Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
The 600-year-old Forbidden City Has Also Adopted Artificial Intelligence

Cultural relics that have been passed down for hundreds or even thousands of years are constantly being eroded by time. How to better protect cultural relics and pass them down in a more complete manner is a major challenge in this field. Today, AI technology has begun to cross over into the field of cultural relic protection, allowing more cultural relics to continue their lives.
The Forbidden City, China's national memory, began construction in the fourth year of Emperor Yongle's reign (1406) during the reign of Emperor Chengzu of the Ming Dynasty and was completed in the eighteenth year (1420). This year marks its 600th anniversary.
During these six hundred years, the Forbidden City has remained standing despite all the ups and downs, and has now caught up with the wave of artificial intelligence.
At the just concluded WAIC 2020 World Artificial Intelligence Conference, Shan Jixiang, former director of the Palace Museum, delivered a keynote speech at the conference.It introduces how the Forbidden City uses technology to achieve cultural relic protection and cultural dissemination.
The Forbidden City embraces AI: taking visitors back to the Qing Dynasty
In recent years, the Forbidden City has become a veritable Internet celebrity, not only with tens of millions of fans on media platforms, but also through successful marketing, it has become a top cultural symbol. Since 2013, the Forbidden City has launched exclusive apps, and 10 apps have been released so far, including "A Day in the Life of an Emperor", "Auspiciousness in the Forbidden City", "Daily Forbidden City", etc.
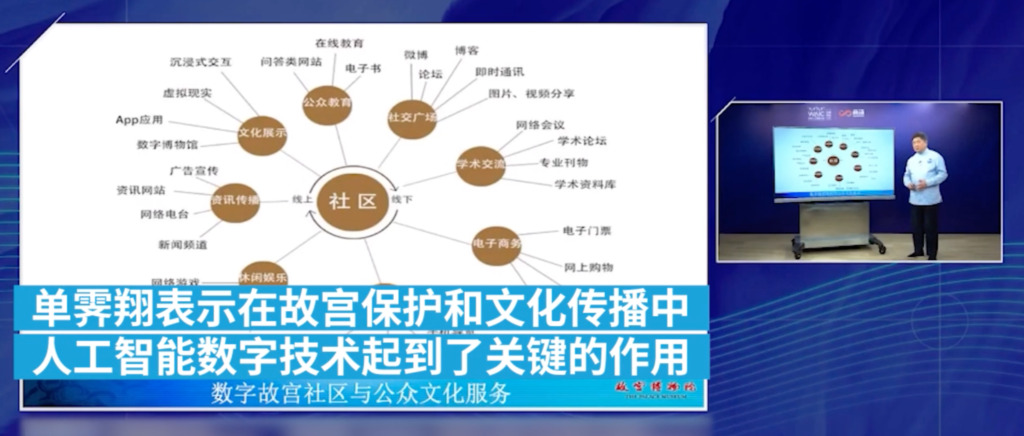
In addition to using technology to achieve cultural dissemination,The Forbidden City also uses AI technology to protect, restore, and fully display cultural relics, allowing visitors to see a more complete Forbidden City.
Digital museum: Visitors can also interact with cultural relics
On December 22, 2015, after two years of construction,The Duanmen Digital Museum of the Palace Museum was finally completed and unveiled for the first time.
Duanmen was the main gate of the Forbidden City in the past.By collecting high-precision cultural relic data and combining it with academic research, cultural relics and historical and cultural heritage are reproduced in the digital world.

Shan Jixiang introduced that tourists here,You can talk to more than 1,200 ancient buildings and see 1,500 large carpets that have not been exhibited.
For example, visitors can call up a piece of calligraphy and copy it, and then ask the system to score it.
Another digital pavilion is the "Digital Treasure Pavilion".It consists of 18 high-definition screens in 9 columns and 2 rows, and selects more than 160 artifacts from the Forbidden City collection in 12 categories, using high-precision 3D models to build a virtual "Treasure Pavilion".
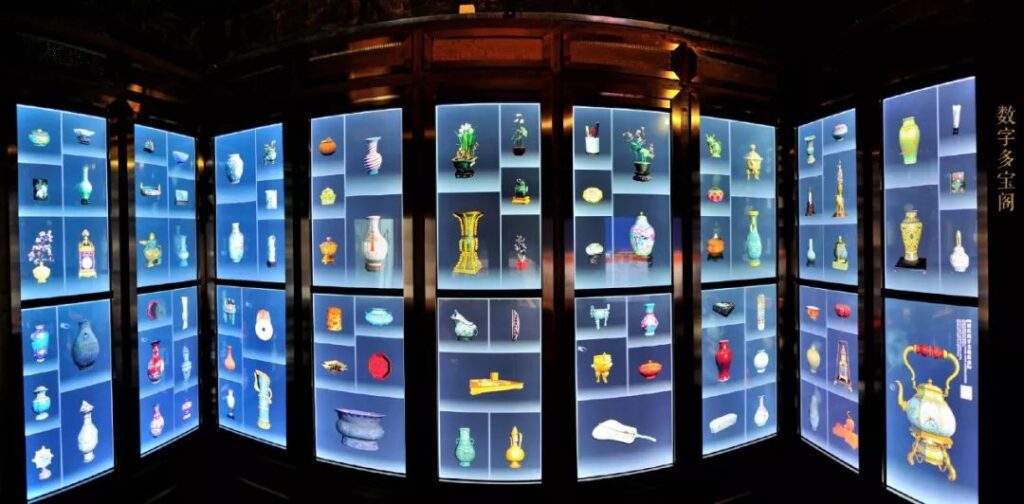

About 50 of the artifacts can be touched, zoomed, and rotated to various angles to view the details, and there are 7 artifacts that use multimedia to further explain the information contained in them to the audience.
In addition, the "Digital Treasure Pavilion" also uses digital means to let people understand the production and use process of cultural relics.
VR tour: panoramic tour of unopened areas
Digital museums not only allow people to view artifacts up close, but also allow visitors to visit previously inaccessible spaces.
Shan Jixiang gave an example, saying that Emperor Qianlong's study, the Sanxiting Hall, only has an area of 8 square meters and is divided into two parts, the inner and outer parts, by lattices. The area is too small, so it is difficult to open to tourists, and people could only look through the glass before.
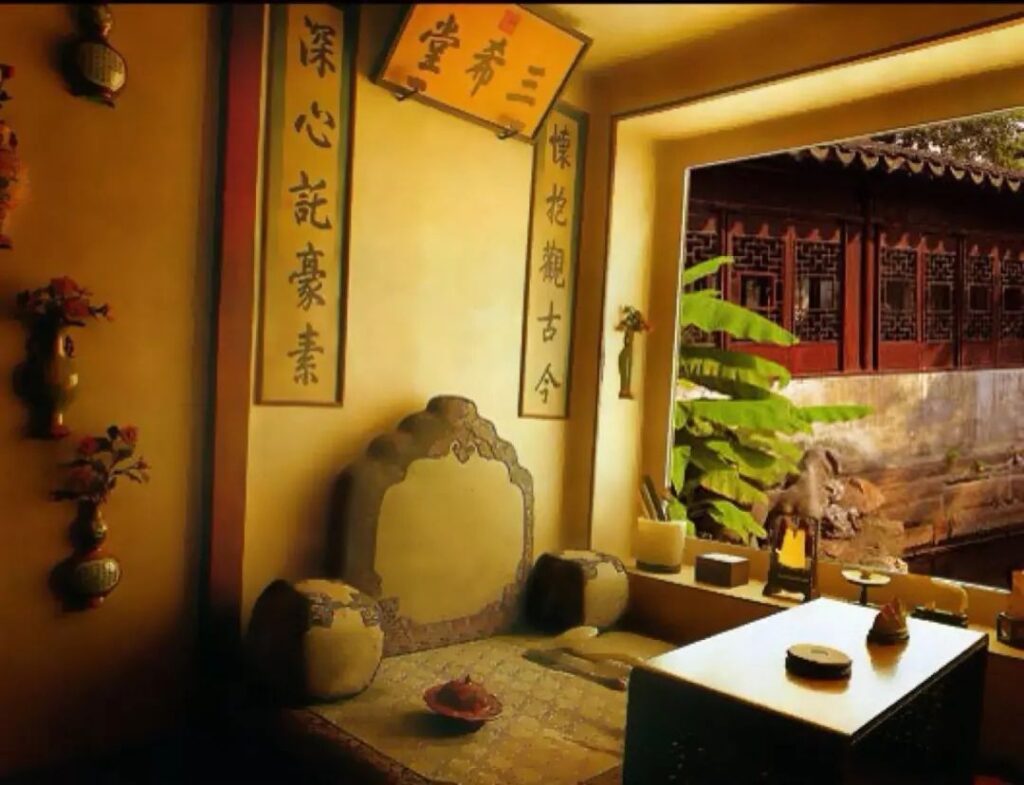

After using digital technology, a high-definition projection system was used to construct an immersive three-dimensional virtual environment wrapped on three sides, highly simulating the Sanxi Hall. Visitors can also "walk into" the Sanxi Hall in VR, appreciate the original furnishings there, and feel the interior space of the palace.Visitors can also admire themselves wearing ancient costumes in front of a digital screen.
In addition, some ancient buildings cannot be visited due to renovations, but through VR technology, tourists can still have a clear view of them.
For example, the Hall of Mental Cultivation is under renovation this year and cannot be entered.However, tourists can walk into the "Digital Yangxin Palace" and have a different experience.
“Tourists can sit on the emperor’s throne and review memorials themselves, stamp their own seals, and the system will evaluate whether you reviewed it better than the emperor.Here, you can interact with the ministers. These ministers are very good at chatting. Each minister can say more than 500 sentences. They will give you positive responses to whatever you say, which will make you happy."Shan Jixiang introduced.
AI monitoring environment: serving as the “health doctor” of cultural relics
In addition to digital museums, Shan Jixiang also said that artificial intelligence has many applications in the field of cultural heritage protection, such asExhibition hall temperature and humidity, wall settlement monitoring, termite monitoring, ancient building disease monitoring, visitor flow monitoringwait.
However, we have not yet learned how the Forbidden City uses AI to monitor the environment, but this type of technology has long been used in the protection of other cultural relics and has become a "health doctor" for cultural relics.
For example, cultural relics exposed outdoors, such as the Dunhuang murals and the Terracotta Warriors and Horses of the Qin Shihuang Mausoleum, are often faced with the risk of weathering and rain erosion.
In response to the protection difficulties of this type of cultural relics, Zhang Jiawan's team from the Information Technology Research Center for Cultural Heritage Protection and Inheritance at Tianjin University,Developed preventive protection technology with the "model of correlation between cultural relics and risk sources" as its core.
The team worked with the Dunhuang Academy to conduct a survey of 11 caves and 47 monitoring points.Continuous annual monitoring of the murals and painted sculptures.

Accurately sense and measure the tiny changes in the body through micro-change monitoring technology;At the same time, with the help of image analysis, machine learning, photogrammetry and other related technologies, a multi-scale quantitative analysis of the four types of diseases in the entity was carried out.
The team monitored some murals in the Mogao Grottoes in Dunhuang from 2014 to 2016, and then analyzed the monitoring results. For the first time, the team discovered subtle changes in the murals at the 0.1 mm level within a short period of one year. This result is generally considered by authoritative experts in the field of cultural relics protection to be a substantial breakthrough in this field.

Zhang Jiawan said that this technology is to find a way to deal with risks.“We need to build an integrated platform for perception, analysis, assessment, and response.”
At present, the same technology has been applied in heritage sites such as the Dunhuang Academy, the Summer Palace, and the Labrang Monastery.
AI + Art Conservation: A Broad Field with Great Potential
The above is just the tip of the iceberg of what we have seen in the protection of cultural relics by technology. All over the world, AI technology has provided convenience for many cultural relic restoration workers, making more cultural relics "alive".
With the help of technology, the Forbidden City is giving tourists more and more surprises.
Shan Jixiang said,“How to bring museum culture into every household through artificial intelligence is an endless topic.”The results that have been achieved now give us reason to believe that this topic will eventually bear fruit.
-- over--