawing
| GLM-Z1-32B-0414 | GLM-4-32B-0414 |
| write a Python program that shows a ball bouncing inside a spinning hexagon. The ball should be affected by gravity and friction, and it must bounce off the rotating walls realistically | Use HTML to simulate a scene where a ball is released from the center of a rotating hexagon. Consider the collision between the ball and the hexagonal border and the gravity on the ball, and assume that the collision is completely elastic. |
Web Design
| GLM-4-32B-0414 | GLM-4-32B-0414 |
SVG Generation
| GLM-4-32B-0414 | GLM-4-32B-0414 |
Analysis, research and writing
Analysis of the development of AI in Chinese cities: A comparative study of Beijing and Hangzhou. At the same time, we will investigate the cases of foreign cities using AI for urban governance.
2. Operation steps
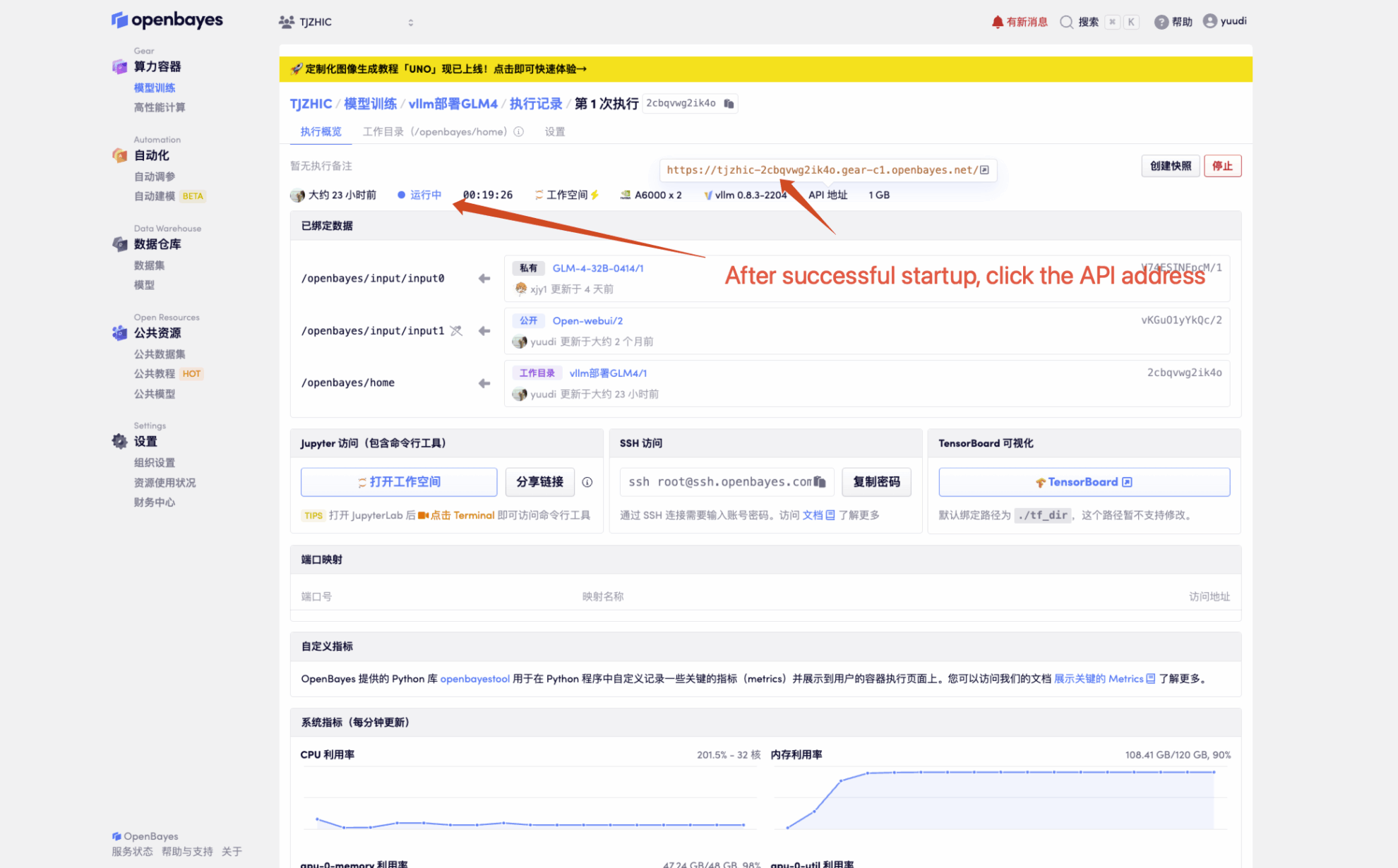
1. After starting the container, click the API address to enter the Web interface
If "Model" is not displayed, it means the model is being initialized. Since the model is large, please wait about 1-2 minutes and refresh the page.
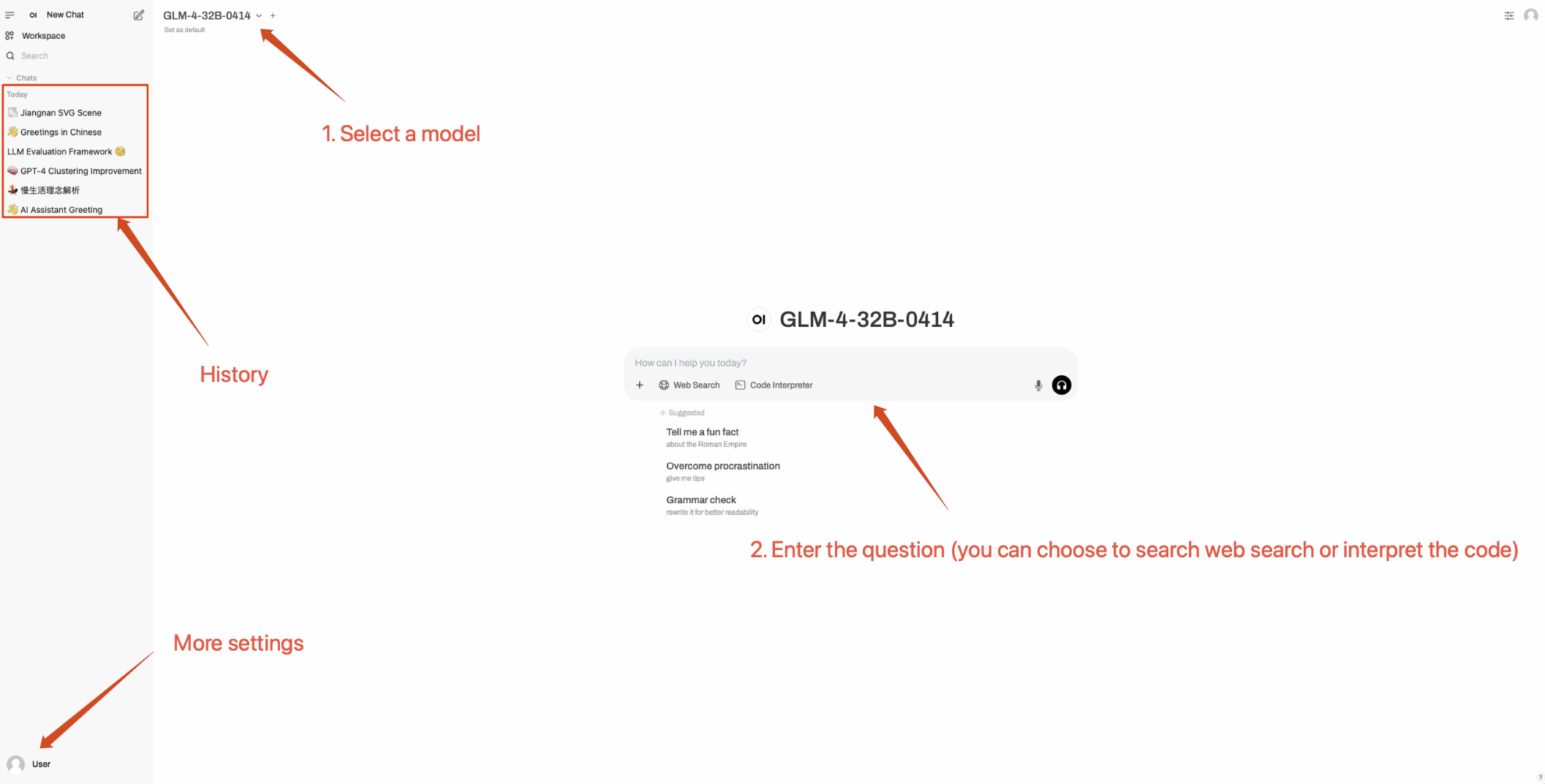
2. After entering the webpage, you can start a conversation with the model
How to use
Exchange and discussion
🖌️ If you see a high-quality project, please leave a message in the background to recommend it! In addition, we have also established a tutorial exchange group. Welcome friends to scan the QR code and remark [SD Tutorial] to join the group to discuss various technical issues and share application effects↓

Citation Information
grateful ZV-Liu For the deployment of this tutorial, the project reference information is as follows:
@misc{glm2024chatglm,
title={ChatGLM: A Family of Large Language Models from GLM-130B to GLM-4 All Tools},
author={Team GLM and Aohan Zeng and Bin Xu and Bowen Wang and Chenhui Zhang and Da Yin and Diego Rojas and Guanyu Feng and Hanlin Zhao and Hanyu Lai and Hao Yu and Hongning Wang and Jiadai Sun and Jiajie Zhang and Jiale Cheng and Jiayi Gui and Jie Tang and Jing Zhang and Juanzi Li and Lei Zhao and Lindong Wu and Lucen Zhong and Mingdao Liu and Minlie Huang and Peng Zhang and Qinkai Zheng and Rui Lu and Shuaiqi Duan and Shudan Zhang and Shulin Cao and Shuxun Yang and Weng Lam Tam and Wenyi Zhao and Xiao Liu and Xiao Xia and Xiaohan Zhang and Xiaotao Gu and Xin Lv and Xinghan Liu and Xinyi Liu and Xinyue Yang and Xixuan Song and Xunkai Zhang and Yifan An and Yifan Xu and Yilin Niu and Yuantao Yang and Yueyan Li and Yushi Bai and Yuxiao Dong and Zehan Qi and Zhaoyu Wang and Zhen Yang and Zhengxiao Du and Zhenyu Hou and Zihan Wang},
year={2024},
eprint={2406.12793},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={id='cs.CL' full_name='Computation and Language' is_active=True alt_name='cmp-lg' in_archive='cs' is_general=False description='Covers natural language processing. Roughly includes material in ACM Subject Class I.2.7. Note that work on artificial languages (programming languages, logics, formal systems) that does not explicitly address natural-language issues broadly construed (natural-language processing, computational linguistics, speech, text retrieval, etc.) is not appropriate for this area.'}
}Build AI with AI
From idea to launch — accelerate your AI development with free AI co-coding, out-of-the-box environment and best price of GPUs.