Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
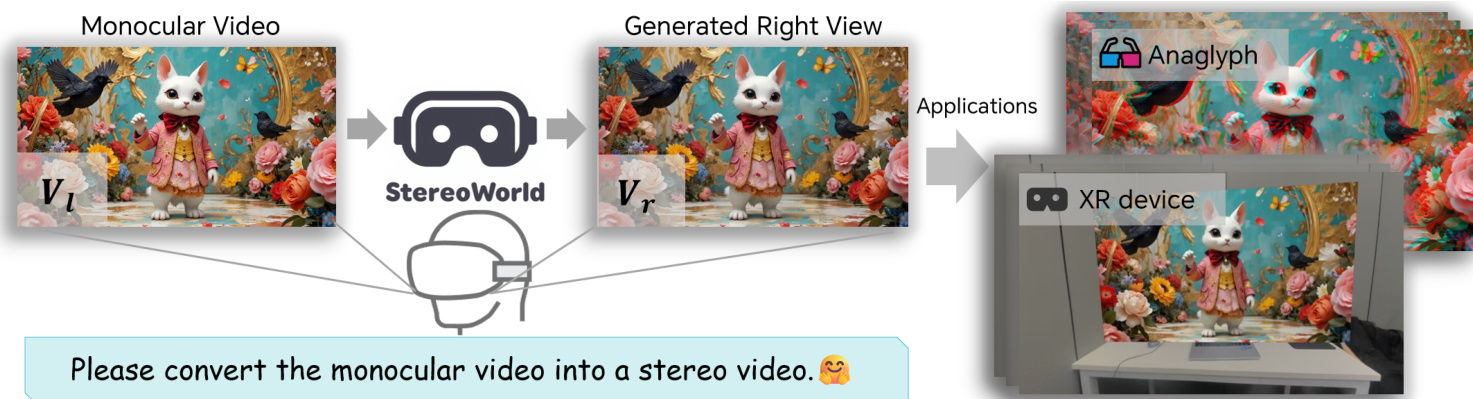
StereoWorld: Geometry-Aware Monocular-to-Stereo Video Generation
StereoWorld: Geometry-Aware Monocular-to-Stereo Video Generation
Abstract
The growing adoption of XR devices has fueled strong demand for high-quality stereo video, yet its production remains costly and artifact-prone. To address this challenge, we present StereoWorld, an end-to-end framework that repurposes a pretrained video generator for high-fidelity monocular-to-stereo video generation. Our framework jointly conditions the model on the monocular video input while explicitly supervising the generation with a geometry-aware regularization to ensure 3D structural fidelity. A spatio-temporal tiling scheme is further integrated to enable efficient, high-resolution synthesis. To enable large-scale training and evaluation, we curate a high-definition stereo video dataset containing over 11M frames aligned to natural human interpupillary distance (IPD). Extensive experiments demonstrate that StereoWorld substantially outperforms prior methods, generating stereo videos with superior visual fidelity and geometric consistency. The project webpage is available at https://ke-xing.github.io/StereoWorld/.
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from Beijing Jiaotong University, Dzine AI, and the University of Toronto propose StereoWorld, an end-to-end framework that converts monocular videos into high-fidelity stereo videos using a pretrained generator with geometry-aware regularization and spatio-temporal tiling, enabling scalable, temporally consistent 3D content generation for XR applications.
Key Contributions
- StereoWorld addresses the challenge of generating high-fidelity stereo video from monocular footage by introducing an end-to-end diffusion-based framework that repurposes a pretrained video generator, jointly conditioning on input video and enforcing geometric accuracy through disparity and depth supervision.
- The method incorporates a spatio-temporal tiling strategy to enable efficient, high-resolution stereo video synthesis while maintaining temporal coherence and 3D structural fidelity, overcoming limitations of multi-stage depth-warping approaches that suffer from artifacts and misalignment.
- To support training and evaluation, the authors curate StereoWorld-11M, the first large-scale, publicly available stereo video dataset with over 11 million frames aligned to natural human interpupillary distance (IPD), and demonstrate state-of-the-art performance with significant improvements in both objective metrics and subjective visual quality.
Introduction
The authors leverage the growing demand for immersive stereo content driven by Extended Reality (XR) devices, where high-quality stereo video is essential but costly to produce due to reliance on specialized dual-camera systems. Prior methods for converting monocular videos to stereo either depend on error-prone 3D scene reconstruction or use a multi-stage depth-warping-inpainting pipeline that disrupts spatial-temporal coherence, leading to artifacts and poor geometric consistency. To overcome these limitations, the authors introduce StereoWorld, an end-to-end diffusion-based framework that adapts a pretrained monocular video generator to directly synthesize high-fidelity stereo videos with explicit geometry-aware supervision through joint RGB and depth modeling. Their approach ensures cross-view alignment and temporal stability while enabling high-resolution generation via a spatio-temporal tiling strategy. A key enabler of this work is the creation of StereoWorld-11M, the first large-scale, high-definition stereo video dataset aligned with human interpupillary distance, which supports both training and realistic evaluation for XR applications.
Dataset
- The authors use a newly curated dataset called StereoWorld-11M, designed specifically for high-fidelity stereo video generation aligned with human visual perception.
- The dataset is built from over 100 high-definition Blu-ray side-by-side (SBS) stereo movies collected online, covering diverse genres including animation, realism, war, sci-fi, historical, and drama to ensure visual variety.
- All videos are standardized into a 1080p resolution, 16:9 aspect ratio, and 24 fps frame rate using SBS format, with left and right views extracted via horizontal cropping and stretching.
- To meet model input requirements, each video is downscaled to 480p resolution, and 81 frames are uniformly sampled at fixed intervals per clip to boost motion diversity and temporal density.
- The processed dataset serves as the primary training source for the base model, providing stereo-aligned video clips optimized for natural viewing comfort with baseline distances matching typical human inter-pupillary distance (IPD).
Method
The authors leverage a pretrained text-to-video diffusion model based on the Diffusion Transformer (DiT) architecture as the foundation for their stereo video synthesis framework. The model operates in a latent space derived from a 3D Variational Auto-Encoder (3D VAE), which encodes input videos into compact representations. The DiT backbone integrates self-attention and cross-attention modules to jointly model spatio-temporal dynamics and cross-view interactions. Training follows the Rectified Flow framework, where the forward process defines a linear trajectory between data and noise: zt=(1−t)z0+tϵ, with ϵ∼N(0,I). The model learns a velocity field vΘ(zt,t) that maps noise z1 back to data z0 via an ODE, optimized using Conditional Flow Matching (CFM) loss to regress the target vector field ut(z0∣ϵ).
To adapt this monocular generator for stereo synthesis, the authors introduce a conditioning strategy that concatenates left-view and right-view latents along the frame dimension, enabling the model to naturally fuse cross-view information through its existing 3D attention mechanisms. This avoids architectural modifications and preserves computational efficiency. Refer to the framework diagram for a visual overview of the training and inference pipelines.
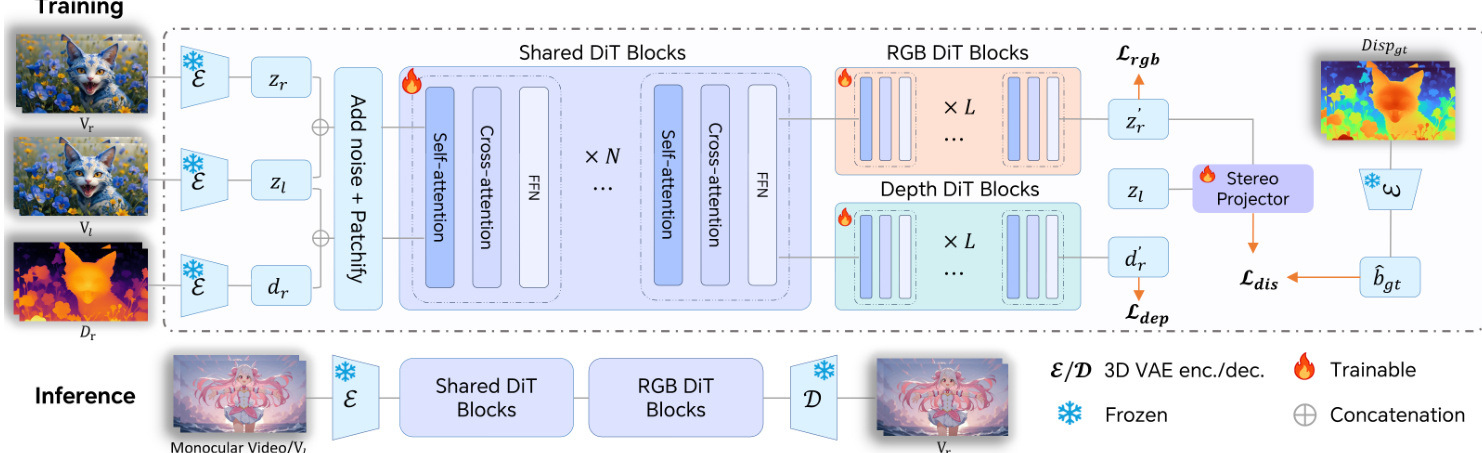
To enforce geometric consistency, the authors introduce a geometry-aware regularization composed of disparity and depth supervision. During training, ground-truth disparity maps are precomputed using a stereo matching network and used to supervise a lightweight differentiable stereo projector that estimates disparity from the generated right-view latent and the input left-view latent. The disparity loss combines a log-scale global consistency term and an L1 pixel-wise error term: Ldis=Llog+λL1LL1. This addresses misalignment and temporal drift between views.
Since disparity supervision is limited to overlapping regions, the authors supplement it with depth supervision. Precomputed depth maps for the right view are encoded into latent space and used to train a separate depth velocity field via the same CFM objective. To avoid gradient conflict between RGB and depth tasks, the final DiT blocks are duplicated into two specialized branches—one for RGB and one for depth—while earlier blocks remain shared to capture joint representations. The overall training objective combines RGB reconstruction, depth consistency, and disparity loss: L=Lrgb+Ldep+λdisLdis.
For long video generation, a temporal tiling strategy is employed during training: with probability p, the first n noisy frames are replaced with clean ground-truth frames to stabilize learning. During inference, long sequences are split into overlapping segments, with the last frames of the prior segment guiding the next to maintain temporal coherence.
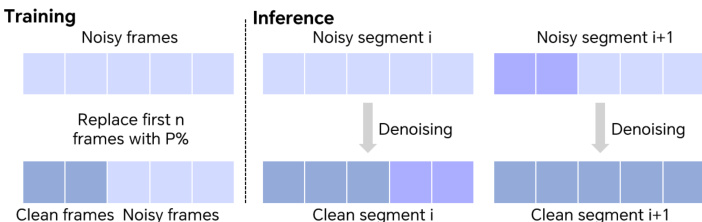
For high-resolution inference, a spatial tiling strategy is applied: the input video is encoded into latents, split into overlapping tiles, denoised independently, and then stitched back together with fused overlaps before decoding. This enables scalable generation without memory constraints.
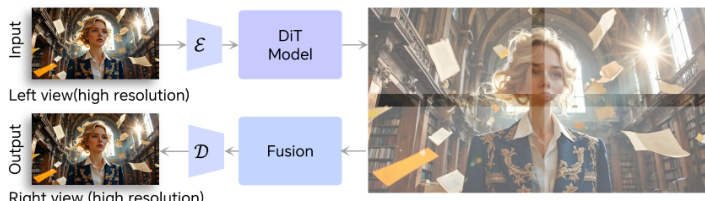
The inference pipeline uses only the shared and RGB DiT blocks, taking a monocular video as input and producing a geometrically consistent right-view video, ready for stereoscopic applications such as anaglyph or XR device rendering.
Experiment
- Introduced temporal tiling with probabilistic clean frame replacement during training to improve long-range temporal consistency and reduce flickering in generated videos.
- Applied spatial tiling via block-wise latent diffusion to enable high-resolution video synthesis beyond the 480p training resolution while preserving spatial detail and coherence.
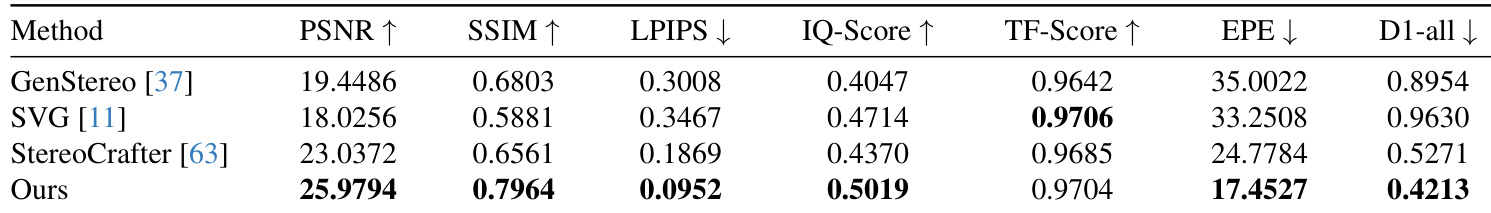
- Achieved state-of-the-art performance on quantitative metrics: on the test set, obtained 25.98 PSNR, 0.796 SSIM, 0.095 LPIPS, 0.502 IQ-Score, and 0.970 TF-Score, outperforming GenStereo, SVG, and StereoCrafter.
- Demonstrated superior geometric accuracy with 17.45 EPE and 0.421 D1-all, indicating more accurate disparity estimation and stronger stereo correspondence than baselines.
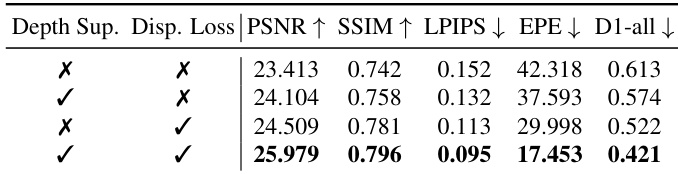
- Ablation studies confirmed the importance of depth and disparity supervision, with full model achieving best results (25.98 PSNR, 0.796 SSIM, 17.45 EPE, 0.421 D1-all).
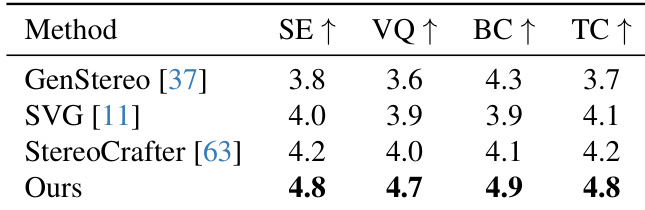
- Human evaluation with 20 participants showed significant improvements across all perceptual metrics: Stereo Effect (4.8), Visual Quality (4.7), Binocular Consistency (4.9), and Temporal Consistency (4.8), validating enhanced 3D immersion and visual fidelity.
The authors evaluate their method against three baselines using quantitative metrics for visual fidelity and geometric accuracy. Results show their approach achieves the highest PSNR, SSIM, IQ-Score, and lowest LPIPS, EPE, and D1-all, indicating superior image quality and stereo correspondence. Their method also matches or exceeds baselines in temporal stability, as reflected in TF-Score.
The authors conduct a human evaluation across four perceptual dimensions and find that their method achieves the highest scores in all categories: Stereo Effect, Visual Quality, Binocular Consistency, and Temporal Consistency. Results indicate that participants perceived their generated stereo videos as more immersive, visually clear, spatially aligned, and temporally stable compared to all baselines.
The authors evaluate the impact of depth and disparity supervision in their model, showing that combining both components yields the best performance across all metrics. Results indicate that disparity supervision alone improves geometric accuracy more than depth supervision, but the full model with both signals achieves the highest PSNR, SSIM, and lowest LPIPS, EPE, and D1-all scores. This demonstrates that the two supervision signals are complementary and essential for generating geometrically accurate and visually faithful stereo videos.