Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Qian Xuesen's "Spiritual Realm" Prophecy Came True! Shanghai Jiaotong University and Tsinghua University and Other Teams Built the world's First VR Sports Intervention System REVERIE to Reshape the brain-body-mind Health of Adolescents

In recent years, the problem of adolescent obesity has become increasingly serious and has evolved into a global public health crisis. It is reported that from 1990 to 2022, the number of obese children and adolescents aged 5 to 19 worldwide has increased by about 3 times. Helping young people lose weight healthily, become more sunny, and develop lifelong exercise habits through scientific exercise methods has become an important issue in the current global public health field.
"I am currently working closely with the team of Academician Jia Weiping, and with a multidisciplinary team of experts from sports science, clinical medicine, psychology and brain science to develop a "spiritual realm" system for the intelligent and refined management of people's health in the future. I hope to use artificial intelligence and virtual reality to answer the difficult problems that have plagued the scientific community for many years:What are the effects of real-world physical exercise and virtual world (metaverse) VR exercise on human physical and mental health?". This was the research work revealed to the outside world by Professor Sheng Bin of Shanghai Jiao Tong University in an exclusive interview with The Paper in March 2022. Three years later, this result was published in Nature Medicine. But behind this research that took several years is actually a 35-year legacy of memories and dreams.
On June 23, 2025, the team of Professor Li Huating from the Shanghai Sixth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine/Institute of Active Health Strategy and Development, and the team of Professor Sheng Bin from the School of Computer Science and Technology of Shanghai Jiao Tong University/Key Laboratory of Artificial Intelligence of the Ministry of Education, through cross-medical and engineering collaborative research, jointly with the team of Researcher Wang Jihong from Shanghai University of Sport, the team of Professor Zeng Rong from Shanghai University of Science and Technology/Shanghai Clinical Research Center, and the team of Professor Lin Shuide from the National University of Singapore, published a research paper in Nature Medicine titled "Adaptive AI-based virtual reality sports system for adolescents with excess body weight: a randomized controlled trial".
The research team created the world's first virtual reality (VR) intelligent exercise intervention system REVERIE (Real-world Exercise and VR-based Exercise Research In Education) for weight control in overweight or obese adolescents.The system innovatively utilizes a virtual coach twin agent driven by deep reinforcement learning and based on the Transformer architecture, and is optimized through iterative user interaction. It can provide safe, immersive, empathetic and effective sports guidance, and its biomechanical performance and exercise heart rate response are not significantly different from real-world sports of the same type.
The research team completed the world's first randomized controlled trial (RCT) of virtual reality exercise intervention focusing on overweight and obese adolescents. The study innovatively adopted a multi-dimensional evaluation system and added an equal-intensity real exercise reference group based on the traditional control design.The combined effects of VR exercise intervention on the body, mind and brain health of overweight and obese adolescents were systematically analyzed.It not only covers metabolic indicators, but also includes dimensions such as physical fitness, mental health and willingness to exercise, and accurately evaluates the potential impact of intervention measures on adolescents' cognitive functions (Figure 1).


Technical architecture and research findings
The problem of adolescent obesity is continuing to worsen, which not only significantly increases the risk of metabolic diseases, but may also cause persistent cognitive decline. Although exercise intervention is the most effective means, adolescents generally face real difficulties such as low willingness to exercise, social barriers and lack of professional guidance. It is urgent to establish a more targeted and humane exercise intervention system.
As early as the 1990s, Mr. Qian Xuesen brilliantly translated Virtual Reality as "spiritual realm" and predicted that this technology would "greatly expand the perception of the human brain, thus allowing people to enter an unprecedented new world, and a new historical era is about to begin." This echoes the "ultimate display" concept proposed by Ivan Sutherland, the "father of computer graphics" in the 1960s. Although VR technology has initially shown results in the medical field and has shown intervention potential, it lacks personalized feedback and high-quality verification research, which limits its application.
Based on this, the team developed REVERIE, the world's first virtual reality sports system designed specifically for teenagers, which combines immersive experience with intelligent coaching.A deep reinforcement learning strategy of "template-driven combined with real-time feedback" is adopted to achieve personalized dynamic guidance.
first step,The team used high-precision motion capture technology.The actions of professional coaches in the process of teaching table tennis and football were systematically collected, and an expert coach template was constructed as a paradigm benchmark.
Step 2,Using the professional coaching template as the target behavior model,Combine the Transformer architecture with deep reinforcement learning technology to train a virtual coach agent with autonomous teaching capabilities.
Step 3.After deployment and operation, the system continuously collects interaction data between the virtual coach agent and the youth user.Continuous reinforcement learning and strategy fine-tuning for virtual coaching agents to achieve personalized sports intervention for adolescents. The results of the study showed that the REVERIE system can provide safe, effective, immersive and empathetic sports coaching, with biomechanical performance and exercise heart rate response similar to real-world sports activities of the same type of sport (Figure 2).
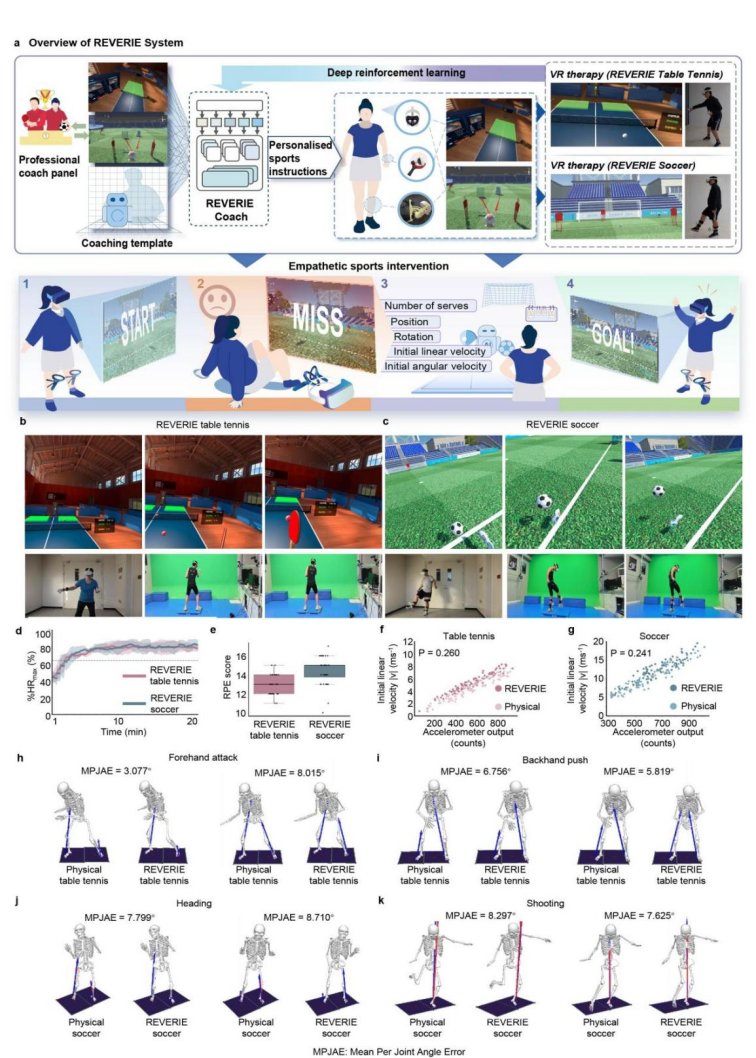
In randomized controlled clinical studies,A total of 227 overweight or obese adolescents were included.The subjects were randomly assigned to the control group, real table tennis group, real football group, VR table tennis group and VR football group. The control group maintained their original life and exercise habits, while the exercise group added three corresponding exercise intervention courses per week on the basis of the original physical education classes in school. The real exercise group and the virtual exercise group controlled the exercise intensity in the same intensity range through an armband that monitored the heart rate in real time, and the skill training content of the two groups was consistent. All subjects received uniform dietary management during the study, and the intervention lasted for eight weeks.
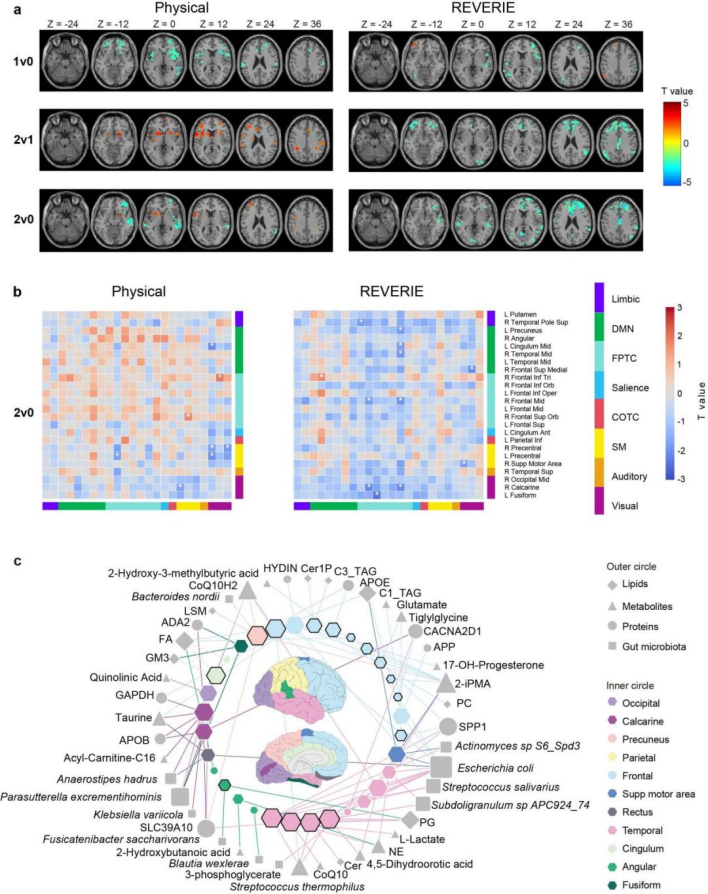
The results show thatVR exercise is comparable to real exercise in terms of fat loss and metabolic improvement, and has advantages in terms of athletic ability, mental health, and maintenance of exercise willingness.Especially in cognitive function, the VR exercise group showed enhanced perception and working memory accuracy. Brain functional imaging showed that VR exercise triggered more complex, hierarchical and reconstructive brain network activities, dynamically regulating the interaction between key neural networks and enhancing neural efficiency and plasticity (Figure 3 a, b).
To further explore the possible mechanisms of VR and real exercise interventions on overweight and obese adolescents, the research team used multi-omics integrated analysis and found that the characteristics of the intestinal microbiome, metabolome, and lipidome changed significantly after VR exercise, while significant changes in the proteome were mainly observed after real exercise intervention. The brain regions associated with differential multi-omics characteristics were particularly concentrated in the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, and precuneus, and were closely related to cognitive behavioral indicators (Figure 3 c). The mechanism of improved cognitive function after VR exercise may include two pathways:First, it affects cognitive function through the gut microbiota-brain axis; second, the interaction between proteins and metabolites jointly affects cognitive function.
Research significance and future prospects
This study built REVERIE, the world's first virtual reality sports intervention system based on deep reinforcement learning.The first virtual coach agent that combines the Transformer architecture with reinforcement learning.It has pioneered a new form of digital sports intervention;Completed the world's first RCT of VR exercise for overweight and obese adolescents.It provides high-level evidence-based medicine for virtual reality exercise therapy; it innovatively integrates task-state functional magnetic resonance imaging technology and multi-omics analysis to reveal the possible neural and molecular mechanisms by which VR exercise improves cognitive function.
The REVERIE system not only provides a new "physiological-psychological-cognitive" trinity digital solution for adolescent obesity intervention,It also provides a theoretical basis for the in-depth application of virtual reality technology in the medical field; it not only provides a revolutionary technical path for obesity intervention strategies, but also provides a practical paradigm for precise health management enabled by artificial intelligence.
The REVERIE system helps overweight and obese adolescents lose weight while promoting motor skill acquisition.Lay a foundation for continuous movement; improve neuronal efficiency and neuroplasticity, significantly improve memory, attention and mental agility; establish the willingness to actively move,Enable young people to shift from "passive participation" to "active choice".When skill acquisition, cognitive improvement and willingness formation form a closed loop, it is hoped that exercise can be integrated into daily life and sustainable exercise habits can be formed. This will allow young people to gain a healthy body, agile mind and a positive attitude through exercise, fundamentally solving the problem of obesity and laying a solid healthy foundation for their growth.
Nature Medicine also published a commentary titled "Virtual reality sports to tackle pediatric obesity", stating that "REVERIE is a landmark study that lays the foundation for future investigations and supports the use of virtual reality sports as an innovative, effective and safe strategy to improve and enhance the health of overweight adolescents."
Sheng Bin from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, co-corresponding author of this study, believes that virtual reality is essentially the exploration of human cognition of the origin of the world under the philosophical assumption of "brain in a vat".The REVERIE study has broken through this assumption - VR is no longer a closed perception simulation experiment, but more like a symphonic resonance intervention of the human physiological nervous system in a digital mode.Its impact on the body and mind is showing a multi-dimensional map of physiology, biochemistry and brain science. This is not only a technological iteration, but also a leap in cognitive paradigm: when VR reconstructs the perception matrix through the coordinated stimulation of vision, touch and even the vestibular system, people need to look at it from a future perspective: during the peak period of adolescent neuroplasticity, the duration threshold and frequency rhythm of VR intervention still need to be decoded through future research. "The current exploration is just the beginning and the first step of human exploration in this regard" - only continuous future research can truly outline a new coordinate system for human physical and mental health in the digital intelligence era.
About the Author
Professor Li Huating from the Institute of Active Health Strategy and Development of the Sixth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Professor Sheng Bin from the Key Laboratory of Artificial Intelligence of the Ministry of Education, School of Computer Science and Technology of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Professor Lin Shuide from the National University of Singapore, and Professor Zeng Rong from ShanghaiTech University/Shanghai Clinical Research Center are the co-corresponding authors of this article.
The co-first authors of this article include Wang Jihong, researcher at Shanghai University of Sport, Qin Yiming, postdoctoral fellow at Tsinghua University School of Medicine, Wu Qian, doctoral student at the Sixth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (supervisor: Professor Li Huating), Zeng Dian, postdoctoral fellow at Tsinghua University School of Medicine, Dr. Gao Xiaojing from ShanghaiTech University/Shanghai Clinical Research Center, Wang Qinyi, doctoral student at the Sixth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (supervisor: Professor Li Huating), Li Zhen, associate professor at Shanghai University of Sport, Ni Yueqiong, researcher at the Sixth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Li Haoxuan, doctoral student at Shanghai University of Sport (supervisor: Professor Sheng Bin), Zhang Ping, professor at Ohio State University, and Guo Jingyi, assistant researcher at the Sixth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine.
In addition, this study was supported by Professor Jia Weiping of the Sixth People's Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Professor Huang Tianyin and his team, Professor Felipe Fregni of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Professor Wu Jiarui, Director of the National Protein Science Research Facility (Shanghai), Professor Wu Enhua of the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Professor Ma Xindong of Tsinghua University, Professor Xu Aimin of the University of Hong Kong, Professor Huang Zhifeng of Wenzhou Medical University, Professor Jinman Kim of the University of Sydney, Assistant Researcher Huang Xiaojun of Shanghai Sport University, Associate Professor Bi Lei of the Institute of Translational Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Professor Shen Dinggang and his team of the School of Biomedical Engineering, ShanghaiTech University, Baoshan District Education Bureau, Shanghai Women's Football Team and China Table Tennis Academy, and other multidisciplinary experts and research teams. This study was funded by the Education Informatization Teaching Application Practice Community Project and the National Science and Technology Innovation 2030-National Science and Technology Major Project of the National Health Commission.