Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Pedestrian re-identification Is Gaining More and More attention. What Are the Hot Topics?
Pedestrian re-identification technology is widely used in scenarios such as smart cities and autonomous driving, and has achieved rapid development in recent years, thanks to the expansion of training data and the development of deep learning.
In the vast crowd, can you find the person you are looking for at a glance?
Nowadays, this task may be a piece of cake for computers, thanks to the rapid development of pedestrian re-identification technology in recent years.
Person Re-identification, also known as person re-identification, or ReID for short, is a technology that uses computer vision technology to determine whether a specific person exists in an image or video sequence. In simple terms,It is able to identify the same target person in different scenes through features such as clothing, body shape, hairstyle, etc., so it is also called cross-border tracking technology.

Person re-identification has become a key research direction in the field of computer vision after face recognition.
Although facial recognition technology is very mature, in many situations, such as dense crowds, low-resolution surveillance cameras, or biased shooting angles, faces often cannot be effectively recognized.Pedestrian re-identification has become an important supplement.
Therefore, face re-recognition has received more and more attention in recent years, and its related applications have become increasingly extensive.
To understand a technology, we must first understand what problem it solves, how it achieves breakthroughs, what stage it has reached, and what challenges it faces. Next, we will conduct a comprehensive analysis.
Where is pedestrian re-identification used?
First of all, as mentioned above, pedestrian re-identification is an important supplement to face recognition technology.
The premise of face recognition is a clear frontal face photo. However, when the image only shows the back or other angles where the face cannot be seen, face recognition fails. At this time, pedestrian re-identification can continue to track the target person through features such as posture and clothing.
At present, pedestrian re-identification technology is widely used in the fields of security, autonomous driving, etc. For example:
Smart Security:Police investigators can use ReID to help quickly screen suspicious persons;
Intelligent search system:In places with large traffic volume, such as airports and train stations, ReID can be used to find lost children and elderly people;
Smart Business:ReID can dynamically track user trajectories in real time based on photos of pedestrian appearance, so as to understand the user's interests in the mall and optimize the user experience;
Autonomous Driving System:Through ReID, pedestrians can be better identified and the safety of autonomous driving can be improved.
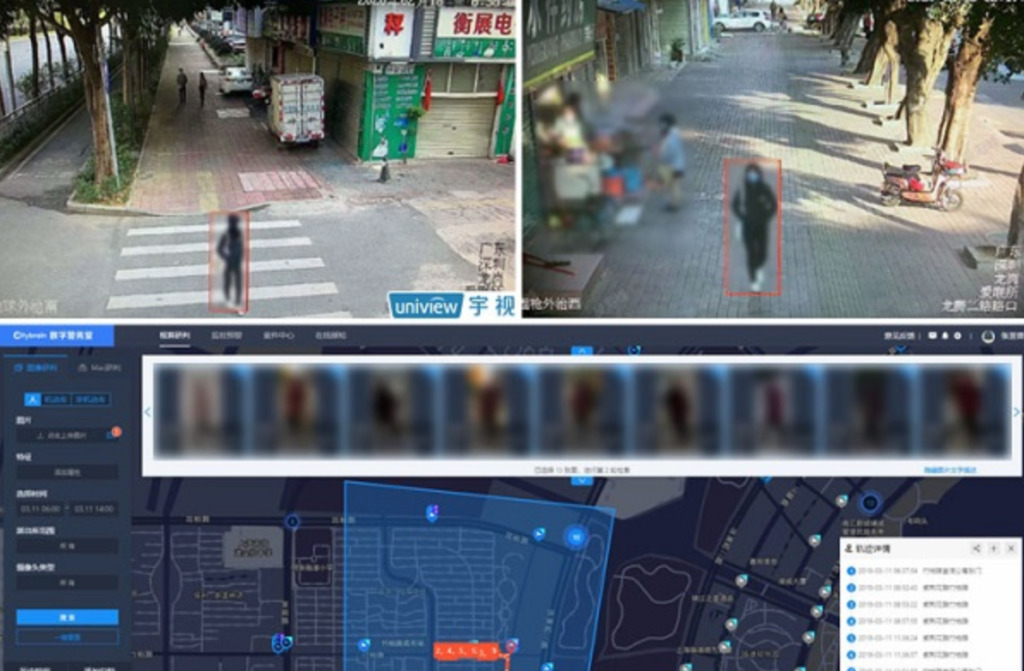
The key to technological breakthroughs: large-scale data sets
According to relevant researchers, the realization of pedestrian re-identification technology generally requires the following five steps:
- Data collection;
- Bounding box generation;
- Training data annotation;
- Model training;
- Pedestrian retrieval
Among them, data collection as the first step is the basis of the entire pedestrian re-identification research.In recent years, the significant breakthroughs in person re-identification have been achieved thanks to the promotion and support of large-scale data sets.
This article will introduce several commonly used pedestrian detection datasets for your research and model training.
INRIA Person Dataset Pedestrian Detection Dataset
The INRIA Person dataset is currently one of the most popular and widely used static pedestrian detection datasets.Released by INRIA (French National Institute for Information and Automation) in 2005. This dataset is used to detect upright pedestrians in images and videos.
This dataset contains data in two formats.
Category 1: original images and corresponding upright pedestrian annotations;
Category 2: positive images of upright pedestrians and corresponding negative images normalized to 64×128 pixels.

The basic information of the dataset is as follows:
INRIA Person Dataset
Publishing Agency: INRIA
Quantity included:The training set and test set have a total of 2573 images
Data format:Positive samples are in .png format, negative samples are in .jpg format
Data size:969MB
Update time:2005
Download address:https://orion.hyper.ai/datasets/5331
Related papers:
UCSD Pedestrian Video Dataset
UCSD Pedestrian Pedestrian video data was collected and organized by the University of California and City University of Hong Kong and released in February 2013.
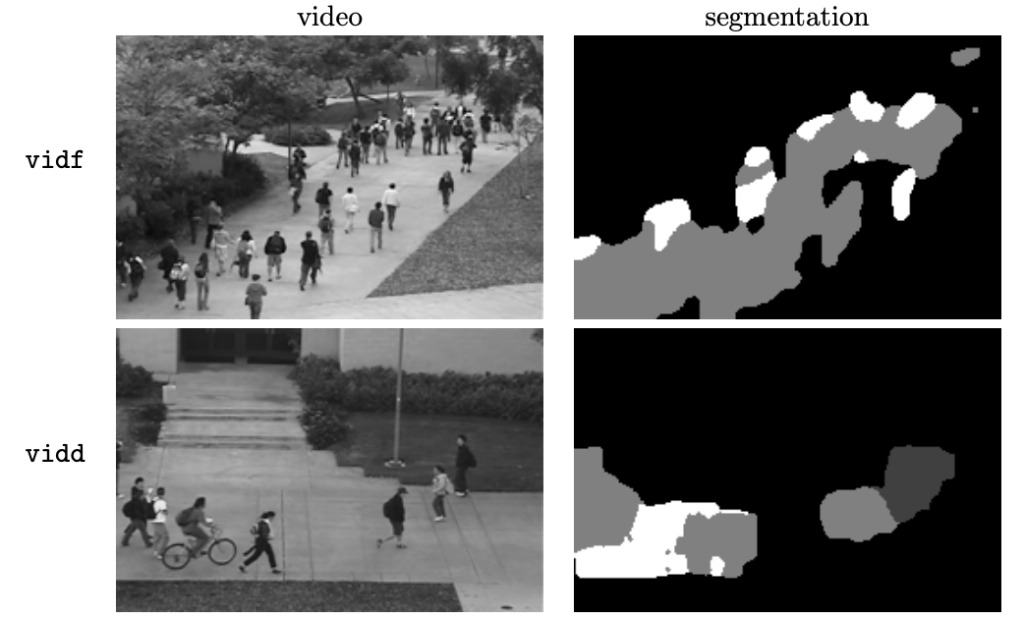
This dataset is used for motion segmentation and crowd counting.The dataset contains videos of pedestrians on the sidewalk of UCSD (University of California, San Diego), all from a fixed camera.
All videos are 8-bit grayscale, 238×158 in size, 10 frames/second. The original video is 740×480, 30 frames/second, which can be provided upon request.
The video directory contains the videos of two scenes (split into two directories, vidf and vidd). Each scene is in its own vidX directory and is split into a set of .png segments.

The basic information of the dataset is as follows:
UCSD Pedestrian Dataset
Publishing Agency: UCSD, City University of Hong Kong
Quantity included:About 10 hours of video
Data format:.png
Data size:vidf: 787MB; vidd: 672MB
Update time:February 2013
Download address:https://orion.hyper.ai/datasets/9370
Related papers:
Caltech Pedestrian Detection Benchmark
The Caltech Pedestrian Detection Benchmark database was released by the California Institute of Technology in 2009 and is continuously updated every year.
This database is currently the largest pedestrian database, containing about 10 hours of video.It is mainly shot by on-board cameras of vehicles traveling in normal traffic environments in the city, with a video resolution of 640×480 and 30 frames per second.
A total of about 250,000 frames (about 137 minutes), 350,000 rectangular boxes, and 2,300 pedestrians are annotated in the video. In addition, the temporal correspondence between the rectangular boxes and their occlusion are also annotated.

The basic information of the dataset is as follows:
Caltech Pedestrian Dataset
Publishing Agency: California Institute of Technology
Quantity included:The training set and test set have a total of 2573 images
Data format:.jpg
Data size:11.12GB
Update time:July 2019
Download address:https://orion.hyper.ai/datasets/5334
Related papers:
What are the advanced methods?
The research in the field of person re-identification has been going on for nearly three decades. In recent years, this technology has made great progress thanks to the large-scale data sets and the development of deep learning.
Here we cite two of the latest methods for your study and reference.
Eliminate the style differences between different cameras
In the top international computer vision conference CVPR 2020, the Chinese Academy of Sciences published a paper Unity Style Transfer for Person Re-Identificationmiddle,A UnityStyle adaptation method is proposed, which can unify the style differences between different cameras.

Whether it is the same camera or different cameras, when shooting pictures, there will be large differences due to the influence of time, lighting, weather, etc., which will bring difficulties to target query.
To solve this problem, the research team first created UnityGAN to learn the style changes between cameras and generate shape-stable styleunity images for each camera, which they call UnityStyle images.
at the same time,They use UnityStyle images to smooth out style differences between different images, so that the query (query target) and the gallery (image library) are better matched.
They then applied the proposed method to the re-identification model, expecting to obtain more style-robust deep features for query.

The team conducted extensive experiments on widely used benchmark datasets to evaluate the performance of the proposed framework, and the experimental results confirmed the superiority of the proposed model.
Solving the pedestrian occlusion problem
Paper published by Megvii Research Institute at CVPR 2020 "High-Order Information Matters: Learning Relation and Topology for Occluded Person Re-Identification"middle,It solves the most common and challenging problem in this field - pedestrian occlusion.

In this paper, the framework proposed by Megvii Research Institute includes:
- A first-order semantic module (S), which can extract the semantic features of the key point regions of the human body;
- A high-order relation module (R), which can model the relation information between different semantic local features;
- A high-order human topology module (T) that learns robust alignment and predicts the similarity between two images.
These three modules are jointly trained in an end-to-end manner.

Previously, we haveThe hottest ECCV in history has opened, and these papers are so interesting.The paper "Please Don't Disturb Me: Pedestrian Re-identification under Interference from Other Pedestrians" published by Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Sun Yat-sen University, and Tencent Youtu Lab was introduced in the paper. The method proposed in the paper solves the problem of incorrect retrieval results caused by background pedestrian interference or human body occlusion in crowded scenes. Students who are interested can review it again.
Hot technologies, but still have difficulties
At present, pedestrian re-identification still faces considerable challenges, including data, efficiency, performance and other aspects.
In terms of data, the video data obtained will be very different due to different scenes (such as indoors and outdoors), changes in style in different seasons, differences in light at different times (such as day and night), etc. These are all interference factors for pedestrian re-identification.These interference factors not only affect the model recognition accuracy, but also the recognition efficiency.

Therefore, although we have seen that pedestrian re-identification has even surpassed human resolution capabilities in existing cases, there are still many problems to be solved.
Go to the following link:https://orion.hyper.ai/datasets,Search for "pedestrians" or clickRead the original article,More pedestrian detection datasets are available.
-- over--