Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
This year's AI Predicted the European Cup Champion, and All of Them Were Slapped in the Face

The European Cup, which lasted for a month, finally came to an end.
In the early morning of July 12 (Monday) Beijing time, Italy faced England in the final of this European Cup. The two teams tied 1-1 in 120 minutes, and Italy defeated England 3-2 in a penalty shootout to win the European Cup.
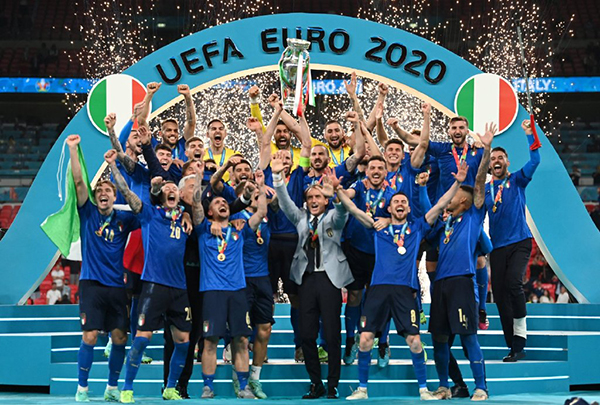

The last time Italy won the European Cup was in 1968, and it was runner-up in 2000 and 2012. This year, it won the championship again after 53 years. This has made the European Cup, which was delayed by one year, a hot topic around the world in recent days.
As early as a few months before the competition, many research institutions announced their predictions for the competition. Each AI combined the data, game results and player performance of each team in recent years to predict the favorites to win the European Cup and the results of individual games.
It now seems that most AI predictions have been proven wrong.
The Analyst: France has the best chance of winning the championship
The data website The Analyst made an AI prediction on the probability of each team winning the European Cup.AI prediction results show that France has the highest probability of winning, with a winning rate of 20.5 %, but in the end the French team was eliminated in the quarterfinals.
Comparing the prediction results of The Analyst's AI with the final results, it seems that there is indeed a huge difference. Italy, which actually won the championship, was considered the sixth favorite to win, while England, the final runner-up, was even ranked ninth on the prediction list.

Goldman Sachs: We think the champion is Belgium!
Goldman Sachs' forecast is more mature and stable. After the group stage ended and the top four were formed, Goldman Sachs chose to adjust the model and review it based on the final results.
Goldman Sachs first used a large data set of more than 6,000 international football matches since 1980 to model the number of goals scored by each team (excluding friendly matches), and quantified these data into four dimensions to assess the team's chances of winning:
1. Team Strength: World Football ELO Rating
2. Recent momentum: Number of goals scored and conceded in recent games
3. Home advantage: 0.4 more goals scored at home
4. Big Game Effect: Performance in big games is better than in other games

Based on the above data and dimensions, Goldman Sachs researchers believe thatBelgium will eventually win the championship, and the top four are: Spain, Belgium, Italy and Portugal.
Faced with the final reality, the researchers also said humorously: Although we carefully considered the randomness of the game, we also predicted that the result was highly uncertain. It turns out that even with complex statistical techniques, football is still a difficult game to predict.
Why are football games so hard to predict?
In this year's European Cup, it seems that most AI predictions of the results have been slapped in the face.
In this European Cup, the Netherlands and France were unexpectedly eliminated early, and dark horse teams such as the Czech Republic and England unexpectedly qualified, which attracted more attention and heated discussions.
In addition to The Analyst and Goldman Sachs, many institutions have been involved in predicting the results of sports events in recent years, usually combining traditional statistics and machine learning methods.
Usually this kind of event prediction AI,It will collect tens of billions of data points from tens of thousands of games played by more than a thousand teams around the world in recent years, and structure all factors that may affect the game (such as player injuries, transfers, weather conditions, etc.).
RecombinationBookmaker's Handicap and Odds, use artificial intelligence algorithms such as machine learning and deep learning to build models, and obtain match prediction results through analysis and matching.

Currently, artificial intelligence relies on quantifiable data for observation. But if the data is not true, the results will inevitably be inaccurate.In addition, the model cannot incorporate factors that are difficult to quantify, such as the team's immediate status, player emotions, fan emotions at the scene, etc.
Debs Balme, director of data analytics company Merkle, said:Predictions in soccer matches are inherently more complex than in other games.Due to the characteristics of football matches, the number of matches is much less than that of basketball, baseball and other sports, and the available data is also less. For example, baseball players have to play 162 games in a season, while the football league has only 38 games in a season. In addition to other competitions such as cup competitions, even the top teams can only play more than 50 games in a season. Therefore, the difficulty of predicting football matches is much higher than that of other sports events.
The excitement of not being able to determine the winner until the last minute and the uncertainty in the game are one of the reasons why football is the most popular and entertaining sport in the world, and also the greatest charm of sporting events.