Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Will Robots Completely Replace Workers? Don’t Worry, Only human-machine Combination Can Make Work Less Tiring

With the development of machinery and automation technology, the manufacturing industry has been actively following and using the most advanced technology to improve production efficiency. A large number of factories have invested heavily in the introduction of automated production equipment, which inevitably leads to problems caused by technical failures. How to balance human operators and industrial AI should be given equal attention.
Data released by Oxford Economics, a well-known British analysis agency: By 2030, ten years from now, 20 million manufacturing jobs around the world will be replaced by industrial robots.
For every new robot entering the workforce, an average of 1.6 human manufacturing workers will be replaced.
Foxconn, the electronics manufacturing giant, had a total of 1.3 million workers during its peak production period. In recent years, Terry Gou has been actively seeking the transformation to "Industry 4.0" and mentioned in an interview that "in the next five years, 80% of the workers will be laid off or trained for transformation."
To this end, Foxconn's "Million Robots" plan has already put robot workers into use in its Zhengzhou factory, Chengdu tablet factory, and computer/peripheral factories in Kunshan and Jiashan.
In 2016 alone, Foxconn reduced the number of workers at its Kunshan factory from 110,000 to 50,000, directly replacing 60,000 workers.
The booming development of robots, robotic arms, and industrial AI makes us feel that the dream of Industry 4.0 is just around the corner.
Industrial robots: Not yet a perfect solution
In mid-2018, a horrific accident occurred at General Motors' Nexteer Lingyun Wuhu plant.
A 39-year-old experienced operator was changing a tool on a handling robot on an automated production line when the robot suddenly started for no reason and the operator was trapped in the handling robot and unable to escape.
Although he was rescued in time by his colleagues, he eventually died in the hospital due to his serious injuries.
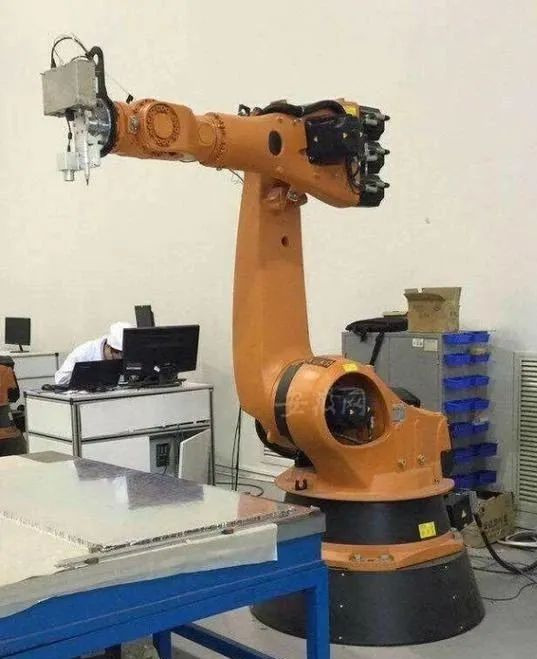

The robot involved in the accident is an industrial handling robot, shaped like a crane, with thick arms, and is used to lift and carry heavy objects.
Machines have their own instabilities, and humans have their own weaknesses.
Semi-supervised industrial AI: Human-machine collaboration makes work less tiring
Industrial assembly may seem like a simpler procedure in the manufacturing process, but in reality it involves repetitive and tedious steps, and some omissions and errors may occur due to human factors.
An American startup called Invisible AI uses AI technologies such as computer vision to avoid the hidden dangers that may arise in this link.
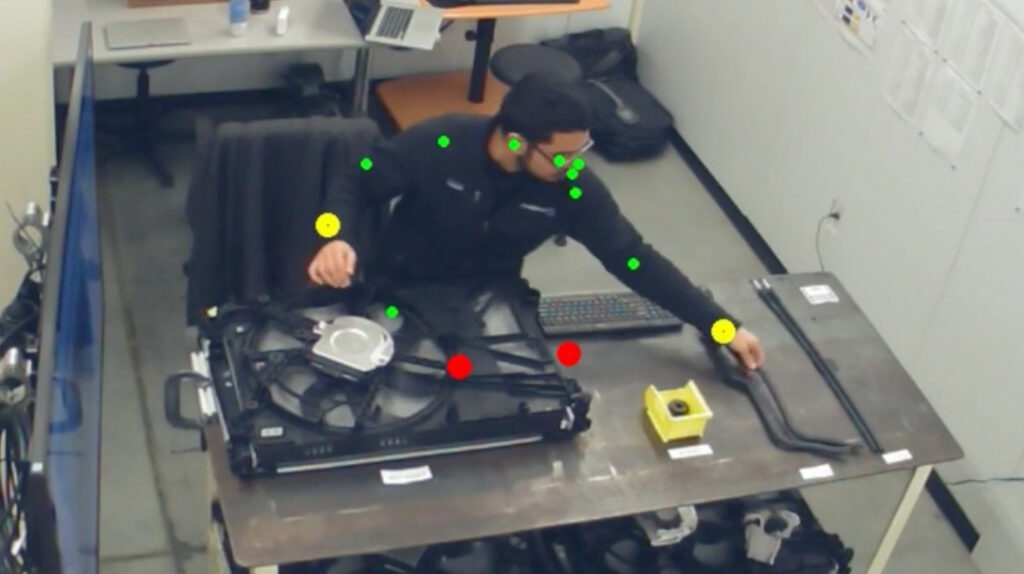
Invisible AI has launched a camera-based computer vision solution that can be applied to factory production lines. It monitors the assembly process of workers through video and provides timely reminders when errors occur.
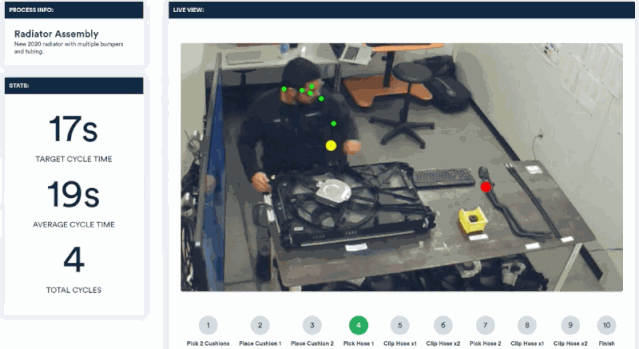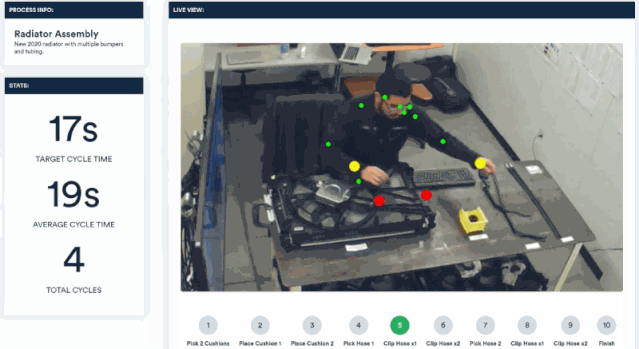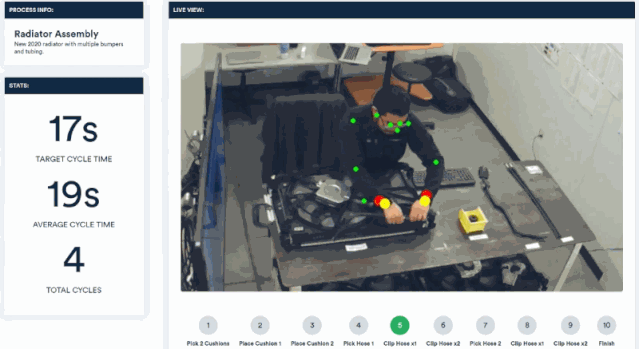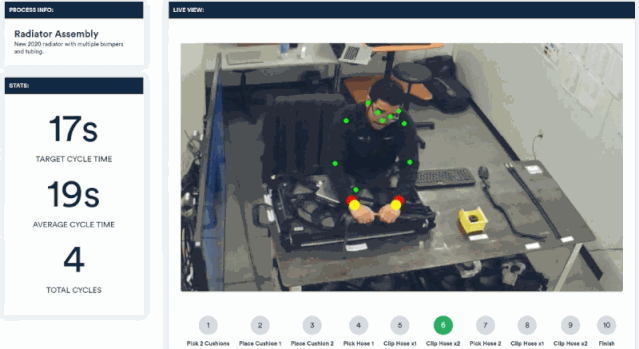
Cameras integrated with visual algorithms are an important process in system construction and deployment. Through this computer vision platform, a rigorous and efficient employee assistant is created.
By analyzing real-time video, the postures and movements of workers' wrists, body and other parts can be tracked. Without the need for sensors, they can be compared with standard movement specifications to point out irregularities in the assembly process.
The system can also identify other problems in the workflow, such as missing parts, damage, etc.
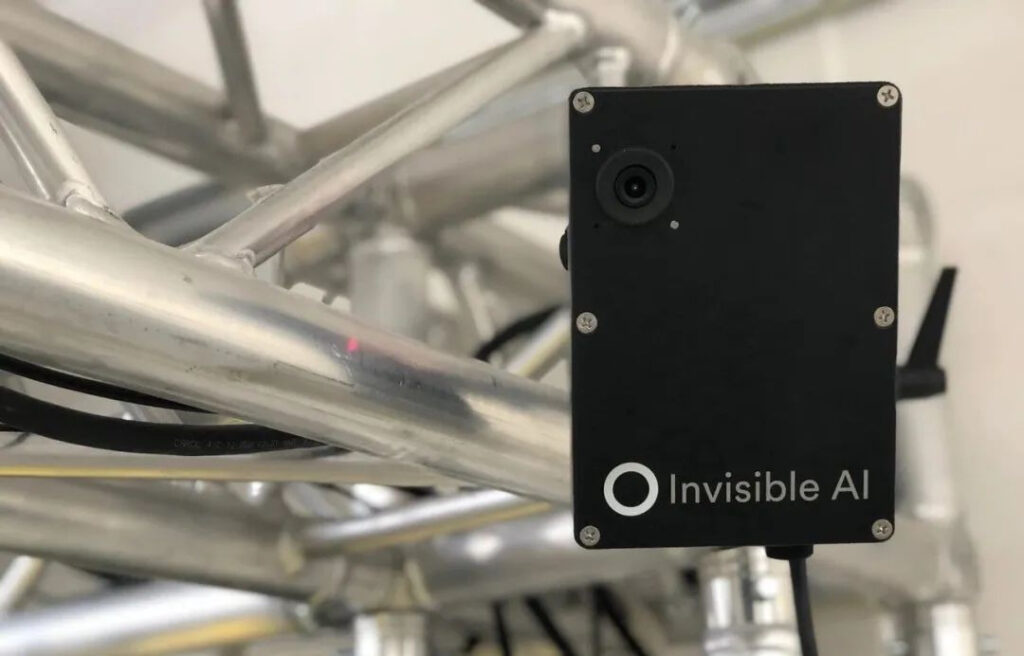

By leveraging the chipset, Invisible AI is able to create a powerful low-bandwidth camera system for its platform, while the machine learning models used for analysis are 100 times smaller than other solutions.
Through a simple web dashboard, you can see which assembly steps have problems.
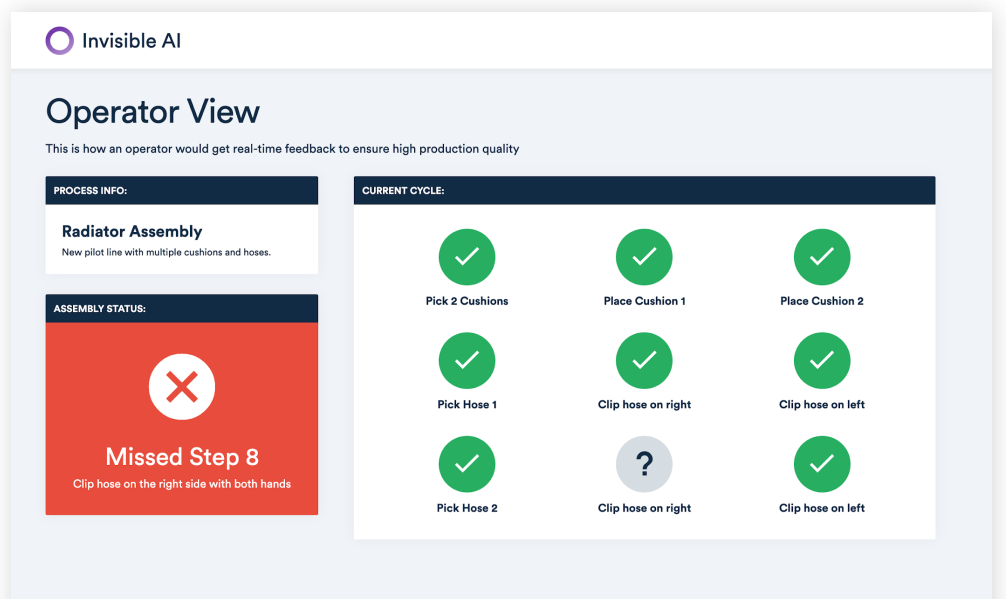
With the help of this technology, assembly workers can get timely help and clearly understand the correct process of production to avoid errors and omissions.
Invisible AI's early partners include Toyota, a well-known automobile manufacturer. At the Toyota Motor Conference in January this year, Invisible AI was highlighted as one of the four important technologies.
Machines replacing people, people replacing machines, is not as good as people and machines
Using robots to assist in industrial production is not a new concept, but there are some differences between using vision-based solutions for reminders and direct robot intervention.
With the vigorous development of technologies such as AI, ordinary robots are moving towards collaborative robots, among which collaborative robotic arms are the most common.
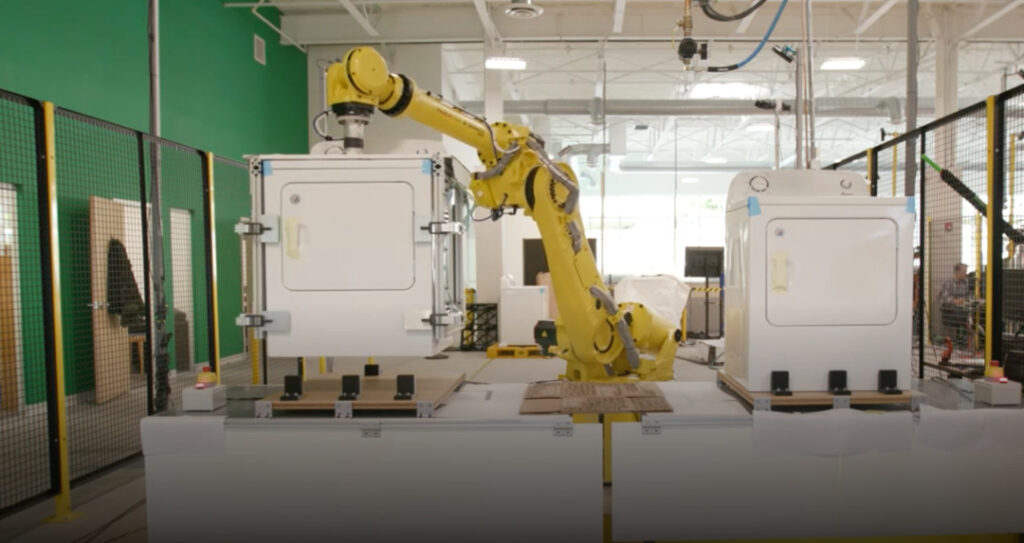

Replacing operators with robots or robotic arms requires extremely high levels of technology iteration and rapid application. For standard products with relatively mature and stable process standards, such as automobiles, large machinery and other products, robotic arms can greatly improve efficiency and speed up production and assembly processes.
However, for mobile phones, game consoles and other fine products that are updated very quickly and have strict production requirements, the cost of modifying and debugging robots is much higher than that of human workers.
Invisible's camera-based visual processing solution essentially retains manual operations, but uses computers to remind and regulate human behavior. It is still very useful in jobs that require manual skills.
We still don’t know when Industry 4.0 will be realized. But whether it is “machines replacing people” or “people replacing machines”, it is making industrial AI continue to develop in a more practical direction.
-- over--