Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
GROMACS 시작하기 튜토리얼: 물 속의 라이소자임
"물 속의 라이소자임"을 예로 들어 분자 동역학 시뮬레이션
튜토리얼 소개
이 튜토리얼은 GROMACS 소프트웨어를 사용한 분자 동역학 시뮬레이션에 대한 소개 튜토리얼입니다. 물 속의 리소자임예를 들어 물 속에 있는 일반적인 단백질의 분자 동역학 시뮬레이션을 준비하고 실행하는 방법을 알아봅니다.
OpenBayes 플랫폼에서 NVIDIA RTX 4090 그래픽 카드를 사용하는 GROMACS의 GPU 버전은 GPU 병렬 컴퓨팅 이후 최대 255ns/일의 속도로 컴퓨팅 효율성이 크게 향상되었습니다! 속도 성능은 다음과 같습니다.
Core t (s) Wall t (s) (%)
Time: 3972.923 198.659 1999.9
(ns/day) (hour/ns)
Performance: 255.471 0.094
GROMACS 소개
GROMACS(GRoningen MAchine for Chemical Simulations)는 분자 동역학 시뮬레이션을 위한 고성능 소프트웨어 패키지입니다. 이는 주로 다양한 조건에서 생물학적 분자(예: 단백질, 지질, 핵산)의 운동 행동을 모델링하고 시뮬레이션하는 데 사용됩니다. 원래 네덜란드의 그로닝겐 대학교에서 개발되었으며, 분자 동역학 분야에서 가장 널리 사용되는 오픈 소스 도구 중 하나가 되었습니다.
GROMACS의 주요 기능
1. 고성능:
• GROMACS는 병렬 컴퓨팅에 최적화되어 있으며 최신 멀티코어 CPU 및 GPU 시스템에서 효율적으로 실행될 수 있습니다.
• 멀티스레드 및 분산 컴퓨팅을 위해 OpenMP 및 MPI를 지원합니다.
2. 다양한 응용 분야:
• 작은 분자부터 큰 단백질 복합체까지의 행동을 시뮬레이션하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
• 생체 분자, 폴리머, 무기 화합물 및 기타 화학 시스템에 대한 연구를 지원합니다.
3. 유연성:
• 사전 처리(예: 토폴로지 생성, 용매화) 및 사후 처리(예: 궤적 분석, 에너지 계산)를 위한 풍부한 도구 세트를 제공합니다.
• AMBER, CHARMM, GROMOS 등 다양한 힘장 지원.
4. 사용 편의성:
• GROMACS에는 사용자 친화적인 명령줄 인터페이스가 포함되어 있습니다.
• 초보자와 고급 사용자 모두에게 적합한 자세한 설명서와 튜토리얼을 제공합니다.
5. 오픈 소스 및 확장 가능:
• 오픈 소스 라이선스를 통해 사용자는 특정 요구 사항에 맞게 GROMACS를 수정하고 확장할 수 있습니다.
• 활발한 사용자 커뮤니티와 개발팀을 보유하고 있습니다.
GROMACS 일반 사용 프로세스
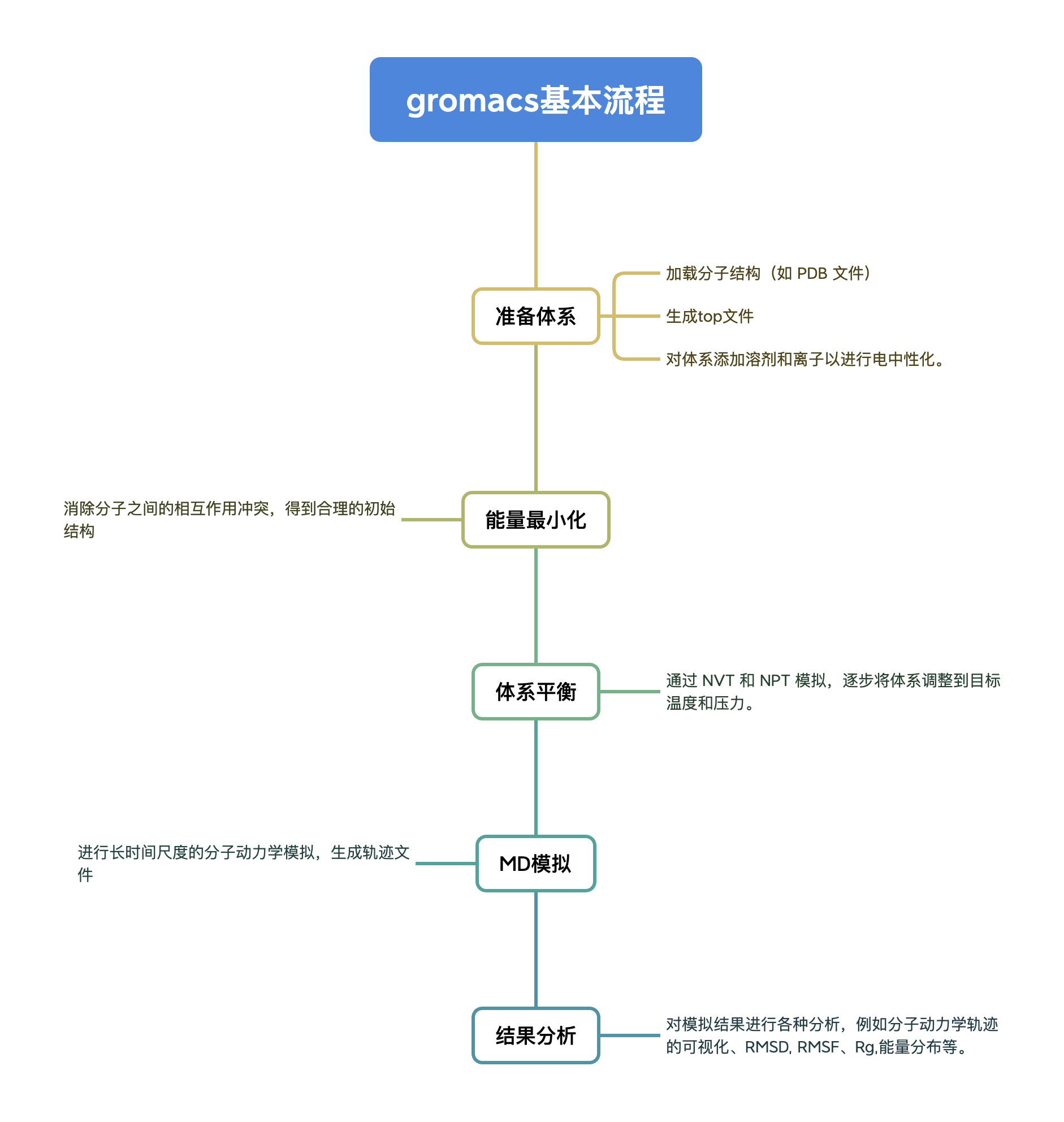
실행 단계
먼저 pdb 단백질 파일과 md 계산 파일을 구성한 다음, 다양한 전처리 과정을 거친 후 마지막으로 10ns 시뮬레이션을 수행하고 결과를 분석합니다. 단계별 설명은 다음과 같습니다.
1. GROMACS를 시작하세요
首先登录平台:https://openbayes.com/
选择「高性能计算」> 创建新容器> 选择算力 RTX 4090> 选择 gromacs GPU
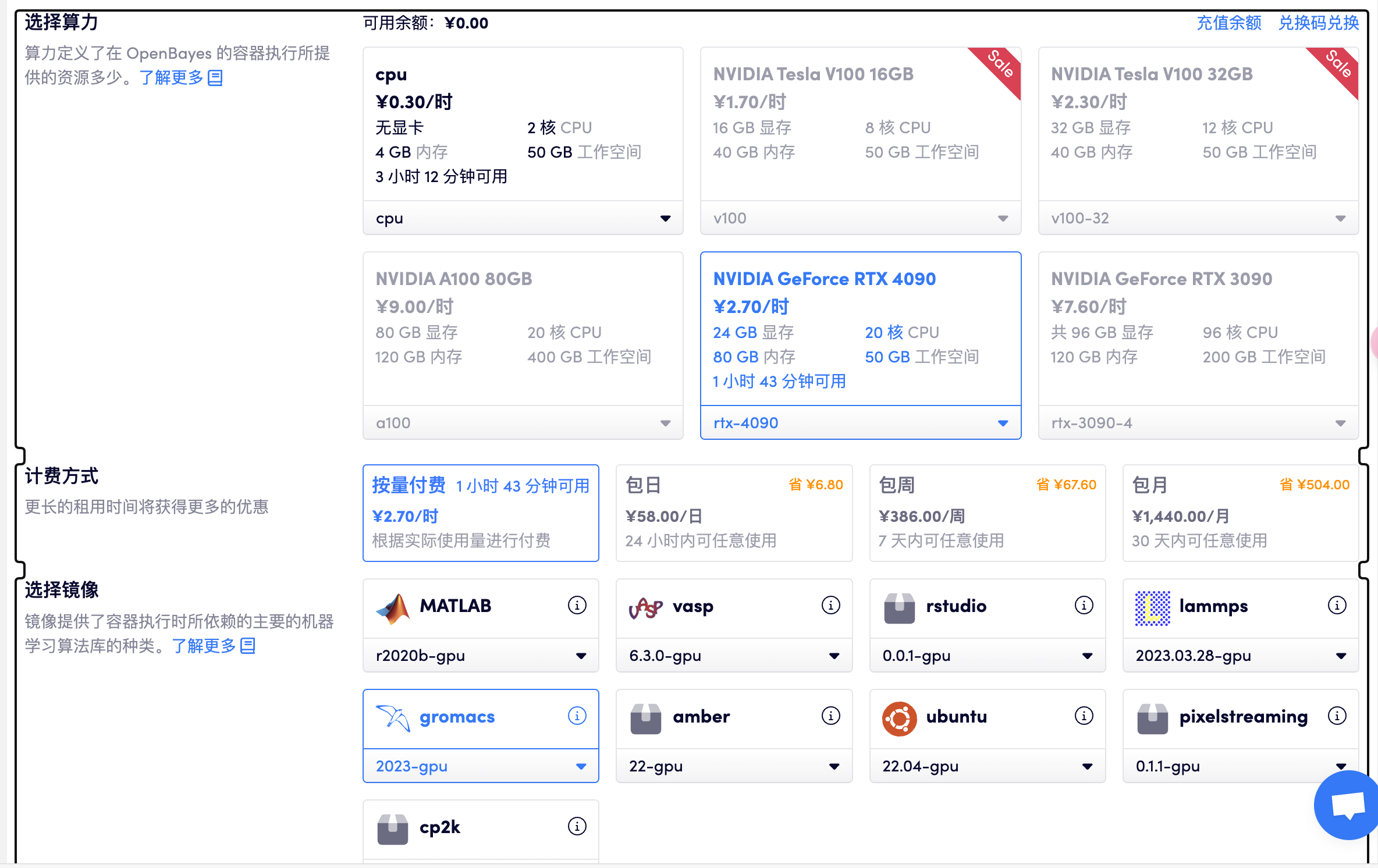
打开工作空间
打开终端
或者采用 SSH 控制服务器:
在 X-shell 或者 mac unix 终端,输入:ssh -p 32699 root@ssh.openbayes.com,再输入密码即可(如下所示)↓
liangzhongzhongzhong@lzr ~ % ssh -p 32699 root@ssh.openbayes.com
The authenticity of host '[ssh.openbayes.com]:32699 ([101.237.34.75]:32699)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:uwPyhP/EYoW49Ez4rvAuaf19czwis2rdS4pImsR0NH8.
This key is not known by any other names.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '[ssh.openbayes.com]:32699' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
root@ssh.openbayes.com's password:
OpenBayes
目录说明
- /openbayes/home 工作空间内的数据保存地址,容器停止后,该目录中的内容不会被删除
- /openbayes/input/input0 - /openbayes/input/input4 为数据目录,不会占用工作空间的存储容量,最多支持同时绑定 5 个
⚠️ 其他目录下的内容在容器关闭后会被自动删除!更多信息请访问 https://openbayes.com/docs/concepts
⚠️ 禁止挖矿,一经发现将立即封号恕不退款
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/openbayes/home# ls
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/openbayes# l(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/openbayes# lhome input 请将文件存在 home 目录下, 当前文件夹下的文件不会被保存.txt
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/openbayes# ls(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/openbaye
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/openbayes/input# cd input0
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/openbayes/input/input0# ls
'#nvt.log.1#' '#topol.top.2#' 1AKI_processed.gro 1aki.pdb em.log ions.mdp mdout.mdp nvt.cpt nvt.log nvt.trr topol.top
'#nvt.log.2#' 1AKI_clean.pdb 1AKI_solv.gro em.edr em.tpr ions.tpr minim.mdp nvt.edr nvt.mdp posre.itp
'#topol.top.1#' 1AKI_newbox.gro 1AKI_solv_ions.gro em.gro em.trr md.mdp npt.mdp nvt.gro nvt.tpr potential.xvg
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/openbayes/input/input0#

调用 GROMACS,设置临时环境变量
export PATH=/data/app/gromacs/bin:$PATH
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/openbayes/home# gmx_mpi -h
:-) GROMACS - gmx_mpi, 2023 (-:
Executable: /data/app/gromacs/bin/gmx_mpi
Data prefix: /data/app/gromacs
Working dir: /output
Command line:
gmx_mpi -h
SYNOPSIS
gmx [-[no]h] [-[no]quiet] [-[no]version] [-[no]copyright] [-nice <int>]
[-[no]backup]
OPTIONS
Other options:
-[no]h (no)
Print help and quit
-[no]quiet (no)
Do not print common startup info or quotes
-[no]version (no)
Print extended version information and quit
-[no]copyright (no)
Print copyright information on startup
-nice <int> (19)
Set the nicelevel (default depends on command)
-[no]backup (yes)
Write backups if output files exist
Additional help is available on the following topics:
commands List of available commands
selections Selection syntax and usage
To access the help, use 'gmx help <topic>'.
For help on a command, use 'gmx help <command>'.
GROMACS reminds you: "All You Need is Greed" (Aztec Camera)
2. 문서 준비
튜토리얼을 실행하기 전에 다음 6개의 파일을 준비해야 합니다: 1aki.pdb, ions.mdp, md.mdp, minim.mdp, npt.mdp, nvt.mdp
이러한 파일은 직접 다운로드하거나 다음과 같이 만들 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 1AKI.pdb 단백질 파일은 다음에서 얻을 수 있습니다. RCSB 웹사이트에서 1AKI.pdb를 받으세요.이 튜토리얼에서는 vim 텍스트 편집기를 사용하여 코드를 복사하여 다른 파일을 만들었습니다.
RCSB 데이터베이스 소개:
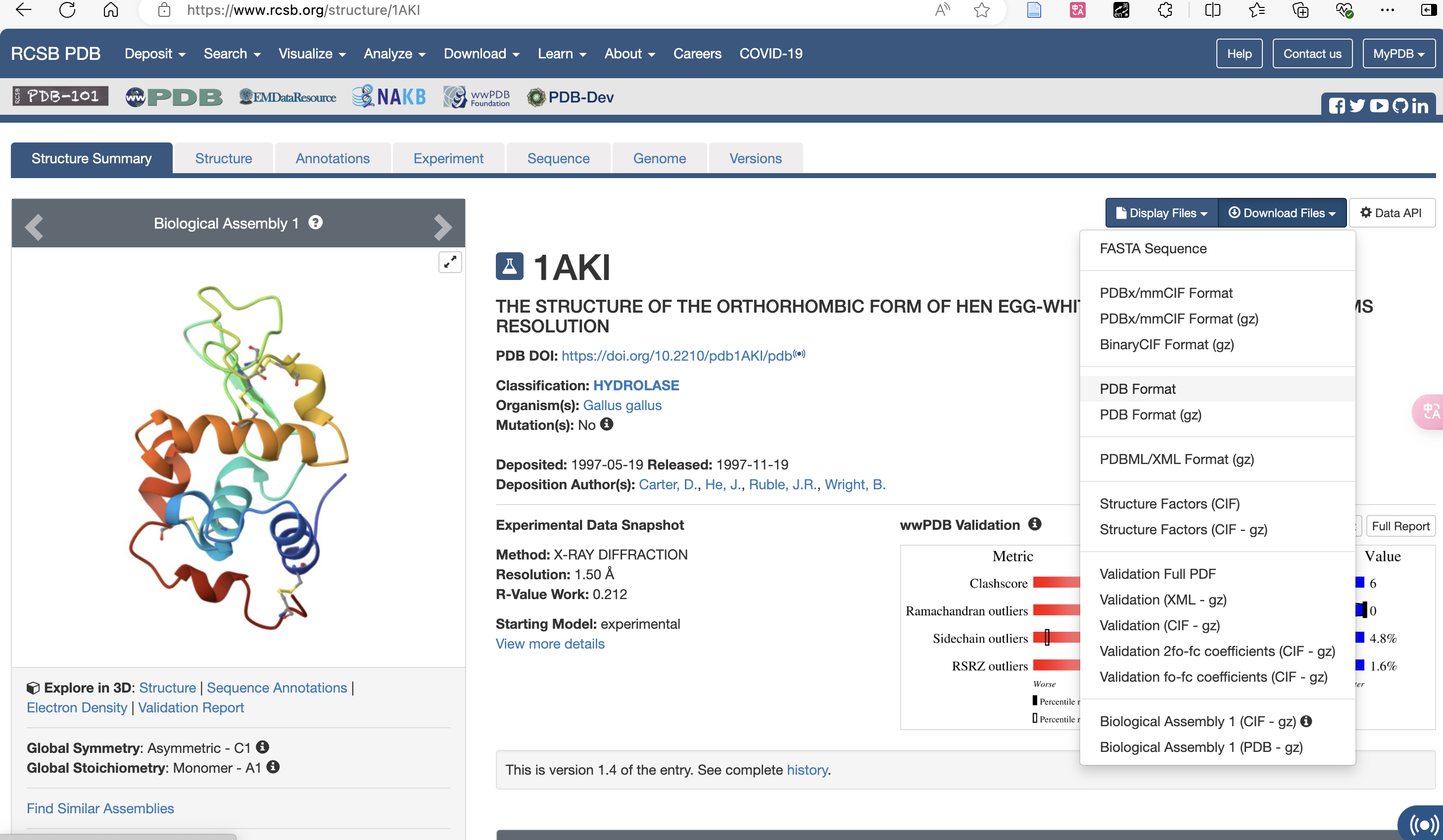
pdb 형식 다운로드:
작업 디렉토리에 업로드
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/input0# ls
1aki.pdb
#查看上传成功
vim ions.mdp
#准备 mdp 文件,输入命令后复制一下内容,按 i 进入插入模式开始编辑。
#编辑完成后,按 Esc 键退出插入模式,输入 :wq 保存并退出。
; ions.mdp - used as input into grompp to generate ions.tpr
; Parameters describing what to do, when to stop and what to save
integrator = steep ; Algorithm (steep = steepest descent minimization)
emtol = 1000.0 ; Stop minimization when the maximum force < 1000.0 kJ/mol/nm
emstep = 0.01 ; Minimization step size
nsteps = 50000 ; Maximum number of (minimization) steps to perform
; Parameters describing how to find the neighbors of each atom and how to calculate the interactions
nstlist = 1 ; Frequency to update the neighbor list and long range forces
cutoff-scheme = Verlet ; Buffered neighbor searching
ns_type = grid ; Method to determine neighbor list (simple, grid)
coulombtype = cutoff ; Treatment of long range electrostatic interactions
rcoulomb = 1.0 ; Short-range electrostatic cut-off
rvdw = 1.0 ; Short-range Van der Waals cut-off
pbc = xyz ; Periodic Boundary Conditions in all 3 dimensions
vim minim.mdp
; minim.mdp - used as input into grompp to generate em.tpr
; Parameters describing what to do, when to stop and what to save
integrator = steep ; Algorithm (steep = steepest descent minimization)
emtol = 1000.0 ; Stop minimization when the maximum force < 1000.0 kJ/mol/nm
emstep = 0.01 ; Minimization step size
nsteps = 50000 ; Maximum number of (minimization) steps to perform
; Parameters describing how to find the neighbors of each atom and how to calculate the interactions
nstlist = 1 ; Frequency to update the neighbor list and long range forces
cutoff-scheme = Verlet ; Buffered neighbor searching
ns_type = grid ; Method to determine neighbor list (simple, grid)
coulombtype = PME ; Treatment of long range electrostatic interactions
rcoulomb = 1.0 ; Short-range electrostatic cut-off
rvdw = 1.0 ; Short-range Van der Waals cut-off
pbc = xyz ; Periodic Boundary Conditions in all 3 dimensions
vim nvt.mdp
title = OPLS Lysozyme NVT equilibration
define = -DPOSRES ; position restrain the protein
; Run parameters
integrator = md ; leap-frog integrator
nsteps = 50000 ; 2 * 50000 = 100 ps
dt = 0.002 ; 2 fs
; Output control
nstxout = 500 ; save coordinates every 1.0 ps
nstvout = 500 ; save velocities every 1.0 ps
nstenergy = 500 ; save energies every 1.0 ps
nstlog = 500 ; update log file every 1.0 ps
; Bond parameters
continuation = no ; first dynamics run
constraint_algorithm = lincs ; holonomic constraints
constraints = h-bonds ; bonds involving H are constrained
lincs_iter = 1 ; accuracy of LINCS
lincs_order = 4 ; also related to accuracy
; Nonbonded settings
cutoff-scheme = Verlet ; Buffered neighbor searching
ns_type = grid ; search neighboring grid cells
nstlist = 10 ; 20 fs, largely irrelevant with Verlet
rcoulomb = 1.0 ; short-range electrostatic cutoff (in nm)
rvdw = 1.0 ; short-range van der Waals cutoff (in nm)
DispCorr = EnerPres ; account for cut-off vdW scheme
; Electrostatics
coulombtype = PME ; Particle Mesh Ewald for long-range electrostatics
pme_order = 4 ; cubic interpolation
fourierspacing = 0.16 ; grid spacing for FFT
; Temperature coupling is on
tcoupl = V-rescale ; modified Berendsen thermostat
tc-grps = Protein Non-Protein ; two coupling groups - more accurate
tau_t = 0.1 0.1 ; time constant, in ps
ref_t = 300 300 ; reference temperature, one for each group, in K
; Pressure coupling is off
pcoupl = no ; no pressure coupling in NVT
; Periodic boundary conditions
pbc = xyz ; 3-D PBC
; Velocity generation
gen_vel = yes ; assign velocities from Maxwell distribution
gen_temp = 300 ; temperature for Maxwell distribution
gen_seed = -1 ; generate a random seed
vim npt.mdp
title = OPLS Lysozyme NPT equilibration
define = -DPOSRES ; position restrain the protein
; Run parameters
integrator = md ; leap-frog integrator
nsteps = 50000 ; 2 * 50000 = 100 ps
dt = 0.002 ; 2 fs
; Output control
nstxout = 500 ; save coordinates every 1.0 ps
nstvout = 500 ; save velocities every 1.0 ps
nstenergy = 500 ; save energies every 1.0 ps
nstlog = 500 ; update log file every 1.0 ps
; Bond parameters
continuation = yes ; Restarting after NVT
constraint_algorithm = lincs ; holonomic constraints
constraints = h-bonds ; bonds involving H are constrained
lincs_iter = 1 ; accuracy of LINCS
lincs_order = 4 ; also related to accuracy
; Nonbonded settings
cutoff-scheme = Verlet ; Buffered neighbor searching
ns_type = grid ; search neighboring grid cells
nstlist = 10 ; 20 fs, largely irrelevant with Verlet scheme
rcoulomb = 1.0 ; short-range electrostatic cutoff (in nm)
rvdw = 1.0 ; short-range van der Waals cutoff (in nm)
DispCorr = EnerPres ; account for cut-off vdW scheme
; Electrostatics
coulombtype = PME ; Particle Mesh Ewald for long-range electrostatics
pme_order = 4 ; cubic interpolation
fourierspacing = 0.16 ; grid spacing for FFT
; Temperature coupling is on
tcoupl = V-rescale ; modified Berendsen thermostat
tc-grps = Protein Non-Protein ; two coupling groups - more accurate
tau_t = 0.1 0.1 ; time constant, in ps
ref_t = 300 300 ; reference temperature, one for each group, in K
; Pressure coupling is on
pcoupl = Parrinello-Rahman ; Pressure coupling on in NPT
pcoupltype = isotropic ; uniform scaling of box vectors
tau_p = 2.0 ; time constant, in ps
ref_p = 1.0 ; reference pressure, in bar
compressibility = 4.5e-5 ; isothermal compressibility of water, bar^-1
refcoord_scaling = com
; Periodic boundary conditions
pbc = xyz ; 3-D PBC
; Velocity generation
gen_vel = no ; Velocity generation is off
vim md.md
title = OPLS Lysozyme NPT equilibration
; Run parameters
integrator = md ; leap-frog integrator
nsteps = 500000 ; 2 * 500000 = 1000 ps (1 ns)
dt = 0.002 ; 2 fs
; Output control
nstxout = 0 ; suppress bulky .trr file by specifying
nstvout = 0 ; 0 for output frequency of nstxout,
nstfout = 0 ; nstvout, and nstfout
nstenergy = 5000 ; save energies every 10.0 ps
nstlog = 5000 ; update log file every 10.0 ps
nstxout-compressed = 5000 ; save compressed coordinates every 10.0 ps
compressed-x-grps = System ; save the whole system
; Bond parameters
continuation = yes ; Restarting after NPT
constraint_algorithm = lincs ; holonomic constraints
constraints = h-bonds ; bonds involving H are constrained
lincs_iter = 1 ; accuracy of LINCS
lincs_order = 4 ; also related to accuracy
; Neighborsearching
cutoff-scheme = Verlet ; Buffered neighbor searching
ns_type = grid ; search neighboring grid cells
nstlist = 10 ; 20 fs, largely irrelevant with Verlet scheme
rcoulomb = 1.0 ; short-range electrostatic cutoff (in nm)
rvdw = 1.0 ; short-range van der Waals cutoff (in nm)
; Electrostatics
coulombtype = PME ; Particle Mesh Ewald for long-range electrostatics
pme_order = 4 ; cubic interpolation
fourierspacing = 0.16 ; grid spacing for FFT
; Temperature coupling is on
tcoupl = V-rescale ; modified Berendsen thermostat
tc-grps = Protein Non-Protein ; two coupling groups - more accurate
tau_t = 0.1 0.1 ; time constant, in ps
ref_t = 300 300 ; reference temperature, one for each group, in K
; Pressure coupling is on
pcoupl = Parrinello-Rahman ; Pressure coupling on in NPT
pcoupltype = isotropic ; uniform scaling of box vectors
tau_p = 2.0 ; time constant, in ps
ref_p = 1.0 ; reference pressure, in bar
compressibility = 4.5e-5 ; isothermal compressibility of water, bar^-1
; Periodic boundary conditions
pbc = xyz ; 3-D PBC
; Dispersion correction
DispCorr = EnerPres ; account for cut-off vdW scheme
; Velocity generation
gen_vel = no ; Velocity generation is off
2. 공식 시뮬레이션 단계
목표: 후속 동적 시뮬레이션의 기반을 마련하기 위해 물리적으로 합리적인 시뮬레이션 시스템을 구축합니다.
1. 분자 구조 로드(PDB 파일):
• PDB 파일(단백질 데이터 뱅크)는 분자(단백질, 핵산, 소분자 등)의 3차원 좌표와 구조 정보를 담고 있습니다.
• GROMACS는 pdb2gmx 도구를 사용하여 이 좌표 정보를 분자 모델로 변환하고 힘장 매개변수를 할당합니다.
• 힘의 장: 결합, 각도, 이면체 위치 에너지, 반데르발스 힘, 전하 상호 작용을 포함한 분자 간의 상호 작용을 설명하는 수학적 모델입니다.
• 일반적인 힘의 장: GROMOS, AMBER, CHARMM.
(일반적으로 사용되는 것은 AMBER99SB 단백질, OPLS-AA/L 전원자력장, charm36 힘장(직접 다운로드 및 구성해야 함), 기타 힘장은 너무 오래되어 논문 게재에 적합하지 않음)
2. 토폴로지 파일 생성:
• 토폴로지 파일(topol.top)은 시뮬레이션 시스템의 각 분자의 힘장 매개변수(원자 유형, 결합 유형 및 매개변수 등)를 정의합니다.
• 좌표 파일과 결합하여 분자 동역학 시뮬레이션의 기초를 형성합니다.
3. pdb2gmx를 실행하고 force field: 15를 선택한 후 Enter를 누릅니다.
#删除水分子(PDB 文件中的 “HOH” 残基)
grep -v HOH 1aki.pdb > 1AKI_clean.pdb
gmx_mpi pdb2gmx -f 1AKI_clean.pdb -o 1AKI_processed.gro -water spce
#选择 15,按回车,OPLS-AA/L all-atom force field (2001 aminoacid dihedrals)
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/input0# pdb2gmx -f 1AKI_clean.pdb -o 1AKI_processed.gro -water spce
:-) GROMACS - gmx pdb2gmx, 2023 (-:
Executable: /data/app/gromacs/bin/gmx_mpi
Data prefix: /data/app/gromacs
Working dir: /input0
Command line:
gmx_mpi pdb2gmx -f 1AKI_clean.pdb -o 1AKI_processed.gro -water spce
Select the Force Field:
From '/data/app/gromacs/share/gromacs/top':
1: AMBER03 protein, nucleic AMBER94 (Duan et al., J. Comp. Chem. 24, 1999-2012, 2003)
2: AMBER94 force field (Cornell et al., JACS 117, 5179-5197, 1995)
3: AMBER96 protein, nucleic AMBER94 (Kollman et al., Acc. Chem. Res. 29, 461-469, 1996)
4: AMBER99 protein, nucleic AMBER94 (Wang et al., J. Comp. Chem. 21, 1049-1074, 2000)
5: AMBER99SB protein, nucleic AMBER94 (Hornak et al., Proteins 65, 712-725, 2006)
6: AMBER99SB-ILDN protein, nucleic AMBER94 (Lindorff-Larsen et al., Proteins 78, 1950-58, 2010)
7: AMBERGS force field (Garcia & Sanbonmatsu, PNAS 99, 2782-2787, 2002)
8: CHARMM27 all-atom force field (CHARM22 plus CMAP for proteins)
9: GROMOS96 43a1 force field
10: GROMOS96 43a2 force field (improved alkane dihedrals)
11: GROMOS96 45a3 force field (Schuler JCC 2001 22 1205)
12: GROMOS96 53a5 force field (JCC 2004 vol 25 pag 1656)
13: GROMOS96 53a6 force field (JCC 2004 vol 25 pag 1656)
14: GROMOS96 54a7 force field (Eur. Biophys. J. (2011), 40,, 843-856, DOI: 10.1007/s00249-011-0700-9)
15: OPLS-AA/L all-atom force field (2001 aminoacid dihedrals)
15
Using the Oplsaa force field in directory oplsaa.ff
going to rename oplsaa.ff/aminoacids.r2b
Opening force field file /data/app/gromacs/share/gromacs/top/oplsaa.ff/aminoacids.r2b
Reading 1AKI_clean.pdb...
WARNING: all CONECT records are ignored
Read 'LYSOZYME', 1001 atoms
Analyzing pdb file
Splitting chemical chains based on TER records or chain id changing.
There are 1 chains and 0 blocks of water and 129 residues with 1001 atoms
chain #res #atoms
1 'A' 129 1001
All occupancies are one
All occupancies are one
Opening force field file /data/app/gromacs/share/gromacs/top/oplsaa.ff/atomtypes.atp
Reading residue database... (Oplsaa)
Opening force field file /data/app/gromacs/share/gromacs/top/oplsaa.ff/aminoacids.rtp
Opening force field file /data/app/gromacs/share/gromacs/top/oplsaa.ff/aminoacids.hdb
Opening force field file /data/app/gromacs/share/gromacs/top/oplsaa.ff/aminoacids.n.tdb
Opening force field file /data/app/gromacs/share/gromacs/top/oplsaa.ff/aminoacids.c.tdb
Processing chain 1 'A' (1001 atoms, 129 residues)
Analysing hydrogen-bonding network for automated assignment of histidine
protonation. 213 donors and 184 acceptors were found.
There are 255 hydrogen bonds
Will use HISE for residue 15
Identified residue LYS1 as a starting terminus.
Identified residue LEU129 as a ending terminus.
8 out of 8 lines of specbond.dat converted successfully
Special Atom Distance matrix:
CYS6 MET12 HIS15 CYS30 CYS64 CYS76 CYS80
SG48 SD87 NE2118 SG238 SG513 SG601 SG630
MET12 SD87 1.166
HIS15 NE2118 1.776 1.019
CYS30 SG238 1.406 1.054 2.069
CYS64 SG513 2.835 1.794 1.789 2.241
CYS76 SG601 2.704 1.551 1.468 2.116 0.765
CYS80 SG630 2.959 1.951 1.916 2.391 0.199 0.944
CYS94 SG724 2.550 1.407 1.382 1.975 0.665 0.202 0.855
MET105 SD799 1.827 0.911 1.683 0.888 1.849 1.461 2.036
CYS115 SG889 1.576 1.084 2.078 0.200 2.111 1.989 2.262
CYS127 SG981 0.197 1.072 1.721 1.313 2.799 2.622 2.934
CYS94 MET105 CYS115
SG724 SD799 SG889
MET105 SD799 1.381
CYS115 SG889 1.853 0.790
CYS127 SG981 2.475 1.686 1.483
Linking CYS-6 SG-48 and CYS-127 SG-981...
Linking CYS-30 SG-238 and CYS-115 SG-889...
Linking CYS-64 SG-513 and CYS-80 SG-630...
Linking CYS-76 SG-601 and CYS-94 SG-724...
Start terminus LYS-1: NH3+
End terminus LEU-129: COO-
Checking for duplicate atoms....
Generating any missing hydrogen atoms and/or adding termini.
Now there are 129 residues with 1960 atoms
Making bonds...
Number of bonds was 1984, now 1984
Generating angles, dihedrals and pairs...
Before cleaning: 5142 pairs
Before cleaning: 5187 dihedrals
Making cmap torsions...
There are 5187 dihedrals, 426 impropers, 3547 angles
5106 pairs, 1984 bonds and 0 virtual sites
Total mass 14313.193 a.m.u.
Total charge 8.000 e
Writing topology
Writing coordinate file...
--------- PLEASE NOTE ------------
You have successfully generated a topology from: 1AKI_clean.pdb.
The Oplsaa force field and the spce water model are used.
--------- ETON ESAELP ------------
GROMACS reminds you: "Any one who considers arithmetical methods of producing random digits is, of course, in a state of sin." (John von Neumann)
몇 개의 파일이 더 있고 "총 요금 8.000 e"가 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 나중에 요금을 중화해야 합니다.
vim 명령을 사용하여 topol.top을 보면 힘장 태그를 볼 수 있습니다.
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/input0# ls
1AKI_clean.pdb 1aki.pdb md.mdp npt.mdp posre.itp
1AKI_processed.gro ions.mdp minim.mdp nvt.mdp topol.top
4. 단백질을 둘러싸는 마름모 십이면체 상자를 만들어 용매 분자를 추가할 수 있습니다.
• 상자 모양 선택: 일반적인 시뮬레이션 상자 모양에는 정육면체, 직교 상자, 마름모 십이면체 등이 있습니다. 일반적으로 분자를 효과적으로 채우고 계산량을 줄일 수 있는 모양이 선택됩니다.
gmx_mpi editconf -f 1AKI_processed.gro -o 1AKI_newbox.gro -c -d 1.0 -bt cubic
#将蛋白质在框中居中(-c),并将其放置在框边缘至少 1.0 nm 的位置(-d 1.0)
Command line:
gmx_mpi editconf -f 1AKI_processed.gro -o 1AKI_newbox.gro -c -d 1.0 -bt cubic
Note that major changes are planned in future for editconf, to improve usability and utility.
Read 1960 atoms
Volume: 123.376 nm^3, corresponds to roughly 55500 electrons
No velocities found
system size : 3.817 4.234 3.454 (nm)
diameter : 5.010 (nm)
center : 2.781 2.488 0.017 (nm)
box vectors : 5.906 6.845 3.052 (nm)
box angles : 90.00 90.00 90.00 (degrees)
box volume : 123.38 (nm^3)
shift : 0.724 1.017 3.488 (nm)
new center : 3.505 3.505 3.505 (nm)
new box vectors : 7.010 7.010 7.010 (nm)
new box angles : 90.00 90.00 90.00 (degrees)
new box volume : 344.48 (nm^3)
5. 상자를 정의하고 용매(물)를 추가합니다.
목적:용매화: 분자를 용매 환경(예: 물 상자)에 넣어 실제 환경에서의 행동을 시뮬레이션합니다.
gmx_mpi solvate -cp 1AKI_newbox.gro -cs spc216.gro -o 1AKI_solv.gro -p topol.top
#结果
Generating solvent configuration
Will generate new solvent configuration of 4x4x4 boxes
Solvent box contains 39252 atoms in 13084 residues
Removed 5451 solvent atoms due to solvent-solvent overlap
Removed 1869 solvent atoms due to solute-solvent overlap
Sorting configuration
Found 1 molecule type:
SOL ( 3 atoms): 10644 residues
Generated solvent containing 31932 atoms in 10644 residues
Writing generated configuration to 1AKI_solv.gro
Output configuration contains 33892 atoms in 10773 residues
Volume : 344.484 (nm^3)
Density : 997.935 (g/l)
Number of solvent molecules: 10644
Processing topology
Adding line for 10644 solvent molecules with resname (SOL) to topology file (topol.top)
#查看一下 top 文件
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/input0# ls
'#topol.top.1#' 1AKI_newbox.gro 1AKI_solv.gro ions.mdp minim.mdp nvt.mdp topol.top
1AKI_clean.pdb 1AKI_processed.gro 1aki.pdb md.mdp npt.mdp posre.itp
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/input0# vim topol.top
#查看 top 文件的末尾
[분자]를 볼 수 있습니다
단백질_사슬_A, 단백질 A 사슬
SOL 물 분자
6. .tpr 파일을 어셈블합니다.
gmx_mpi grompp -f ions.mdp -c 1AKI_solv.gro -p topol.top -o ions.tpr
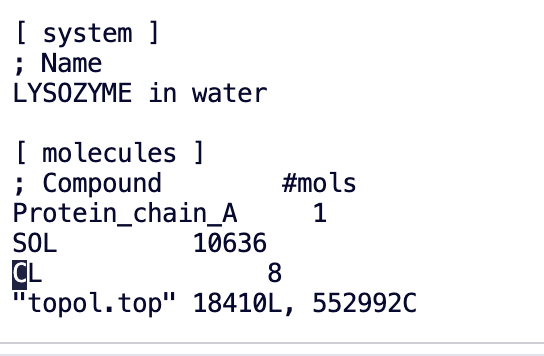
7. 전하를 중화하고 용매 분자를 이온으로 대체합니다.
전하 중화:이온(Na⁺, Cl⁻ 등)을 추가하여 시스템의 전체 전하를 중성화하고 정전기 효과로 인한 시뮬레이션 왜곡을 방지합니다.
gmx_mpi genion -s ions.tpr -o 1AKI_solv_ions.gro -p topol.top -pname NA -nname CL -neutral
Command line:
gmx_mpi genion -s ions.tpr -o 1AKI_solv_ions.gro -p topol.top -pname NA -nname CL -neutral
Reading file ions.tpr, VERSION 2023 (single precision)
Reading file ions.tpr, VERSION 2023 (single precision)
Will try to add 0 NA ions and 8 CL ions.
Select a continuous group of solvent molecules
Group 0 ( System) has 33892 elements
Group 1 ( Protein) has 1960 elements
Group 2 ( Protein-H) has 1001 elements
Group 3 ( C-alpha) has 129 elements
Group 4 ( Backbone) has 387 elements
Group 5 ( MainChain) has 517 elements
Group 6 ( MainChain+Cb) has 634 elements
Group 7 ( MainChain+H) has 646 elements
Group 8 ( SideChain) has 1314 elements
Group 9 ( SideChain-H) has 484 elements
Group 10 ( Prot-Masses) has 1960 elements
Group 11 ( non-Protein) has 31932 elements
Group 12 ( Water) has 31932 elements
Group 13 ( SOL) has 31932 elements
Group 14 ( non-Water) has 1960 elements
Select a group: 13
Selected 13: 'SOL'
Number of (3-atomic) solvent molecules: 10644
Processing topology
Replacing 8 solute molecules in topology file (topol.top) by 0 NA and 8 CL ions.
Back Off! I just backed up topol.top to ./#topol.top.2#
Using random seed -1212354563.
Replacing solvent molecule 3671 (atom 12973) with CL
Replacing solvent molecule 2264 (atom 8752) with CL
Replacing solvent molecule 2559 (atom 9637) with CL
Replacing solvent molecule 8081 (atom 26203) with CL
Replacing solvent molecule 8468 (atom 27364) with CL
Replacing solvent molecule 7439 (atom 24277) with CL
Replacing solvent molecule 9983 (atom 31909) with CL
Replacing solvent molecule 650 (atom 3910) with CL
GROMACS reminds you: "Water is just water" (Berk Hess)
(base) root@liangzhong-4ay9ej85pxvd-main:/input0#
많은 양의 염화물 이온이 첨가된 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
8. 에너지 최소화
8.1 이유: 분자 동역학 시뮬레이션을 수행할 때 얻는 pdb 파일은 X선, 전자 현미경 및 기타 방법을 통해 얻은 것으로, 과도한 에너지를 가진 많은 결합 각도와 왜곡, 수소 결합의 형성 또는 파괴, 분자 간의 특수한 배열, 원자 간의 가까운 거리로 인한 높은 에너지 등이 포함되어 있어 시뮬레이션에서 분자 시스템이 고에너지 상태에서 저에너지 상태로 변환하기 어렵습니다. 이 방법은 시스템의 에너지를 최소화하는 데 필요합니다.
8.2 원리: 에너지 최소화의 기본 원리: 에너지 최소화는 원자 좌표를 반복적으로 계산하고 조정하여 시스템의 총 잠재 에너지를 줄이는 잠재 에너지 함수에 기초합니다. 일반적으로 사용되는 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
① 공액 경사법: 이전 단계의 정보를 활용하여 수렴 속도를 높이는 경사 하강법입니다.
② 가장 가파른 하강 방법: 각 반복은 잠재 에너지 기울기의 반대 방향으로 이동하며 가장 가파른 하강 경로를 통해 에너지를 줄입니다.
③뉴턴-랩슨법: 위치에너지 함수의 2차미분을 이용하여 최소에너지점을 보다 정확하게 찾는 2차미분법입니다.
8.3 목적: 분자의 원자 좌표를 조정하여 시스템의 총 위치 에너지를 줄임으로써 더 안정적인 분자 형태를 찾는 것입니다.
① 불합리한 기하학적 형태를 제거합니다. 에너지 최소화를 통해 초기 구조 내의 불합리한 기하학적 형태(불합리한 원자 중첩 및 늘어남 등)를 제거하고 이로 인해 발생하는 고에너지 상태를 제거하여 시스템을 더욱 안정적으로 만들 수 있습니다.
② 초기 구조 준비: 시뮬레이션 중 불필요한 고에너지 충격을 피하기 위해 초기 구조가 낮은 잠재 에너지 상태에 있는지 확인하세요.
③ 계산 효율 향상 : 시스템의 총 잠재 에너지를 감소시킴으로써 후속 시뮬레이션 및 계산의 안정성과 효율성을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
gmx_mpi grompp -f minim.mdp -c 1AKI_solv_ions.gro -p topol.top -o em.tpr
gmx_mpi mdrun -v -deffnm em

9. 결과를 살펴보세요(튜토리얼 마지막 부분에서 xvg 파일을 시각화하는 방법을 알려드립니다. xmgrace, qtgrace, python, excel을 사용하여 그래프를 만들 수 있습니다. 기본적으로 선 그래프입니다.)
gmx_mpi energy -f em.edr -o potential.xvg
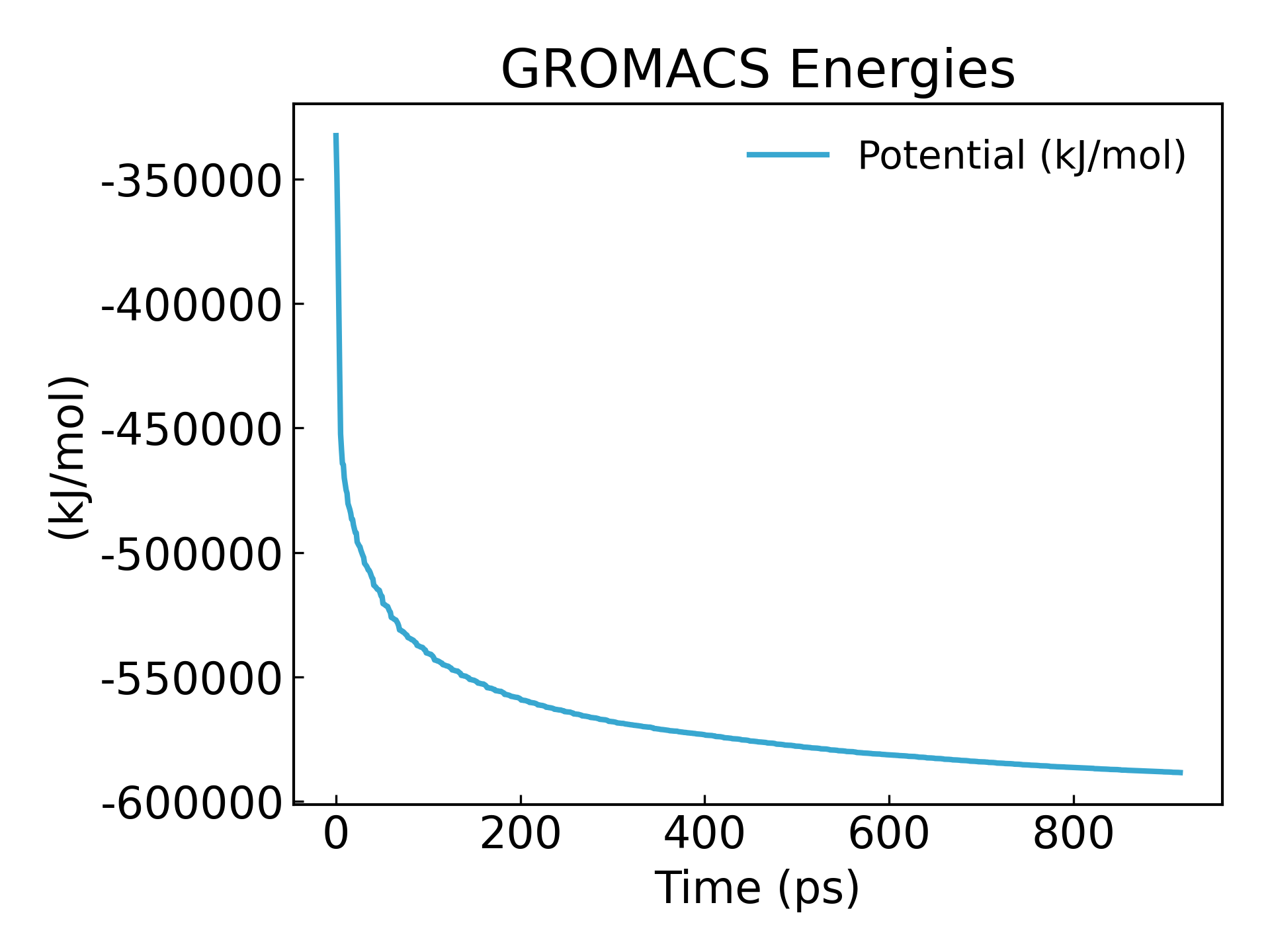
에너지가 -600000 kj/mol로 최소화되는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
10. 시스템 균형
목적: 시스템을 목표 온도 및 압력 조건에 맞게 조정하여 실제 물리적 상태에 가깝게 만드는 것입니다.
(1) NVT 시뮬레이션(일정체적, 일정온도)
• 일정 부피와 일정 온도 앙상블은 시스템의 온도를 목표 값으로 안정화하는 데 사용됩니다.
• 온도 조절기: 일반적으로 사용되는 것은 베렌센 온도 커플러 또는 V-리스케일(개정된 약결합 방식)로, 원자 속도를 조정하여 온도를 제어합니다.
(2) NPT 시뮬레이션(일정압력, 일정온도) :
• 일정 압력 및 일정 온도 앙상블은 시스템 밀도를 목표 값(일반적으로 액체 물의 밀도 ~1 g/cm³)으로 더욱 조정합니다.
• 압력 제어기: 일반적으로 사용되는 방법은 베렌센 압력 커플러 또는 파리넬로-라만 압력 제어 방법입니다.
10.1. (일정한 입자 수, 부피 및 온도)에서 수행되는 100ps 동안 NVT 평형을 수행합니다. 이는 "등온 및 등적"이라고도 합니다.
GPU 가속을 사용하면 매우 빠르게 처리되며 10초 이상 걸립니다.
gmx_mpi grompp -f nvt.mdp -c em.gro -r em.gro -p topol.top -o nvt.tpr
gmx_mpi mdrun -deffnm nvt -nb gpu -pme cpu
#将 PME 任务移至 CPU

gmx_mpi energy -f nvt.edr -o temperature.xvg
#生成温度随时间变化的图像,查看温度是否平衡
16
0
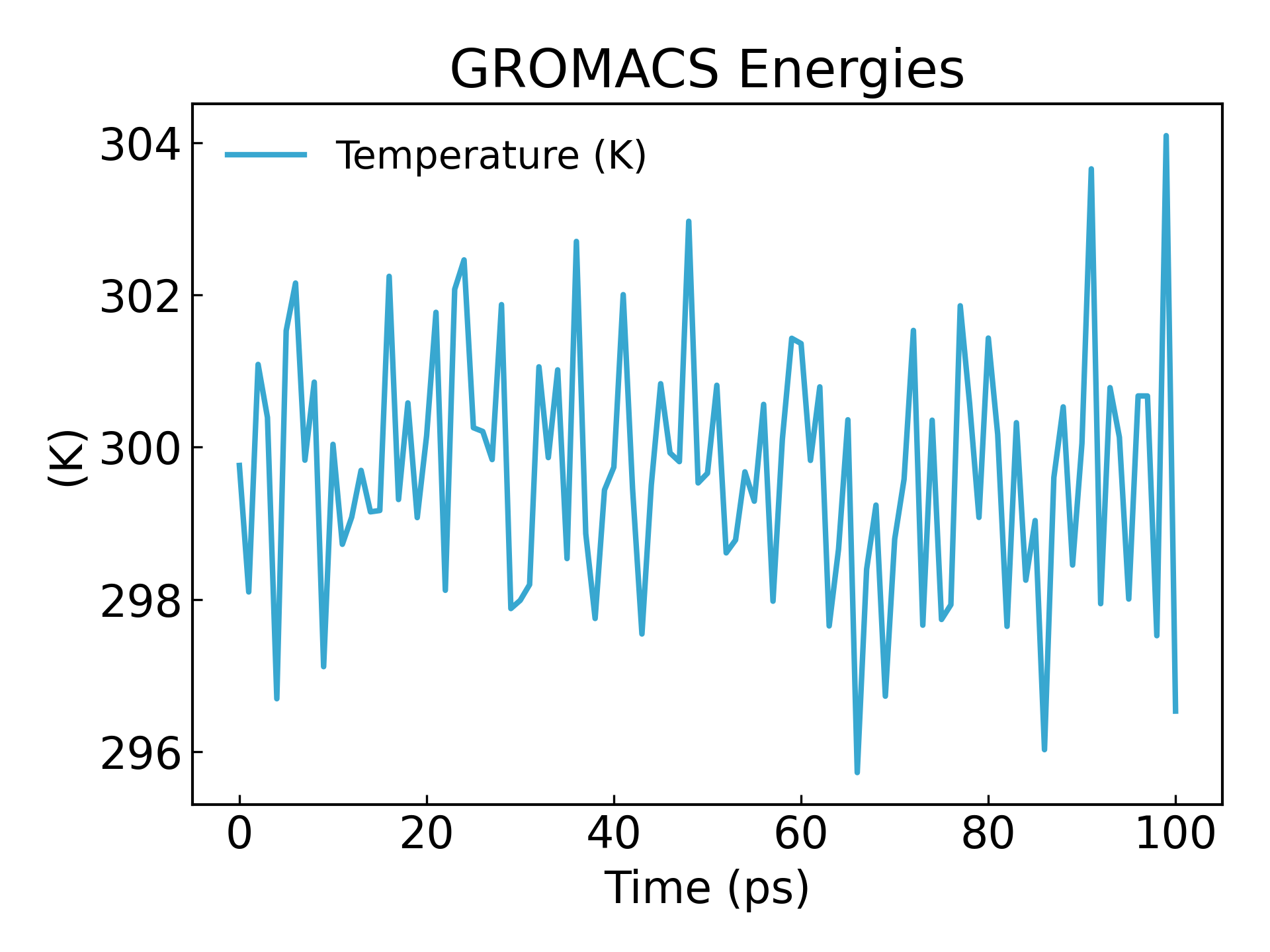
온도도 100ps 이내에서 기본적인 정상상태에 도달하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
10.2. NPT "등온 및 등압" 균형을 이루고 시스템 압력을 안정화하며 100 ps NPT 균형을 수행합니다.
gmx_mpi grompp -f npt.mdp -c nvt.gro -r nvt.gro -t nvt.cpt -p topol.top -o npt.tpr
gmx_mpi mdrun -deffnm npt -nb gpu -pme cpu
#压力是否平衡
gmx_mpi energy -f npt.edr -o pressure.xvg
18
0
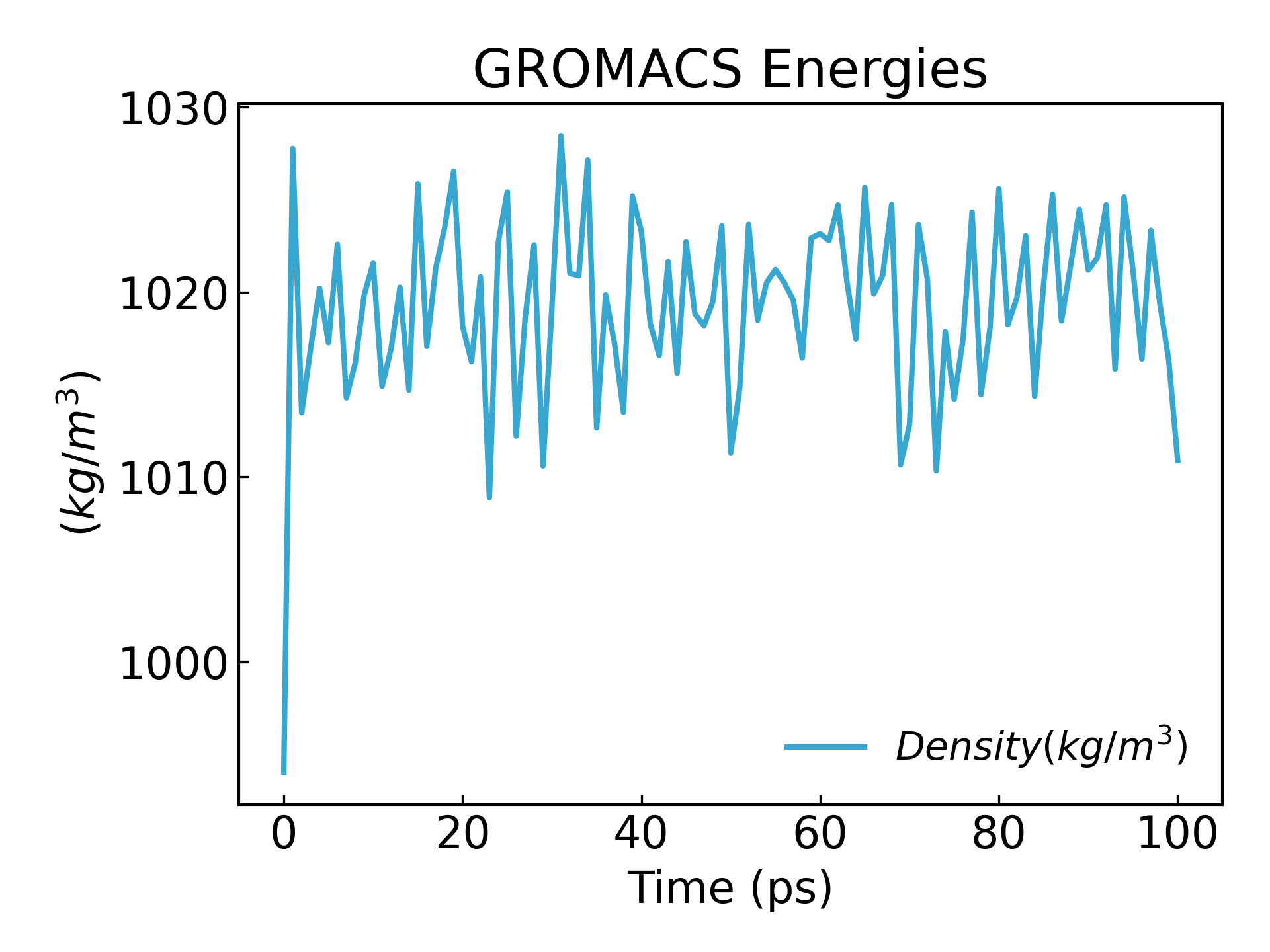
gmx_mpi energy -f npt.edr -o density.xvg
24
0
밀도가 정상 상태에 도달한 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
11. 2개의 평형 단계를 완료한 후, 시스템은 이제 원하는 온도와 압력에서 잘 평형을 이루었습니다. 이제 위치 제약 조건을 해제하고 MD를 실행하여 진행할 수 있습니다.
귀하의 요구 사항에 맞게 시간을 조정할 수 있습니다. 이 튜토리얼은 100ns를 시뮬레이션합니다.
시간 단계 dt = 2 fs (일반 설정):
50000000단계, 2fs의 시간 단계, 100나노초(ns)에 해당
50000000 x2 fs = 10^8 fs = 10^5 ps = 100ns
vim md.mdp
nsteps = 50000000 ; 2 * 50000000 = 100000 ps (100 ns)

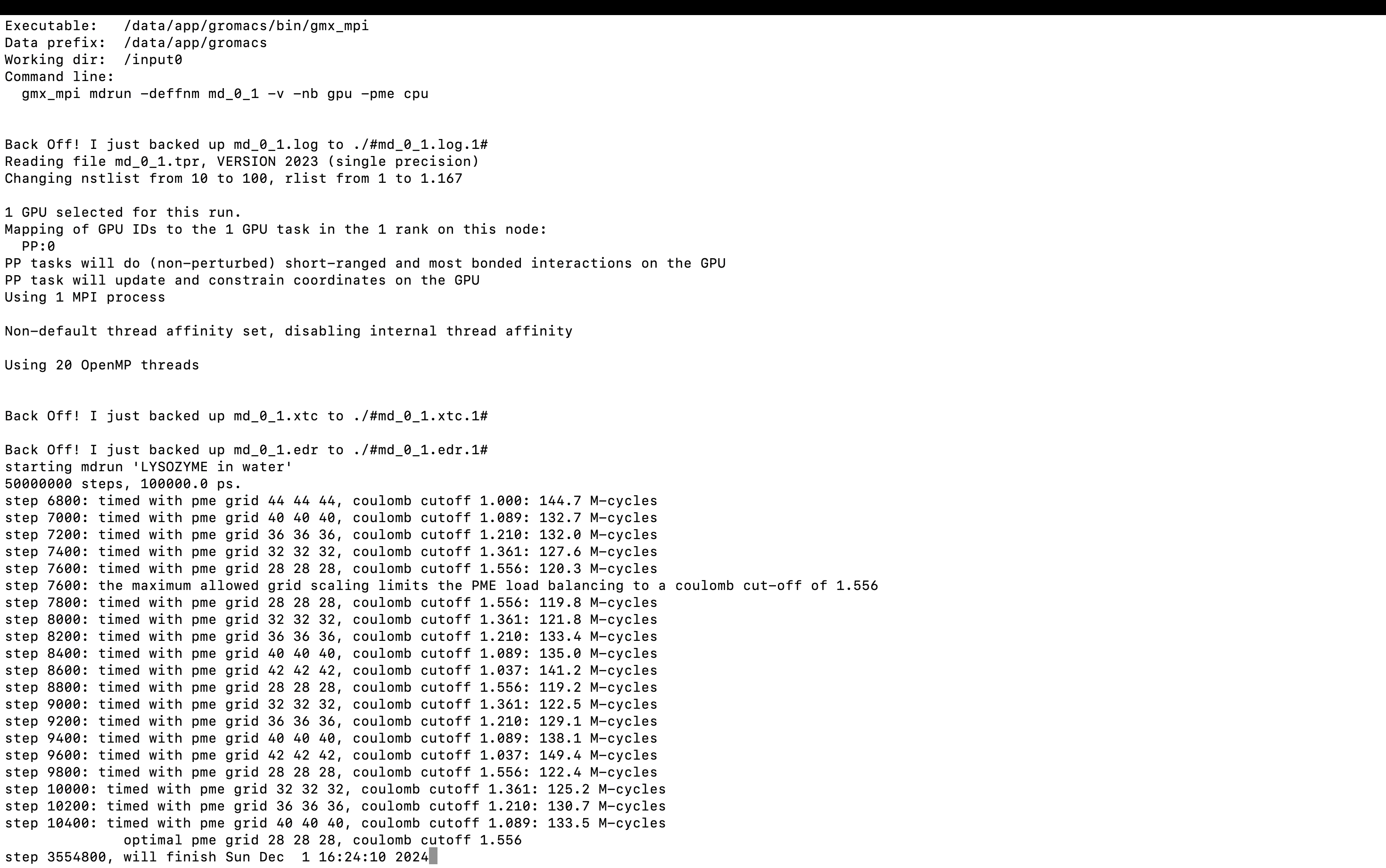
gmx_mpi grompp -f md.mdp -c npt.gro -t npt.cpt -p topol.top -o md_0_1.tpr
##最后一步提交,pme 分配到 CPU 上:
gmx_mpi mdrun -deffnm md_0_1 -v -nb gpu -pme cpu
-v는 실행의 남은 시간을 표시합니다.
3. 결과 분석
1. trjconv는 좌표 제거, 주기성 수정 또는 궤적(시간 단위, 프레임 속도 등)을 수동으로 수정하는 후처리 도구로 사용됩니다. 이는 주기적 경계 조건이 있는 모든 시뮬레이션에서 분자가 상자 가장자리에서 부서지거나 뛰어다닐 수 있기 때문입니다. 상자 안의 분자를 다시 중심에 두고, 분자를 다시 감싸고, 상자의 마름모꼴 십이면체 모양을 복원할 수 있습니다.
-pbc mol: 去除轨迹中的周期性边界条件 (PBC),并基于分子进行修正(即确保每个分子在轨迹中是完整的)。
• -center: 将选定的分子/分组居中到模拟框的中心。
gmx_mpi trjconv -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1.xtc -o md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -pbc mol -center
Select group for centering
Group 0 ( System) has 33876 elements
Group 1 ( Protein) has 1960 elements
Group 2 ( Protein-H) has 1001 elements
Group 3 ( C-alpha) has 129 elements
Group 4 ( Backbone) has 387 elements
Group 5 ( MainChain) has 517 elements
Group 6 ( MainChain+Cb) has 634 elements
Group 7 ( MainChain+H) has 646 elements
Group 8 ( SideChain) has 1314 elements
Group 9 ( SideChain-H) has 484 elements
Group 10 ( Prot-Masses) has 1960 elements
Group 11 ( non-Protein) has 31916 elements
Group 12 ( Water) has 31908 elements
Group 13 ( SOL) has 31908 elements
Group 14 ( non-Water) has 1968 elements
Group 15 ( Ion) has 8 elements
Group 16 ( Water_and_ions) has 31916 elements
Select a group: 1
Selected 1: 'Protein'
Select group for output
Group 0 ( System) has 33876 elements
Group 1 ( Protein) has 1960 elements
Group 2 ( Protein-H) has 1001 elements
Group 3 ( C-alpha) has 129 elements
Group 4 ( Backbone) has 387 elements
Group 5 ( MainChain) has 517 elements
Group 6 ( MainChain+Cb) has 634 elements
Group 7 ( MainChain+H) has 646 elements
Group 8 ( SideChain) has 1314 elements
Group 9 ( SideChain-H) has 484 elements
Group 10 ( Prot-Masses) has 1960 elements
Group 11 ( non-Protein) has 31916 elements
Group 12 ( Water) has 31908 elements
Group 13 ( SOL) has 31908 elements
Group 14 ( non-Water) has 1968 elements
Group 15 ( Ion) has 8 elements
Group 16 ( Water_and_ions) has 31916 elements
Select a group: 0
Selected 0: 'System'
선택 4(“백본”)는 최소 제곱 적합 및 RMSD 계산에 사용되었습니다.
2.RMSD
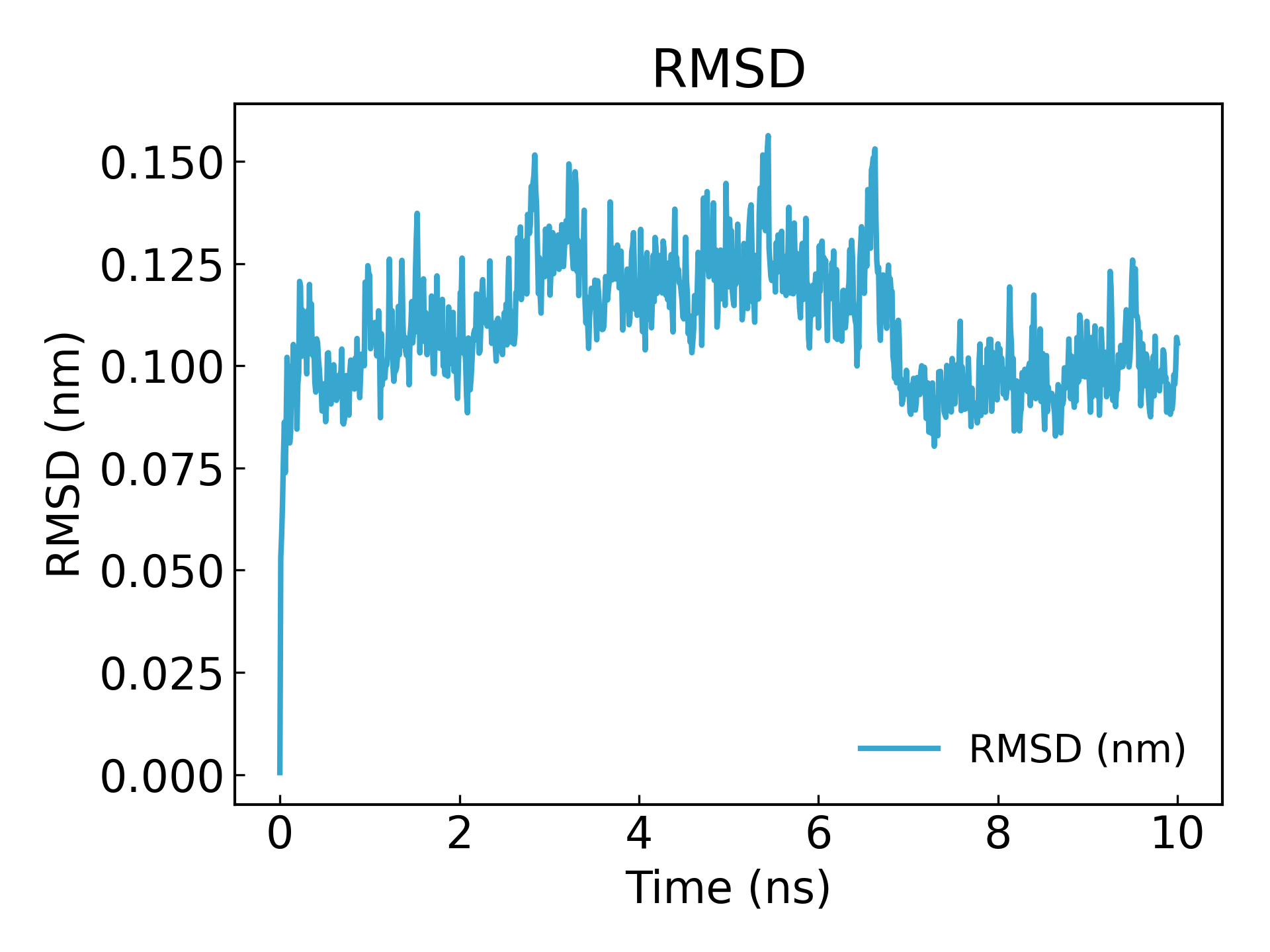
시뮬레이션의 수렴성과 단백질의 안정성을 확인하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.g_rms**시뮬레이션 중 구조의 RMSD와 초기 구조, 0ns를 기준으로 한 특정 순간의 구조 편차는 종종 단백질 구조의 안정성을 평가하는 데 사용됩니다. 이는 단백질 리간드 구조의 안정성과 같은 약물 설계 분야에서 자주 사용됩니다. RMSD 곡선의 변동 범위는 작고 안정적이며, 이는 리간드와 수용체 사이의 친화력이 크다는 것을 나타냅니다.
gmx_mpi rms -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -o rmsd.xvg
최소 제곱 적합 및 RMSD 계산을 위해 4("백본")를 선택하세요.
10ns 후에 평형에 도달한 것을 볼 수 있습니다.(참고: 기사를 게시하거나 제출할 때는 100ns 또는 50ns로 시뮬레이션하는 것이 가장 좋습니다.)
3. 회전 반경 분석
gmx_mpi gyrate -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -o gyrate.xvg
단백질의 회전 반경은 단백질의 밀도를 측정하는 기준입니다. 단백질 구조가 안정적이라면 비교적 안정적인 R g 값을 유지할 가능성이 높습니다. 단백질이 펼쳐지면 R g 값은 시간에 따라 변합니다. 시뮬레이션에서 리소자임의 회전 반경을 분석해 보겠습니다.
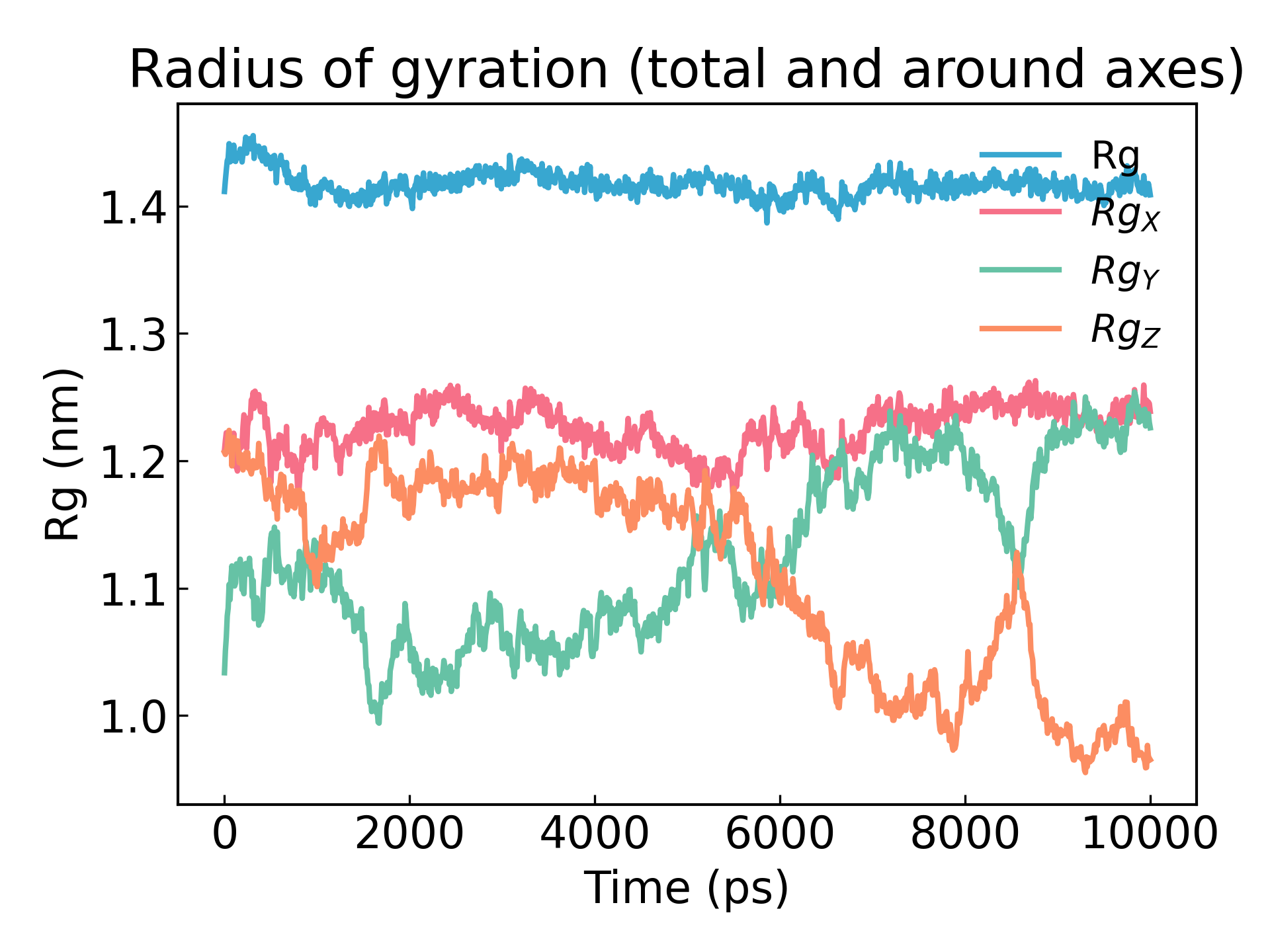
4. 시각화
권장 소프트웨어:DuIvyTools: GROMACS 시뮬레이션 분석 및 시각화 도구
에서:https://github.com/CharlesHahn/DuIvyTools
pip install DuIvyTools
dit xvg_show -f rmsd.xvg -o rmsd_plot.png
dit xvg_show -f rmsd.xvg -o rmsd_plot.png
dit xvg_show -f potential.xvg -o potential_plot.png
dit xvg_show -f temperature.xvg -o temperature_plot.png
dit xvg_show -f density.xvg -o density_plot.png
dit xvg_show -f pressure.xvg -o pressure_plot.png
우리가 만든 데이터 세트를 엽니다
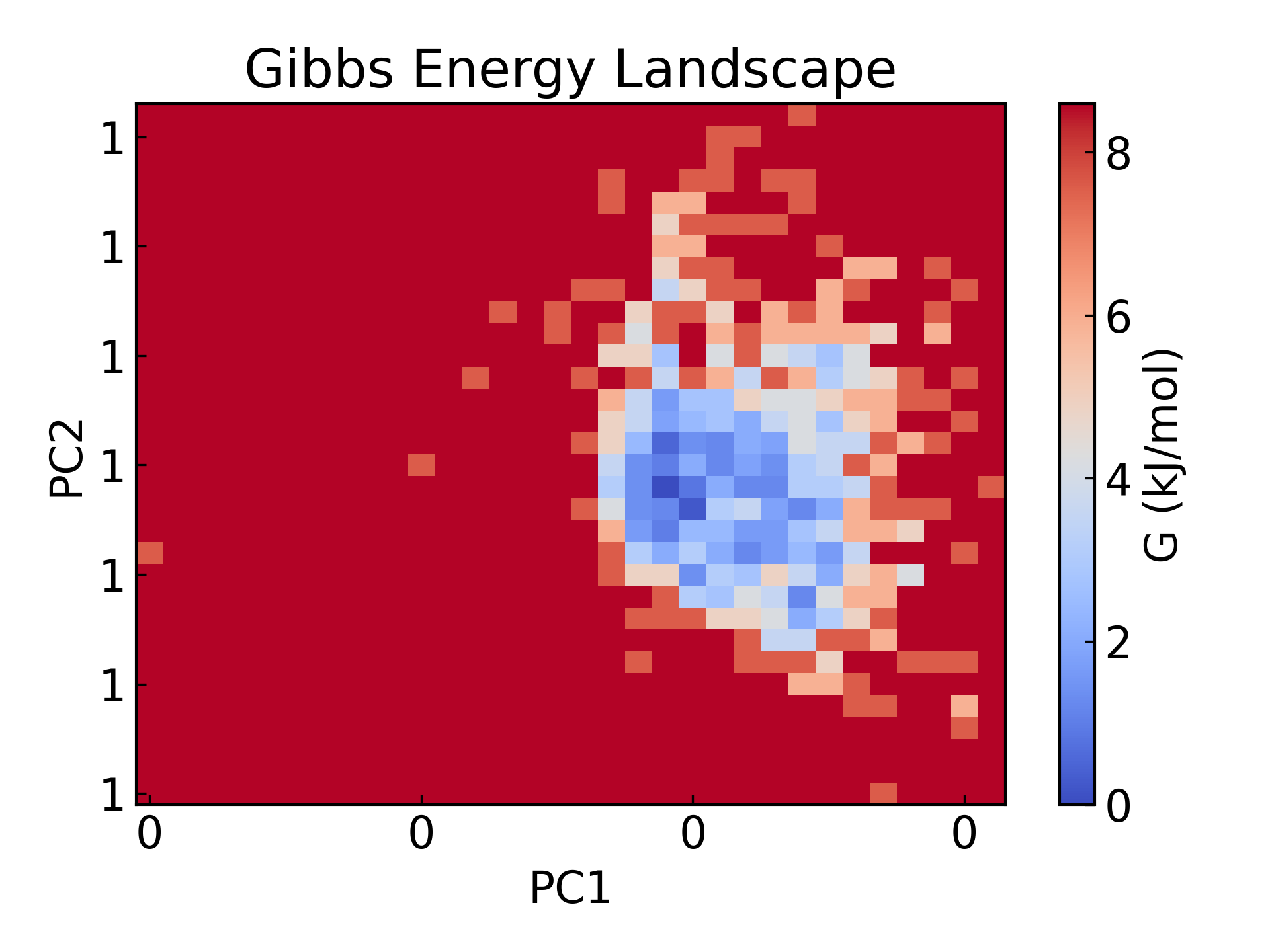
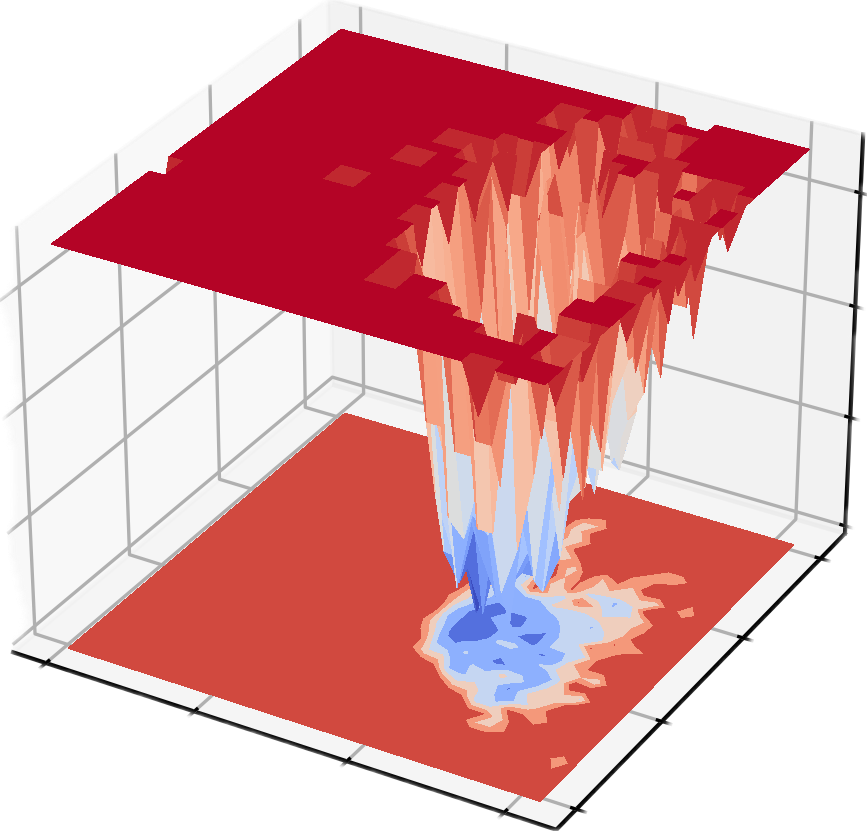
5. GROMACS 에너지 지형 매핑 자유 에너지 지형은 회전 반경과 rmsd를 각각 두 개의 PCA 구성 요소로 표시했습니다.
gmx_mpi gyrate -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -o rg.xvg
gmx_mpi rms -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -o rmsd.xvg
vim rmsd.xvg
#输入以下命令删除以 # 或 @ 开头的行:
:g/^[@#]/d
vim rg.xvg
#输入以下命令删除以 # 或 @ 开头的行:
:g/^[@#]/d
#注意不要有空行,
paste rmsd.xvg rg.xvg > rmsd-rg.xvg
(base) # tail -f rmsd-rg.xvg
9910.0000000 0.0925907 9910 1.37624 1.20925 1.20765 0.931324
9920.0000000 0.0881348 9920 1.38369 1.22248 1.21078 0.932077
9930.0000000 0.0911074 9930 1.39224 1.23799 1.21709 0.928842
9940.0000000 0.0893596 9940 1.38188 1.21942 1.21672 0.922916
9950.0000000 0.0915931 9950 1.37509 1.21939 1.20194 0.922051
9960.0000000 0.0978161 9960 1.38113 1.2262 1.21084 0.919414
9970.0000000 0.0954911 9970 1.37934 1.21241 1.20711 0.937075
9980.0000000 0.0993617 9980 1.38301 1.22353 1.21083 0.92862
9990.0000000 0.1069279 9990 1.37943 1.22317 1.20579 0.924978
10000.0000000 0.1055321 10000 1.37524 1.21648 1.20194 0.92632
^Z
[11]+ Stopped tail -f rmsd-rg.xvg
#查看已经将两个文件整合在一起了,我们只要保留
#从 rmsd-rg.xvg 文件内容可以看到,每一行的数据格式如下:
时间_RMSD(ns) RMSD 时间_Rg(ps) Rg 其他列
(base) tail -f rmsd.xvg
9910.0000000 0.0925907
9920.0000000 0.0881348
9930.0000000 0.0911074
9940.0000000 0.0893596
9950.0000000 0.0915931
9960.0000000 0.0978161
9970.0000000 0.0954911
9980.0000000 0.0993617
9990.0000000 0.1069279
10000.0000000 0.1055321
^Z
[12]+ Stopped tail -f rmsd.xvg
#整理数据为
时间 (ns) RMSD Rg
(base) python
Python 3.8.15 (default, Nov 24 2022, 15:19:38)
[GCC 11.2.0] :: Anaconda, Inc. on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
# 加载数据
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> data = pd.read_csv("rmsd-rg.xvg", delim_whitespace=True, header=None, comment="#")
# 保留需要的列:第 1 列 (RMSD 时间) 、第 2 列 (RMSD) 、第 4 列 (Rg)
>>> cleaned_data = data[[0, 1, 3]]
# 将列名修改为更直观的名称
>>> cleaned_data.columns = ["Time (ps)", "RMSD", "Rg"]
>>> cleaned_data.to_csv("rmsd-rg-cleaned.xvg", sep="\t", index=False, header=False)
>>> exit()
#整理成功
tail -f rmsd-rg-cleaned.xvg
9910.0 0.0925907 1.37624
9920.0 0.0881348 1.38369
9930.0 0.0911074 1.39224
9940.0 0.0893596 1.38188
9950.0 0.0915931 1.37509
9960.0 0.0978161 1.38113
9970.0 0.0954911 1.37934
9980.0 0.0993617 1.38301
9990.0 0.1069279 1.37943
10000.0 0.1055321 1.37524
gmx_mpi sham -tsham 300 -nlevels 100 -f rmsd-rg-cleaned.xvg -ls gibbs.xpm -g gibbs.log -lsh enthalpy.xpm -lss entropy.xpm
dit xpm_show -f gibbs.xpm -o gibbs_2d.png
dit xpm_show -f gibbs.xpm -m 3d -o gibbs_3d.png
#tsham : 设定温度
#-nlevels: 设定 FEL 的层次数量
자유 에너지 풍경(FES)은 분자 시뮬레이션에서 매우 중요한 도구로, 주로 특정 좌표에서 분자 시스템의 자유 에너지 분포를 설명하는 데 사용됩니다. 핵심 기능은 시스템의 열역학적 안정성과 운동 과정을 밝히는 것인데, 이는 일반적으로 다음과 같은 과학 연구 분야에서 매우 중요합니다.
- 정상 상태 및 전이 상태 연구: 단백질 접힘, 화학 반응 및 분자 인식 과정을 분석하는 데 사용되는 시스템의 안정적인 형태(자유 에너지 최소점)와 형태 변환 경로(자유 에너지 장벽)를 밝힙니다.
- 운동 경로와 열역학적 안정성: 서로 다른 상태 사이의 자유 에너지 차이를 정량화하면 분자 상호작용과 구형 전환의 에너지 원동력을 이해하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
- 약물 설계 및 촉매 연구:리간드-수용체 결합 경로, 에너지 장벽, 반응 속도를 예측하여 분자 메커니즘 분석 및 기능 최적화를 위한 이론적 지침을 제공합니다.
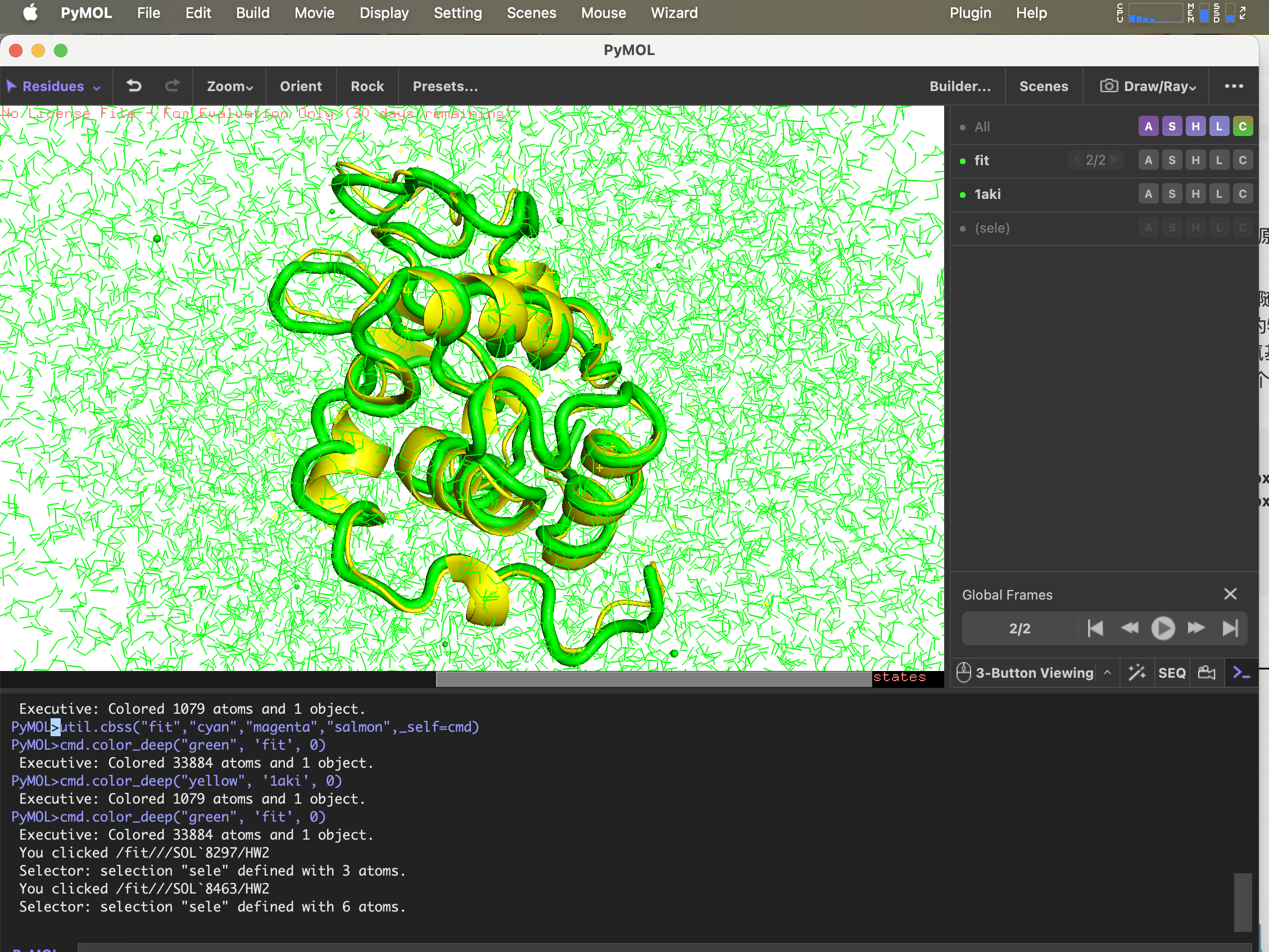
6.g_confrms 형태적 차이의 비교
시뮬레이션 후의 구조를 원본 PDB 파일의 구조와 비교하려면,fit.pdb 두 개의 분자 구조가 포함된 파일, 둘 다 선택하세요 4 (Backbone)
gmx_mpi confrms -f1 1AKI_clean.pdb -f2 md_0_1.gro -o fit.pdb
pymol로 열린 pdb 구조
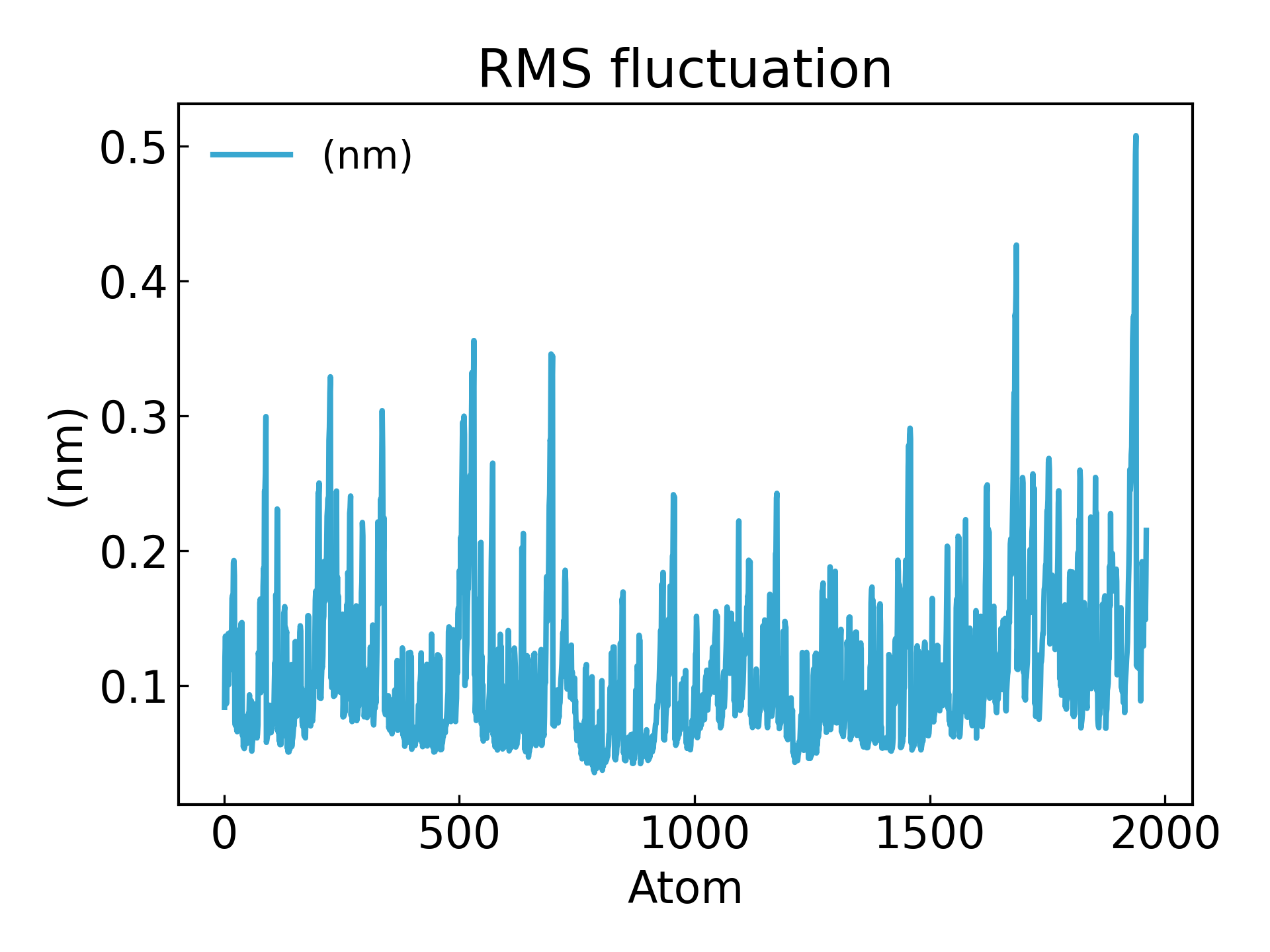
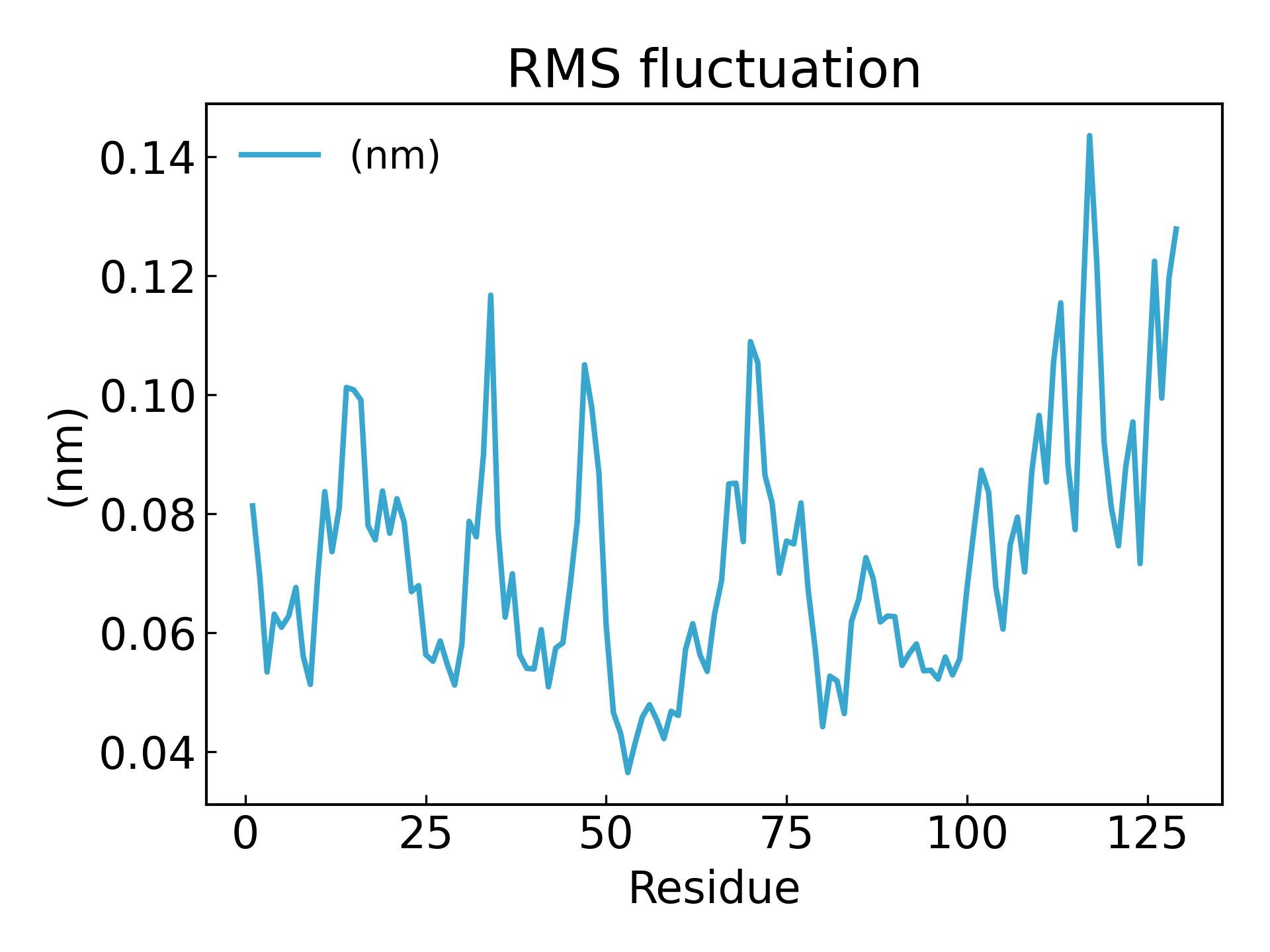
7.g_rmsf 다음 500ps 내에서 제곱평균제곱근 변동(RMSF)과 평균 구조를 계산합니다.g_rmsf 결과적으로 원자번호에 따라 변화하는 곡선이 생성됩니다. 선택하다 1 Protein
아미노산 잔류물의 변동은 RMSF 매개변수를 사용하여 추론할 수 있습니다. 이는 시간이 지남에 따라 각 아미노산 잔류물/원자가 기준 위치에서 벗어난 평균 편차를 설명합니다. 오히려 단백질 구조의 평균 구조에서 변동하는 특정 부분을 분석하는 것이라고 할 수 있습니다. 높은 RMSF 값을 갖는 아미노산 또는 아미노산 그룹은 복합체의 유연성이 더 크다는 것을 나타내는 반면, 낮은 RMSF 값을 갖는 아미노산은 복합체의 유연성이 덜하다는 것을 나타냅니다. 잦은 변동은 안정성을 떨어뜨립니다. RMSF 값은 각 잔류물 위치의 평균 백본 유연성을 측정하는 데 사용되는 동적 매개변수입니다[19].
gmx_mpi rmsf -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -b 500 -o fws-rmsf.xvg -ox fws-avg.pdb
gmx_mpi rmsf -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -b 500 -o fws-rmsf.xvg -ox fws-avg.pdb -res
dit xvg_show -f fws-rmsf.xvg -o rmsf_res.png
# 最后可以放到 pymol 里面看轨迹动画,点击播放即可
gmx_mpi trjconv -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -o trajectory.pdb -skip 10