Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
2.5k Questions! HLE Has Made a Breakthrough in Building a Precise Evaluation System for Large Language Models; Jan-Nano, a Lightweight Large Language Model With 4 Billion Parameters, Is Designed for Deep Research Tasks
In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have made breakthrough progress and are capable of handling diverse tasks such as answering questions and creating content, demonstrating their strong capabilities. Benchmarks are important tools for evaluating the development capabilities of LLMs and are of reference significance for improving and enhancing the capabilities of LLMs. However, the current popular benchmarks are lacking in difficulty design, as cutting-edge LLMs have achieved similar and high scores in many existing evaluations, which limits the accuracy of LLM capability measurement and blurs the space for improving the capabilities of large models.
Based on this, the Center for AI Safety and Scale AI jointly released the multimodal human problem benchmark dataset Humanity's Last Exam (HLE).Aims to build the ultimate seal covering the frontiers of human knowledgeClosedEvaluatesystem.This dataset consists of 2,500 questions from dozens of subject areas, and is committed to providing an accurate and effective LLM capability measurement standard, clarifying the gap between current LLM capabilities and professional academics, and better achieving the rapid improvement of LLM capabilities in the frontier areas of knowledge.
At present, the HyperAI Super Neural Network official website has launched the "HLE Human Problem Reasoning Benchmark Dataset", come and try it~
Dataset download:
From July 14 to July 18, hyper.ai official website updates:
* High-quality public datasets: 10
* High-quality tutorial selection: 5
* This week's recommended papers: 5
* Community article interpretation: 5 articles
* Popular encyclopedia entries: 5
* Top conferences with deadline in July: 4
Visit the official website:hyper.ai
Selected public datasets
1. GSM8K Mathematical Reasoning Dataset
GSM8K is a mathematical reasoning dataset released by OpenAI in 2022, which aims to improve the performance of machine learning models in understanding and solving complex mathematical problems. The dataset contains 8.5k high-quality, language-diverse elementary school math word problems, covering algebra, arithmetic, geometry and other fields. The steps to solve the questions are between 2-8 steps. Its solution mainly involves a series of simple calculations using basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) to get the final answer.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/ZqNLt
2. Crops Disease Crop Disease Dataset
Crops Disease is an agricultural crop disease image dataset designed to help develop computer vision models to automatically detect and classify diseases of different crops. The dataset contains about 1,300 crop disease images, covering common diseases of a variety of crops (such as corn, tomatoes, potatoes, etc.), and each image is annotated with a specific disease category.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/GEDTA

3. OpenScience Multi-domain Synthetic Datasets
OpenScience is a multi-domain synthetic dataset released by NVIDIA in 2023, which aims to improve the accuracy of advanced benchmarks such as GPQA-Diamond and MMLU-Pro through supervised fine-tuning or reinforcement learning. The dataset contains 6 million multiple-choice question-answer pairs with detailed reasoning traces, covering multiple scientific fields such as STEM, law, economics, and humanities.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/YvAo7
4. Skywork-OR1-RL Mathematical Programming Problem Reasoning Dataset
Skywork-OR1-RL is a mathematical programming problem reasoning dataset designed to train the Skywork-OR1 (Open Reasoner 1) mathematical programming reasoning model. The dataset contains 105k mathematical problems and 14k programming problems that are verifiable, challenging, and diverse.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/mxoAv
5. Bird Species Bird Classification Image Dataset
Bird Species is a bird image classification dataset suitable for training computer vision models to identify and classify bird species. The dataset contains 7 different species, each with 1,200 images. The images of each species contain the feather pattern, color, and body structure of the bird of that species. Some of the images are intentionally blurred, tilted, or contain 2 birds of different species, which increases the complexity of the real world and makes the model more robust for accurate classification in natural environments.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/X2X2M

6. NextCoder Code Editing Dataset
NextCoder is a synthetic dialogue coding editing dataset released by Microsoft in 2025. It is used for fine-tuning large language models to help enhance the model's performance in code repair, refactoring, and optimization. It is very suitable for training AI programming assistants and improving code reading and multi-round interaction capabilities. The dataset contains about 381k single-round instruction samples (NextCoderDataset) and 57,000 multi-round dialogue samples (Conversational version), covering 8 languages such as Python and Java.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/e4MIs
7. Psych-101 Psychology Knowledge Question Answering Dataset
Psych-101 is a psychological knowledge question-answering dataset designed to help develop natural language processing models for psychological knowledge question-answering tasks and promote psychology-related AI research, especially in psychology education, sentiment analysis, and mental health applications. The dataset contains trial-by-trial data from 160 psychological experiments and 60,092 participants, totaling 10,681,650 choices.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/NUshw
8. Leukemia Leukemia Image Dataset
Leukemia is a leukemia cell image dataset designed to be used to train computer vision models to automatically detect and classify leukemia cells. The dataset contains 6,778 cell images, including normal cells (3,389) and leukemia cells (3,389).
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/Lwxwj
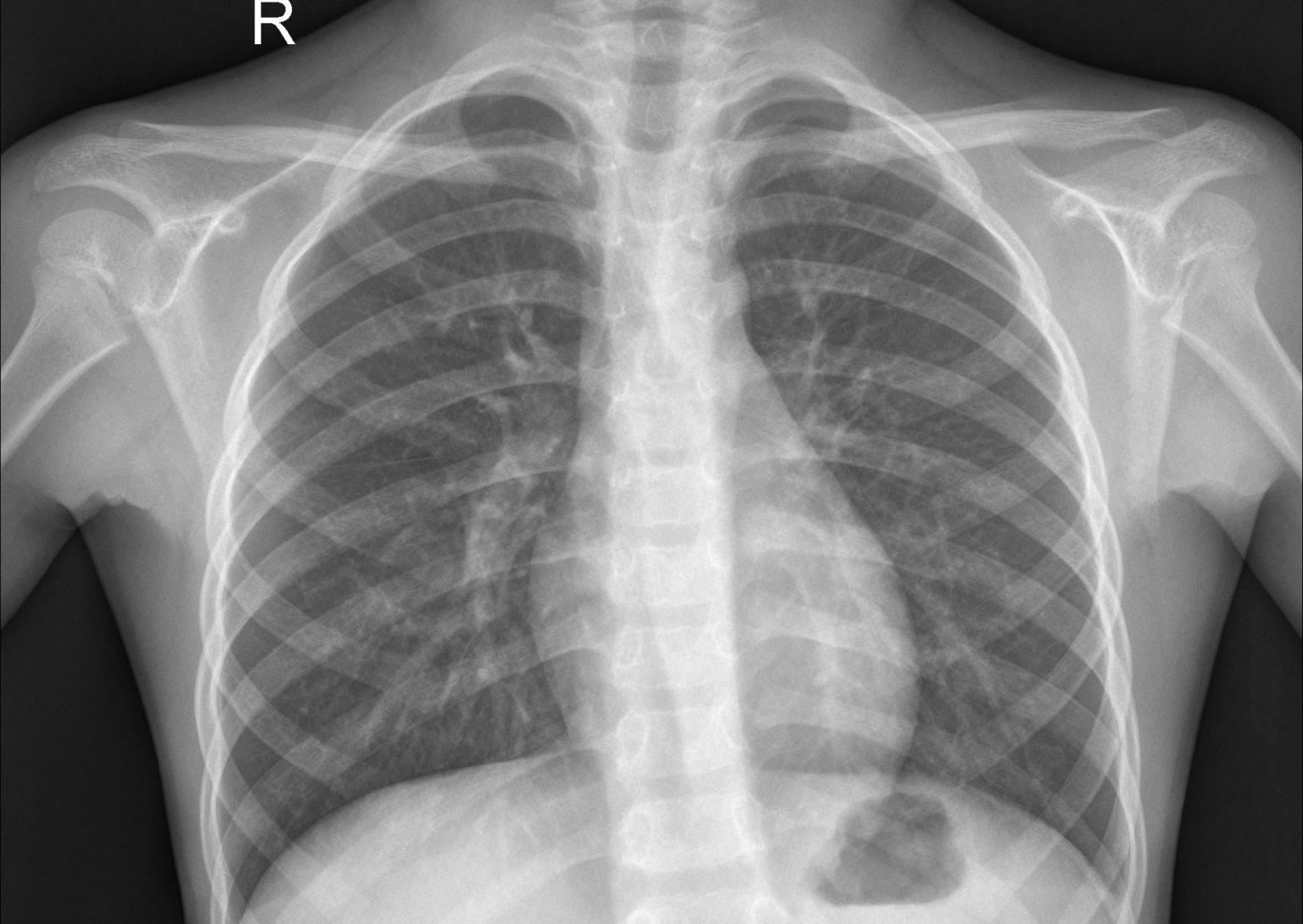
9. X-ray chest pneumonia X-ray image dataset
X-Ray Images for Chest Pneumonia is a dataset of chest X-ray images designed to train and evaluate computer vision models to help automated diagnostic systems detect respiratory diseases such as pneumonia. The dataset contains approximately 5,800 chest X-ray images divided into two categories: normal and pneumonia (bacterial and viral).
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/Pgra4
10. Soil Moisture Soil moisture image dataset
Soil Moisture is a measurement-based soil moisture dataset that aims to study the impact of soil moisture on crop growth, optimize irrigation systems, and improve agricultural production efficiency. It also has important applications in areas such as climate change and water resource management. The dataset contains 200 soil surface images from the rain-fed agricultural area of Bondowoso, Indonesia.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/TtpgP

Selected Public Tutorials
This week we have compiled 4 categories of quality public tutorials:
*AI for Science Tutorials: 2
*Text recognition tutorial: 1
*Multi-modal tutorial: 1
*Large model tutorial: 1
AI for Science Tutorial
1. RFdiffusion: a diffusion protein design model
RFdiffusion is a protein structure generation framework: it uses RoseTTAFold as the backbone network and introduces the denoised diffusion probability model (DDPM) to design new protein structures from scratch. The framework is able to design proteins with complex shapes (such as α-helices and β-folds) and accurately predict the catalytic site scaffold of enzymes.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/q7Ajs
2. Biomni: The first general biomedical agent
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent that can autonomously complete complex research tasks across multiple biomedical branches such as genetics, genomics, microbiology, pharmacology and clinical medicine, marking a new stage in the development of AI-driven scientific discovery.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/aameS
Text Recognition Tutorial
1. OCRFlux-3B: Intelligent Text Recognition Toolkit
OCRFlux-3B is a toolkit based on a multimodal large language model for converting PDFs and images into clean, readable, plain Markdown text. The tool not only provides page-level text conversion capabilities, but also supports the merging of tables and paragraphs across pages, providing powerful support for processing complex document structures.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/BGqmR
Multimodal Tutorial
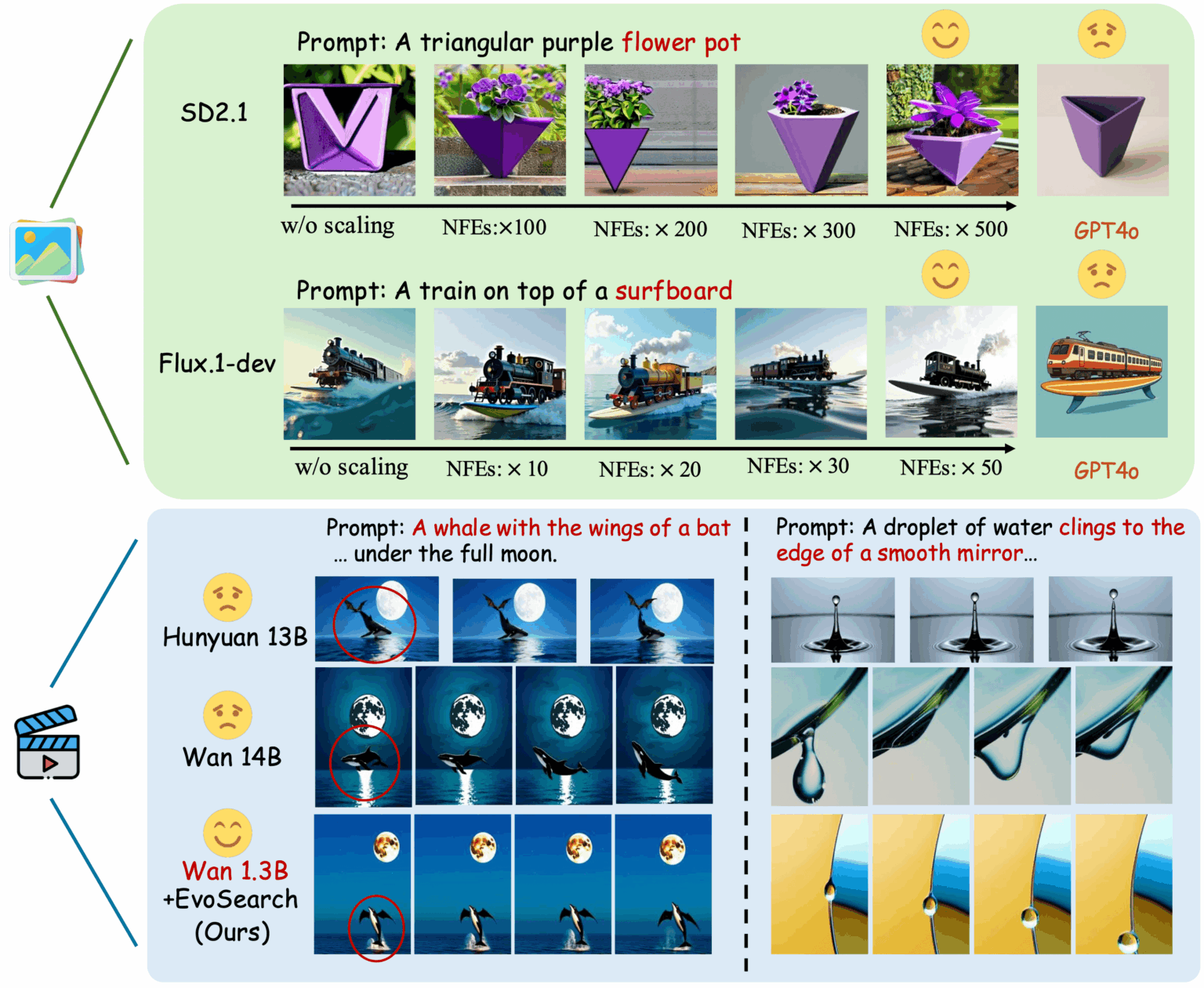
1. EvoSearch-codes: Evolutionary Algorithm Framework
EvoSearch-codes is an Evolutionary Search method launched by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology and the Kuaishou Keling team. It significantly improves the generation quality of the model by increasing the amount of computation during inference, supports image and video generation, and supports the most advanced diffusion-based and flow-based models. The model can achieve significant optimal results on a series of tasks without training or gradient updates, and exhibits good scaling up capabilities, robustness, and generalization.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/zjzrE
Large Model Tutorial
1. Jan-Nano: A compact research-specific language model
Jan-Nano is a 4-billion-parameter lightweight large language model released by the Menlo Research team on July 1, 2025. It is designed for deep research tasks and optimized for the Model Context Protocol (MCP) server to facilitate efficient integration with a variety of research tools and data sources.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/mC8gx
💡We have also established a Stable Diffusion tutorial exchange group. Welcome friends to scan the QR code and remark [SD tutorial] to join the group to discuss various technical issues and share application results~

This week's paper recommendation
1. Test-Time Scaling with Reflective Generative Model
This paper introduces MetaStone-S1, the first reflective generative model, which achieves the performance level of OpenAI o3 through a self-supervised process reward model (SPRM). By sharing the backbone network and using task-specific heads for next token prediction and process scoring respectively, SPRM successfully integrates the policy model and process reward model (PRM) into a unified interface without the need for additional process annotations, reducing PRM parameters by more than 99%, thus achieving efficient inference.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/zFLhf
2. Open Vision Reasoner: Transferring Linguistic Cognitive Behavior for Visual Reasoning
This paper proposes a two-stage paradigm based on Qwen2.5-VL-7B: first large-scale language cold-start fine-tuning, followed by nearly 1000 steps of multimodal reinforcement learning (RL), which exceeds all previous open source attempts. The final model Open-Vision-Reasoner (OVR) achieves state-of-the-art performance on a range of reasoning benchmarks, including 95.3% on MATH500, 51.8% on MathVision, and 54.6% on MathVerse.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/WucU8
3.Reasoning or Memorization? Unreliable Results of Reinforcement Learning Due to Data Contamination
The researchers found that although Qwen2.5 performs well in mathematical reasoning, its pre-training on a large-scale web corpus makes it vulnerable to data contamination in popular benchmarks, which in turn affects the reliability of the results obtained from these benchmarks. To address this problem, the researchers introduced a generator that can generate fully synthetic arithmetic problems of arbitrary length and difficulty, resulting in a clean dataset called RandomCalculation. Using these leak-free datasets, it is proved that only accurate reward signals can continuously improve performance, while noisy or erroneous signals cannot.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/WZp4V
4. NeuralOS: Towards Simulating Operating Systems via Neural Generative Models
This paper introduces NeuralOS, a neural framework that simulates the graphical user interface (GUI) of an operating system by directly predicting screen frames in response to user input such as mouse movements, clicks, and keyboard events. NeuralOS combines a recurrent neural network (RNN) to track the computer state and a diffusion-based neural renderer to generate screen images. It provides a path to create fully adaptive, generative neural interfaces for future human-computer interaction systems.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/hceCb
5. CLiFT: Compressive Light-Field Tokens for Compute-Efficient and Adaptive Neural Rendering
In this paper, we propose a neural rendering method that represents scenes as "Compressed Light Field Tokens (CLiFTs)", which preserves the rich appearance and geometry of the scene. CLiFT achieves computationally efficient rendering by using compressed tokens, while being able to change the number of tokens in a single trained network to represent the scene or render new perspectives.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/aqzHX
More AI frontier papers:https://go.hyper.ai/iSYSZ
Community article interpretation
A joint research team from Meta FAIR, Cambridge University and MIT proposed the all-atom diffusion Transformer ADiT, which broke the modeling barriers between periodic and non-periodic systems. Through two major innovations, all-atom unified latent representation and Transformer latent diffusion, it achieved a breakthrough in generating molecules and crystals with a single model.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/Dnw5r
The Stanford University team and the Arc Institute in Palo Alto, California jointly proposed a new protein sequence design method FAMPNN (Full-Atom MPNN), which can explicitly model the sequence identity and side chain structure of each amino acid residue. The model uses a message passing architecture based on graph neural networks, combined with improved MPNN and GVP modules for full-atom encoding, which can simultaneously process the main chain and side chain information of proteins.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/x04Am
Stanford University, in collaboration with Genentech, Arc Institute, UCSF and other institutions, has developed the first general biomedical AI agent, Biomni, which can autonomously perform a wide range of research tasks across different biomedical subfields and create the first unified environmental agent - mining the necessary tools, databases and solutions from tens of thousands of publications in 25 biomedical fields. System benchmarks show that Biomni achieves strong generalization in heterogeneous biomedical tasks without any task-specific prompt tuning.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/VHpMD
On July 5, the 7th Meet AI Compiler Technology Salon hosted by HyperAI came to a successful conclusion. Dong Zhaohua, senior director of Muxi Integrated Circuit, shared in depth how to apply TVM on Muxi GPU, introduced the technical characteristics of its GPU products, TVM compiler adaptation solutions, actual application cases and ecological construction vision, and demonstrated the technological breakthroughs and application potential of domestic GPUs in the fields of high-performance computing and AI.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/rxxX3
NVIDIA's research team, in collaboration with Mila from the Quebec Institute for Artificial Intelligence in Canada, proposed La-Proteina, an atomic-level protein design method based on partial latent flow matching. It addresses the key challenge of dimensional variability of explicit side chain representations during protein generation, bringing new breakthroughs to the field of protein design.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/0Sw8R
Popular Encyclopedia Articles
1. DALL-E
2. Reciprocal sorting fusion RRF
3. Pareto Front
4. Large-scale Multi-task Language Understanding (MMLU)
5. Contrastive Learning
Here are hundreds of AI-related terms compiled to help you understand "artificial intelligence" here:
July deadline for the top conference
July 11 7:59:59 POPL 2026
July 15 7:59:59 SODA 2026
July 18 7:59:59 SIGMOD 2026
July 19 7:59:59 ICSE 2026
One-stop tracking of top AI academic conferences:https://go.hyper.ai/event
The above is all the content of this week’s editor’s selection. If you have resources that you want to include on the hyper.ai official website, you are also welcome to leave a message or submit an article to tell us!
See you next week!








